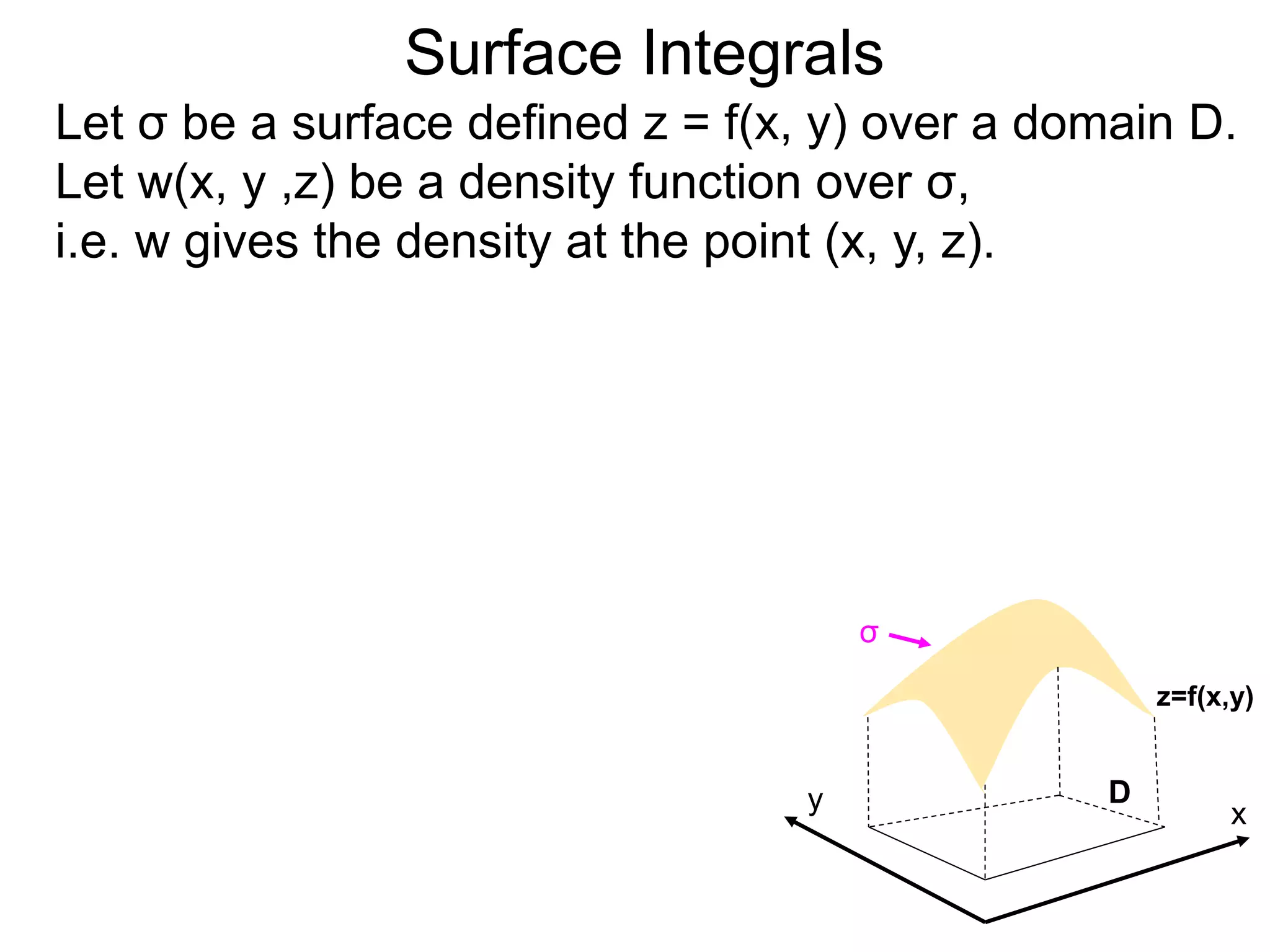
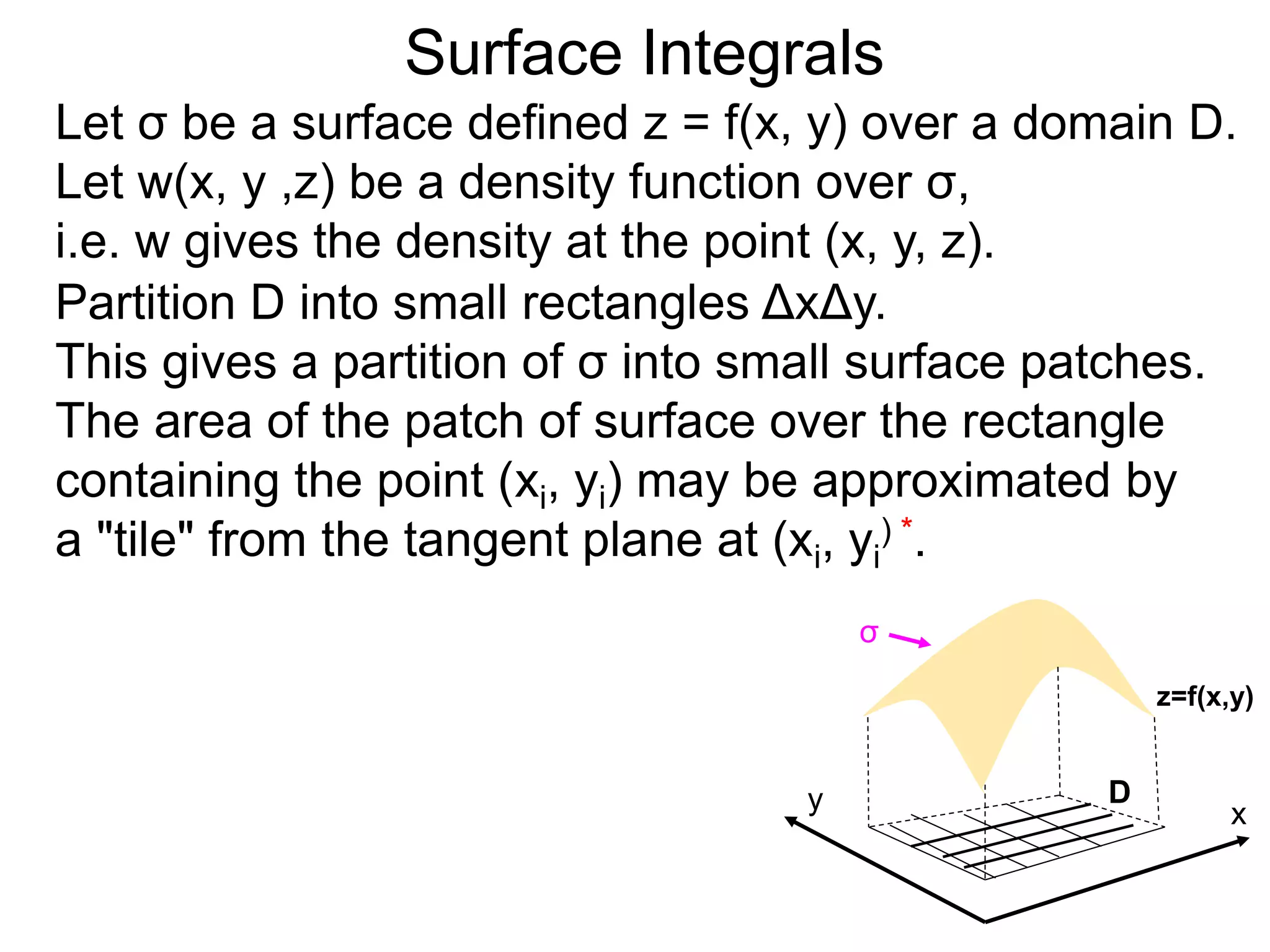
