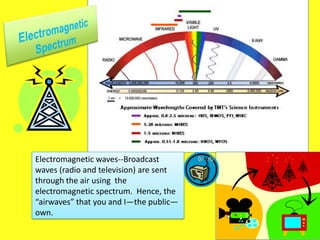
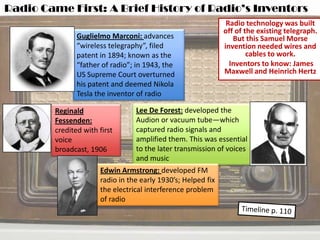
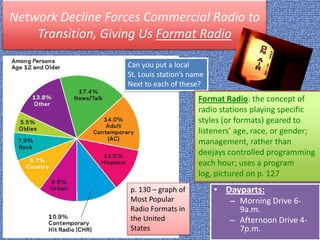
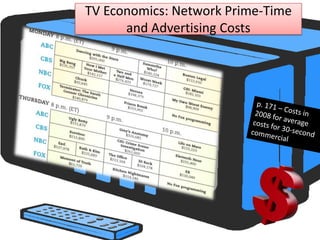
This document provides a summary of the history and development of radio and television technologies. It discusses key inventors and how their innovations led to the establishment of networks and broadcasting systems. It also outlines how technological changes have disrupted traditional broadcast models, leading networks to decline and giving rise to new formats and distribution methods for audio and video content.