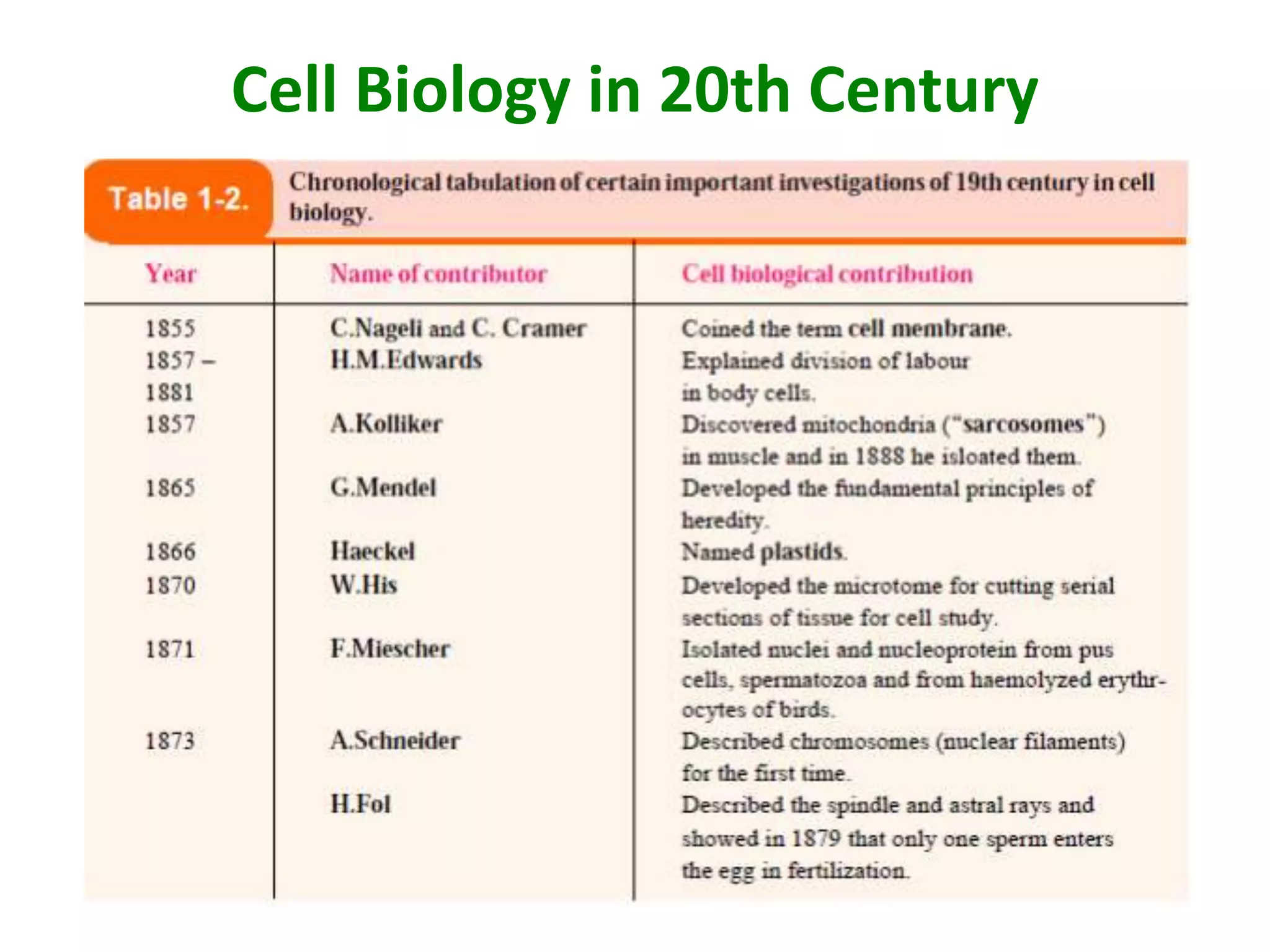
- Cell biology began with ancient Greek philosophers observing common structures in plants and animals in the 4th century BC.
- Advances in microscope technology in the 16th-18th centuries allowed scientists like Hooke, van Leeuwenhoek, and Malpighi to observe cells directly for the first time.
- In 1838, Schleiden proposed that plants are composed of cells, and in 1839, Schwann extended this to animals, establishing the foundations of the cell theory.