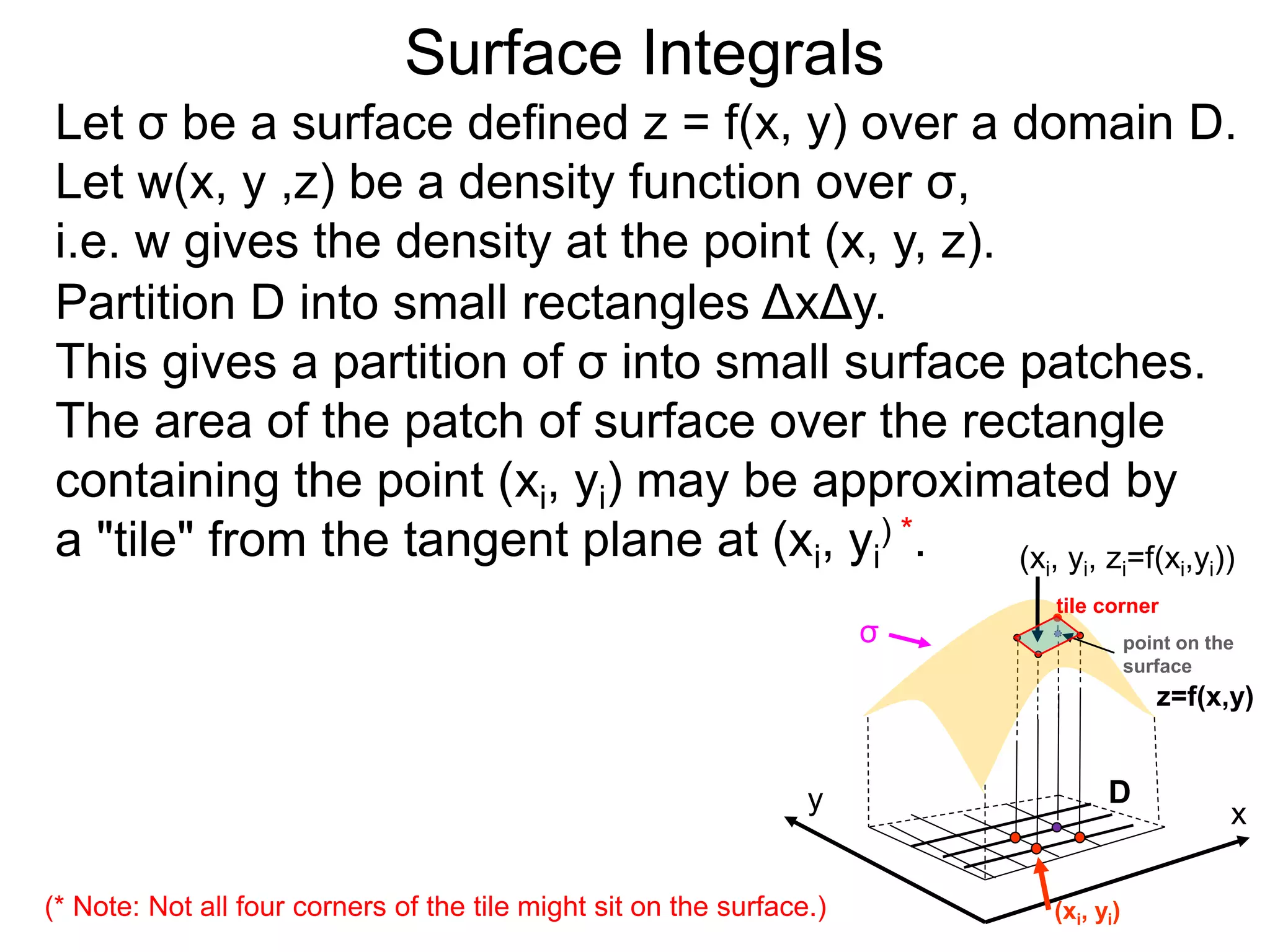
