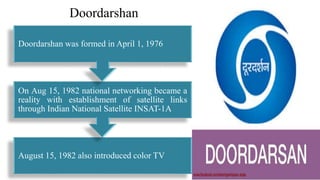
This document provides an overview of the history and development of broadcasting in India. It discusses the evolution from early optical telegraph systems in the 18th century to modern radio and television broadcasting. Key events discussed include the establishment of All India Radio in 1930 and Doordarshan television service in 1959. The document also describes various types of broadcasting systems like public, commercial, and community broadcasting. It highlights the role of organizations like AIR, Doordarshan, and Prasar Bharati in disseminating agricultural information to farmers through radio and television programs.