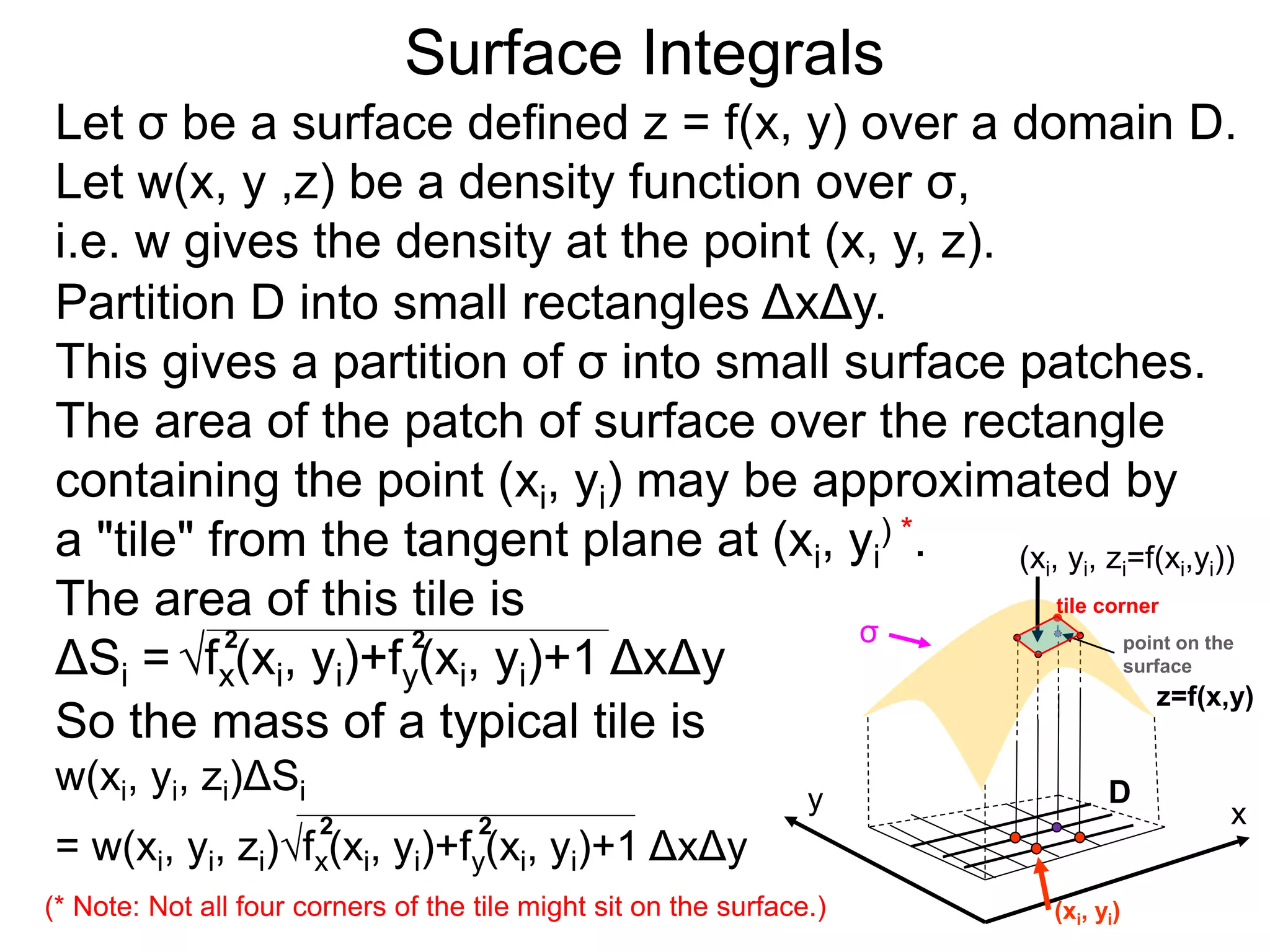
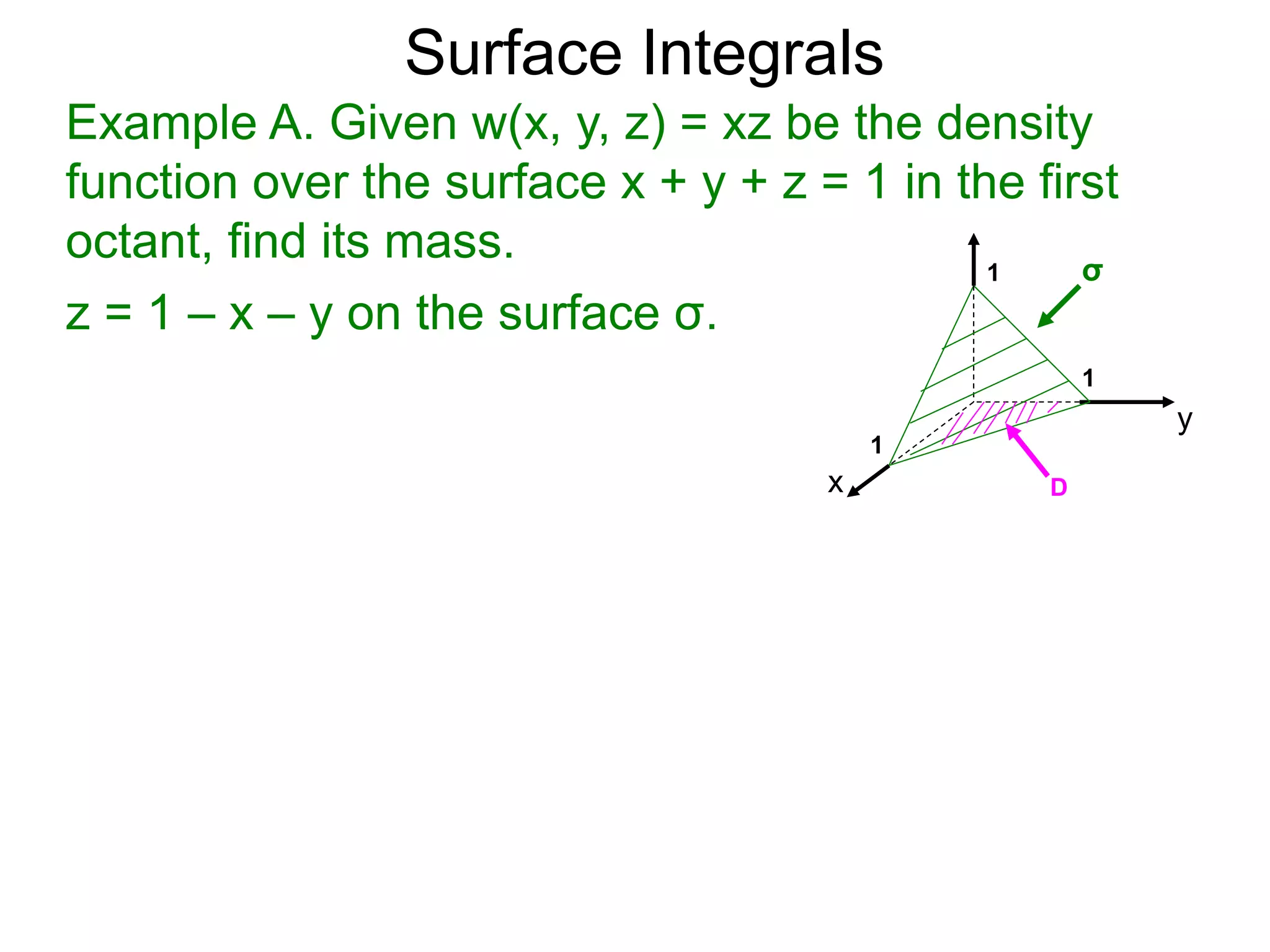
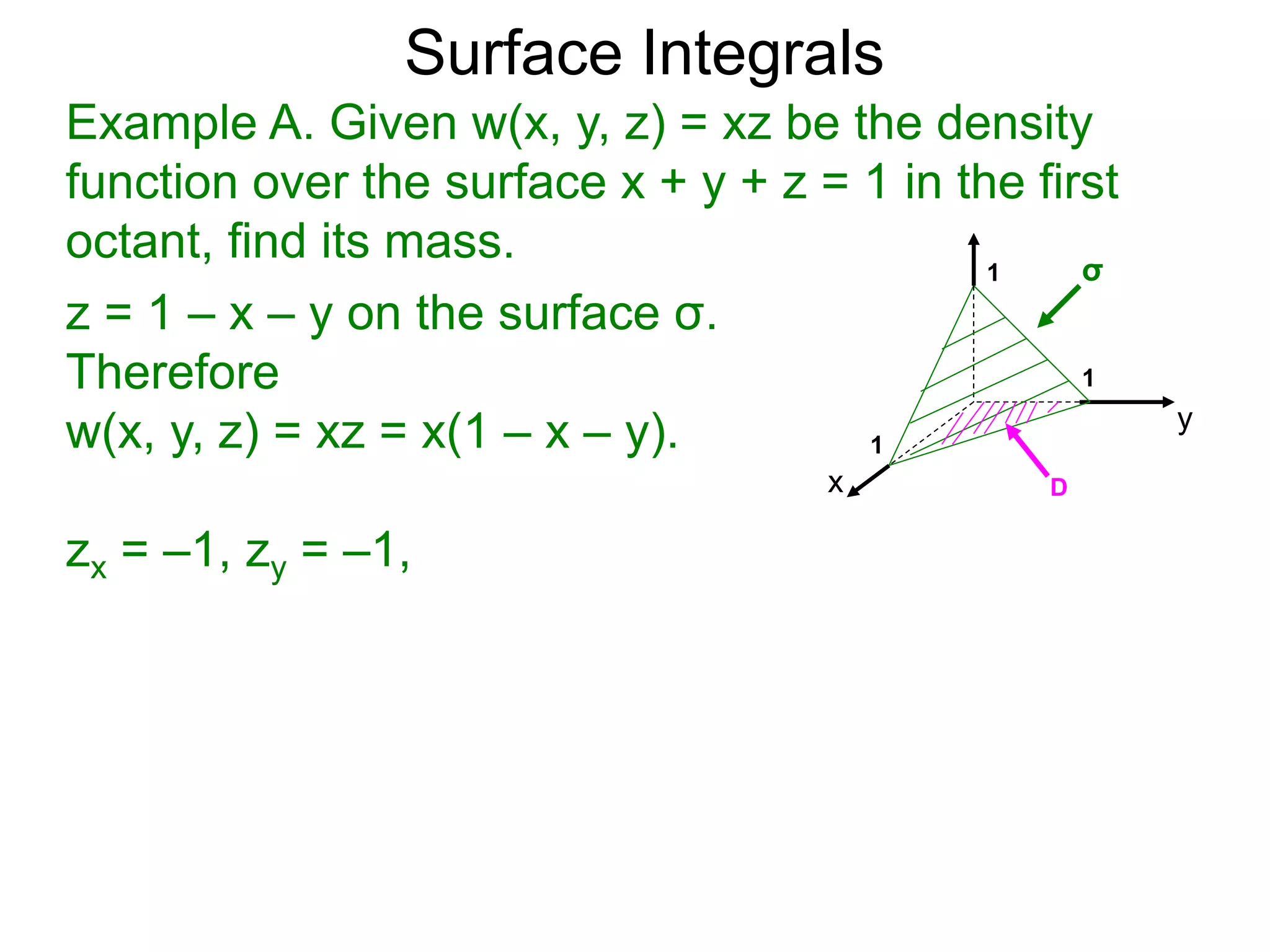
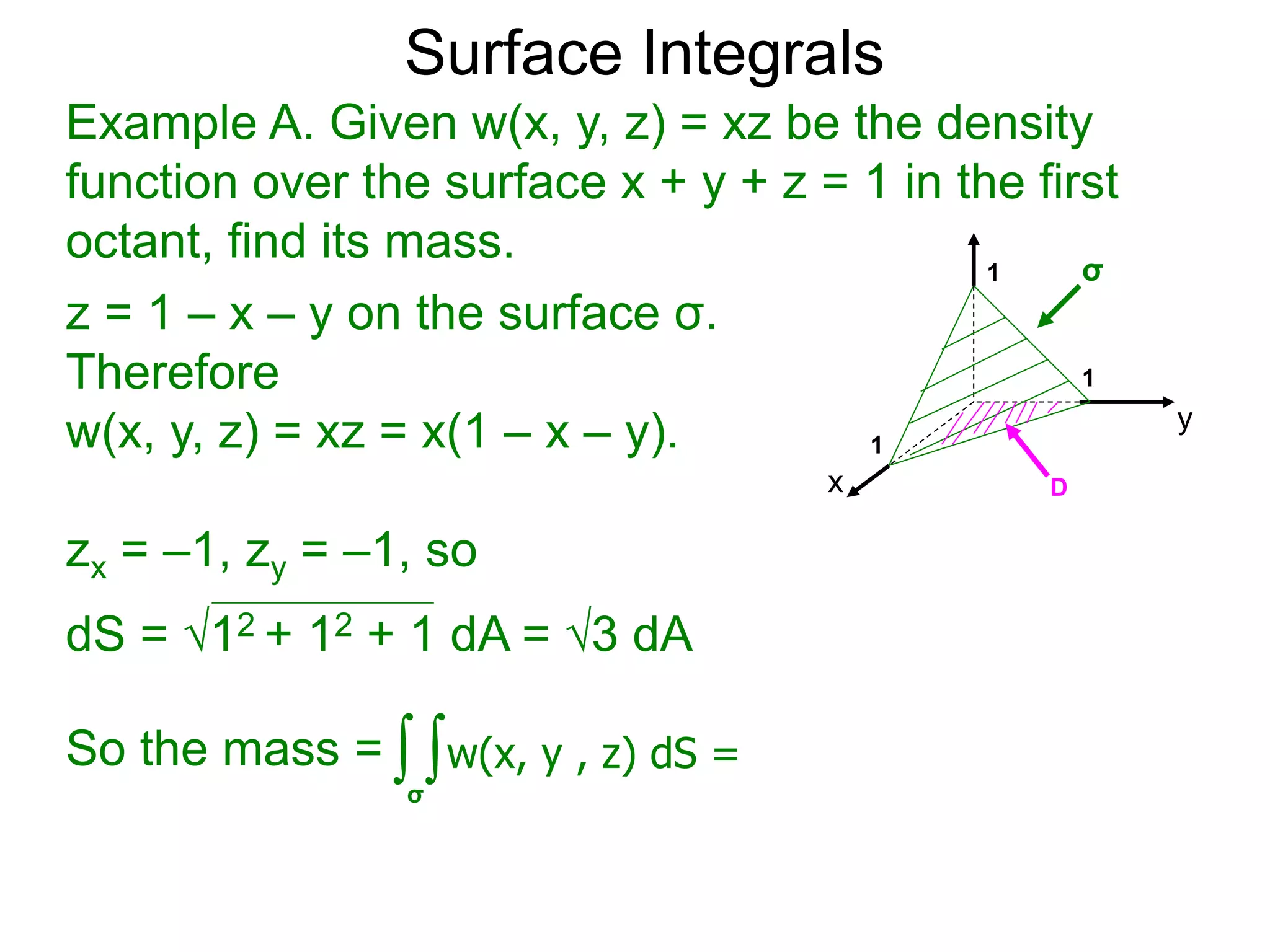
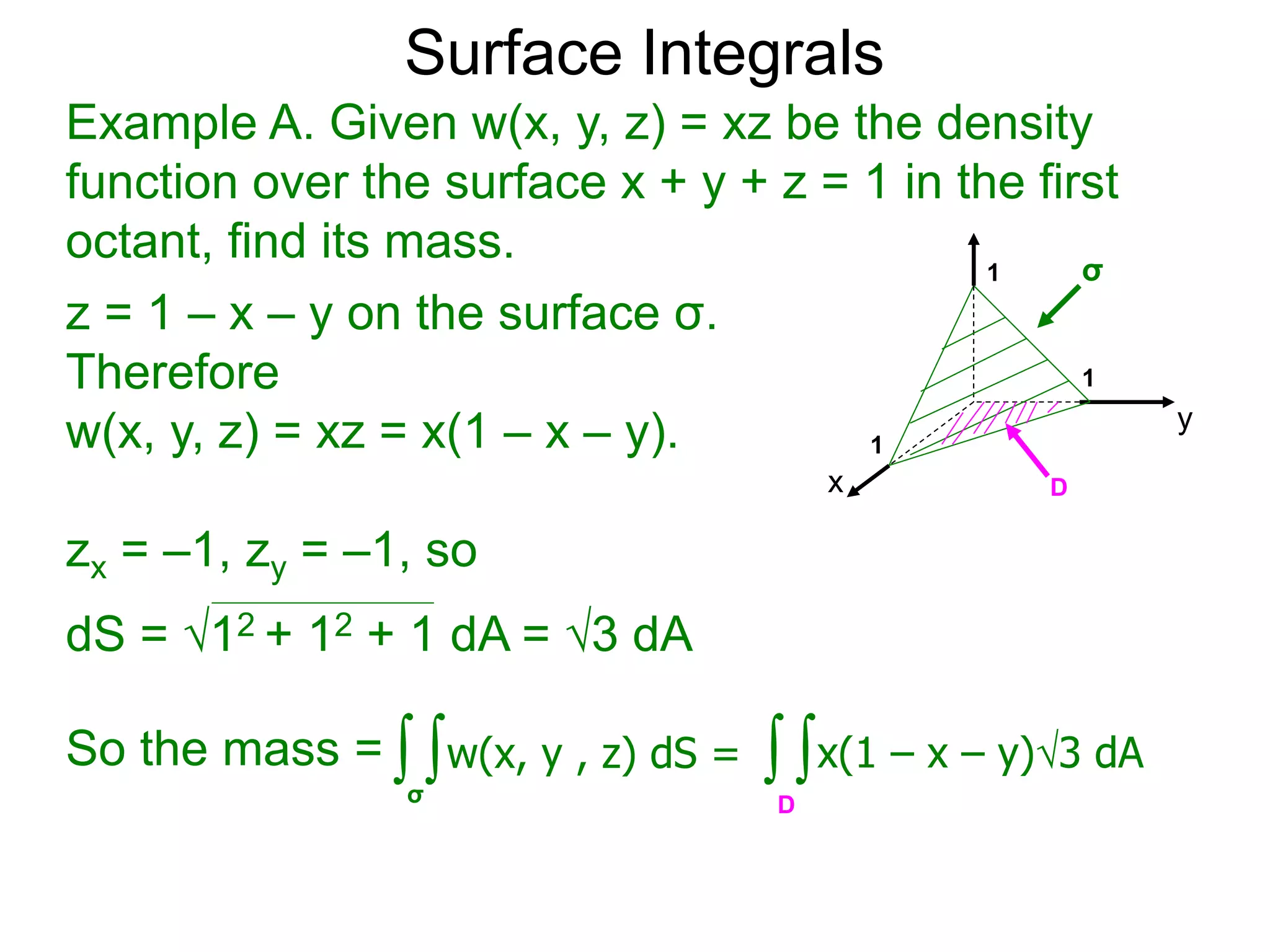
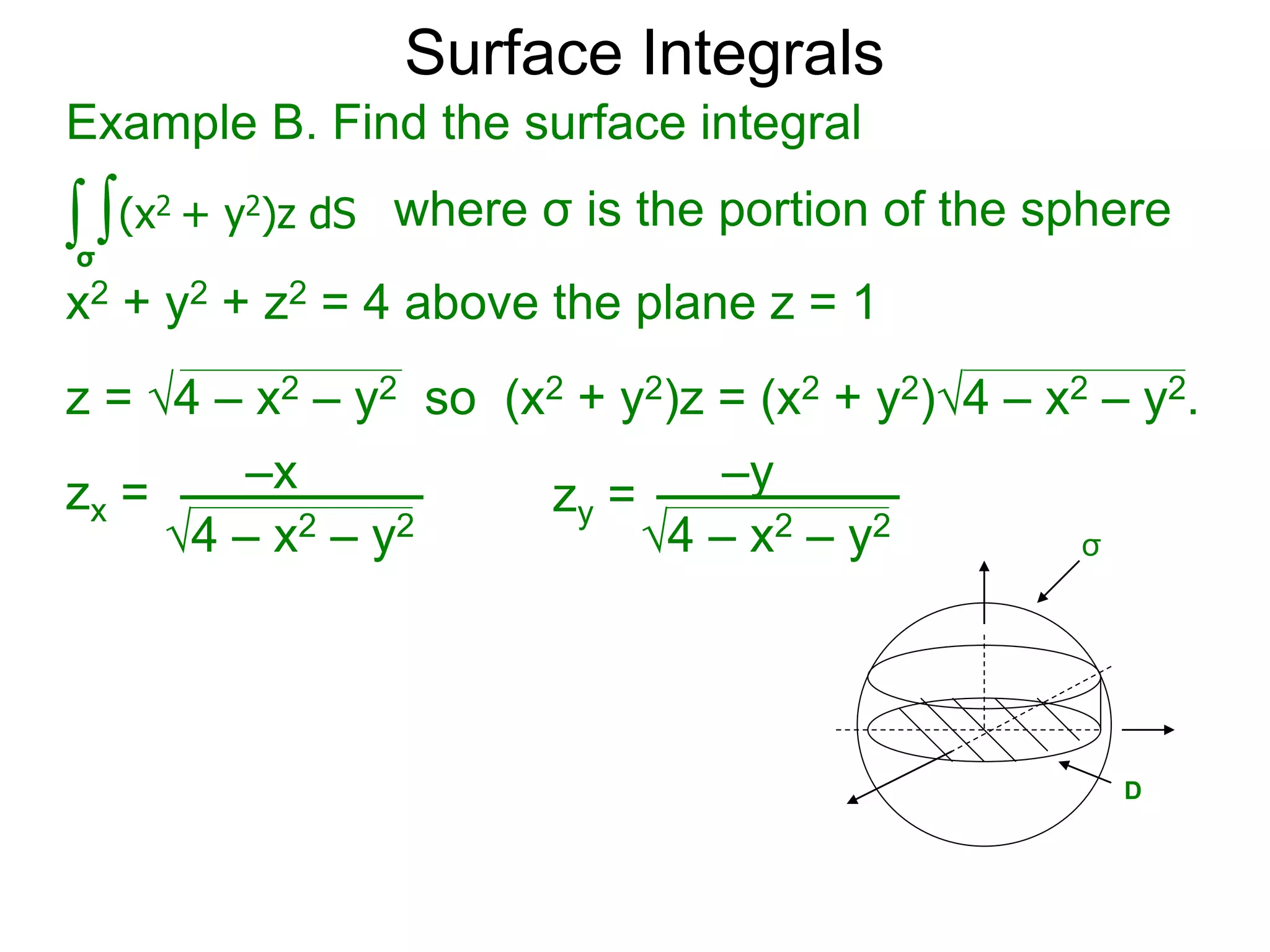
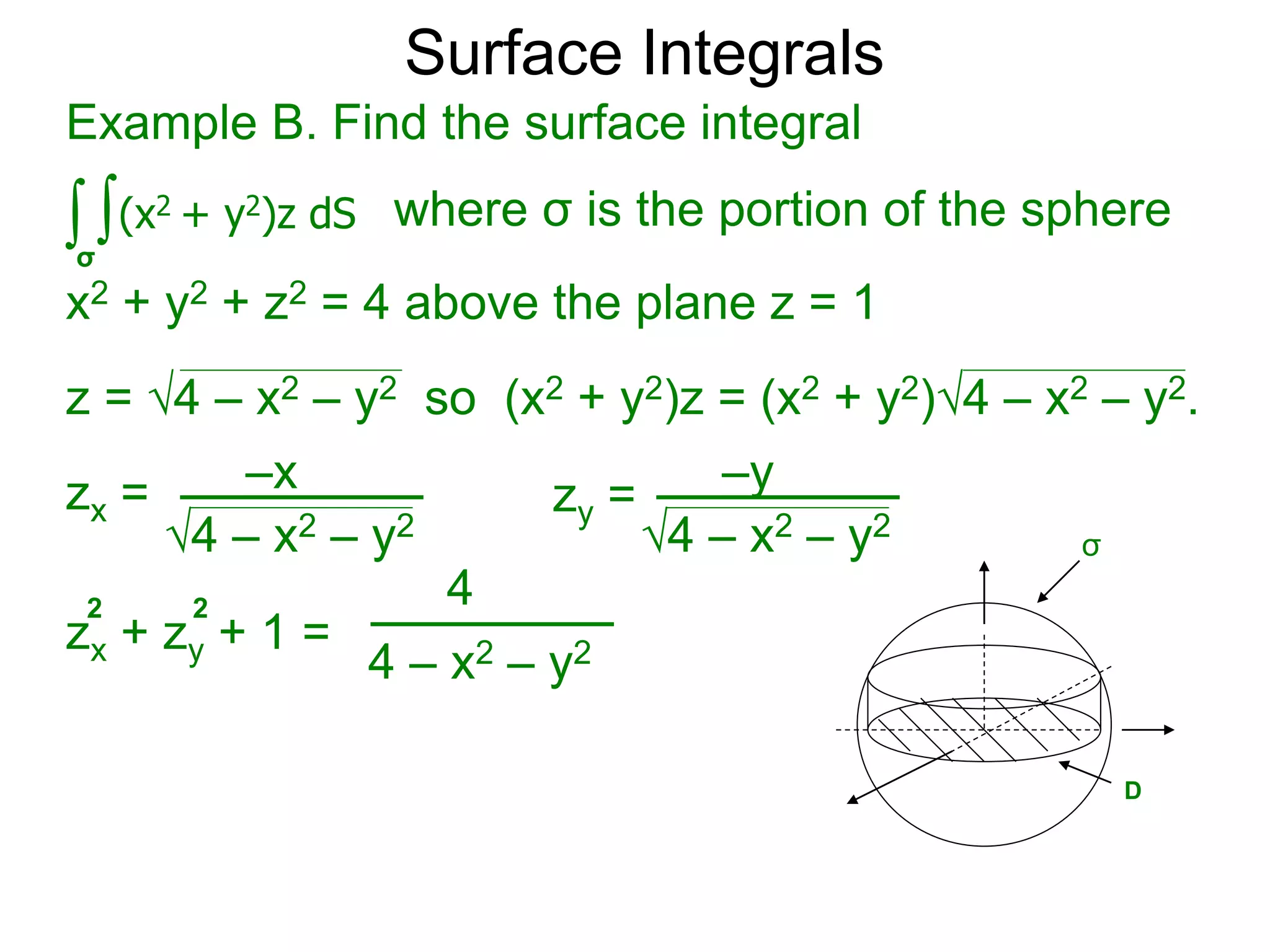
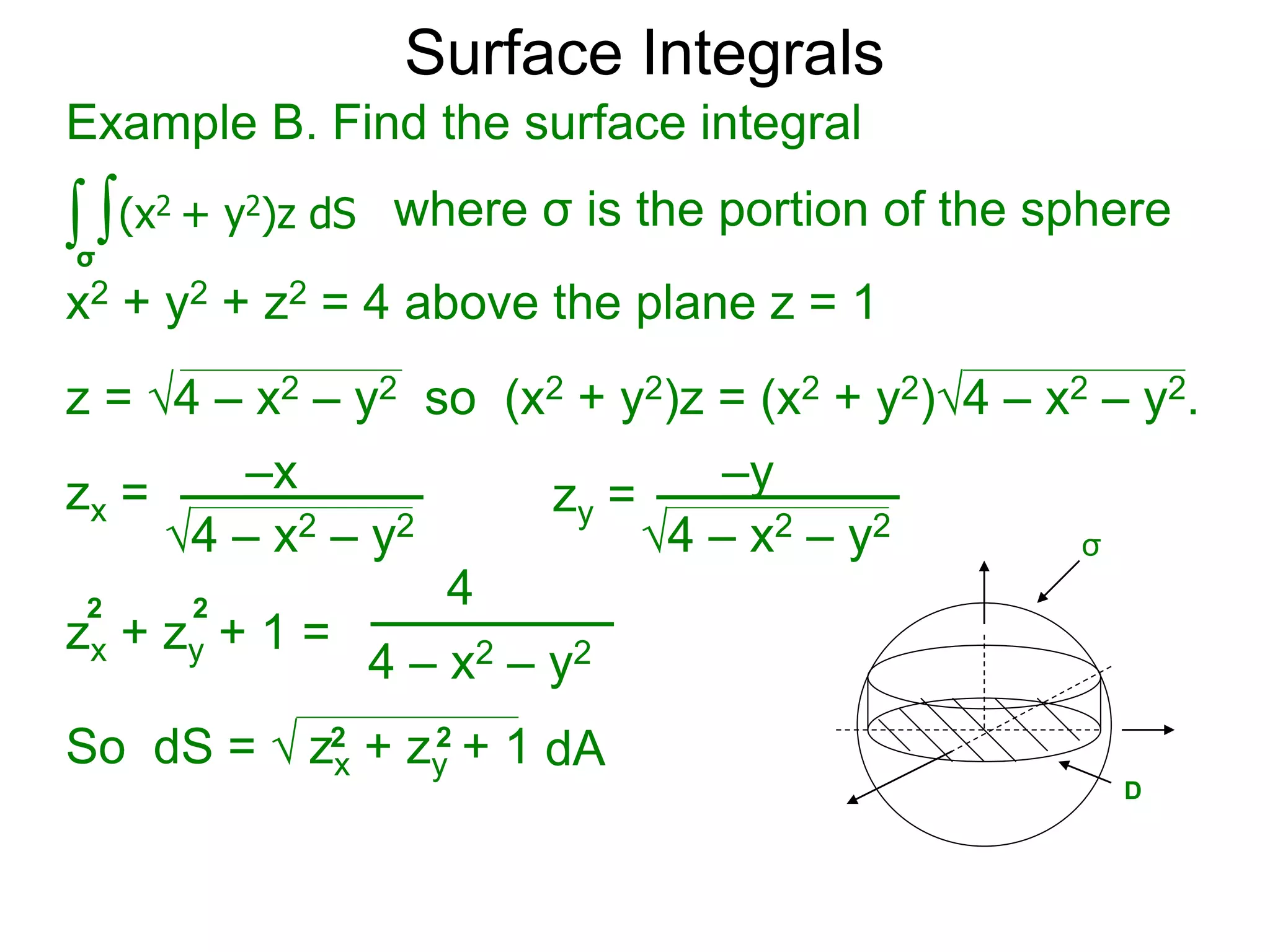
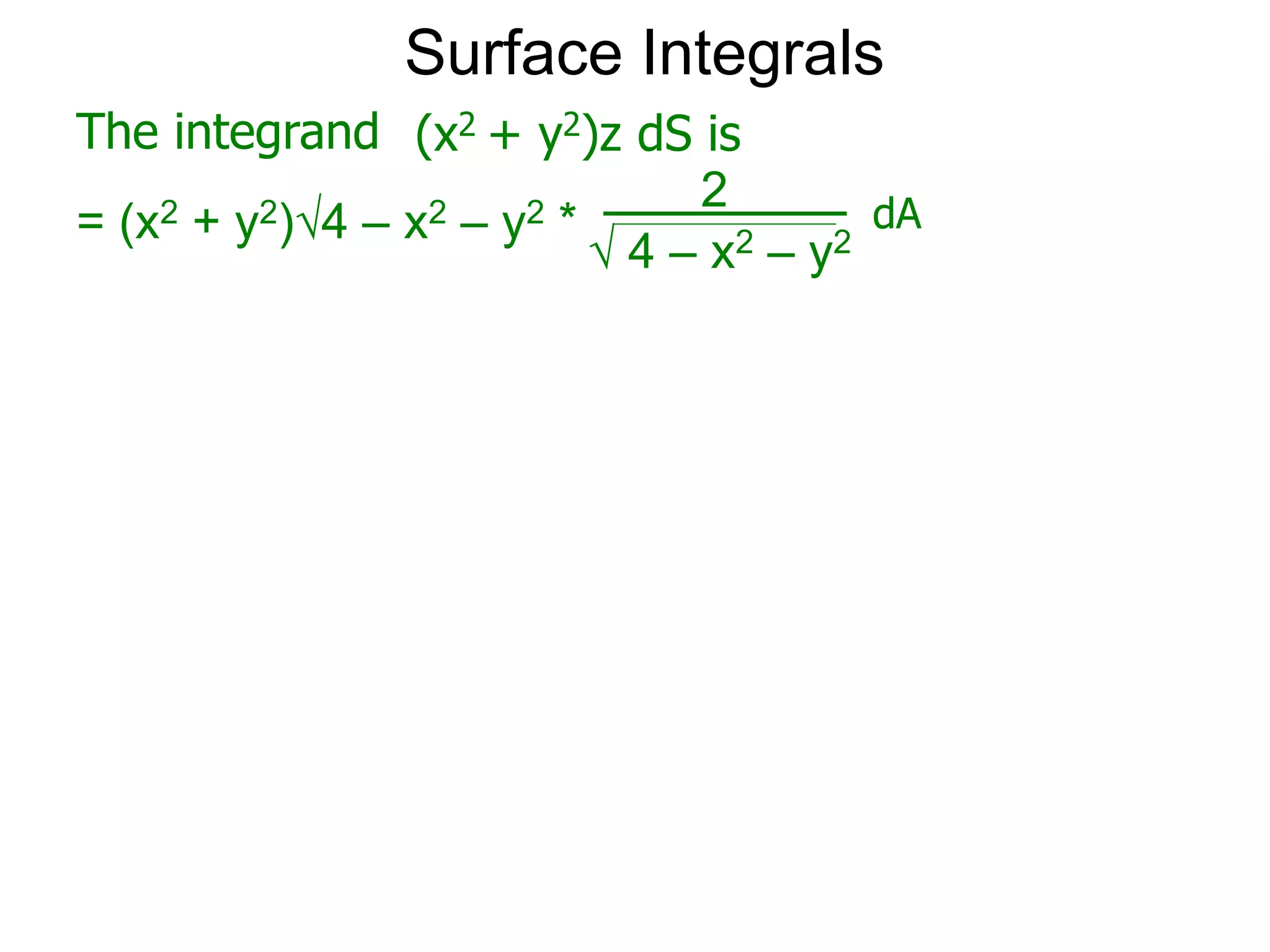
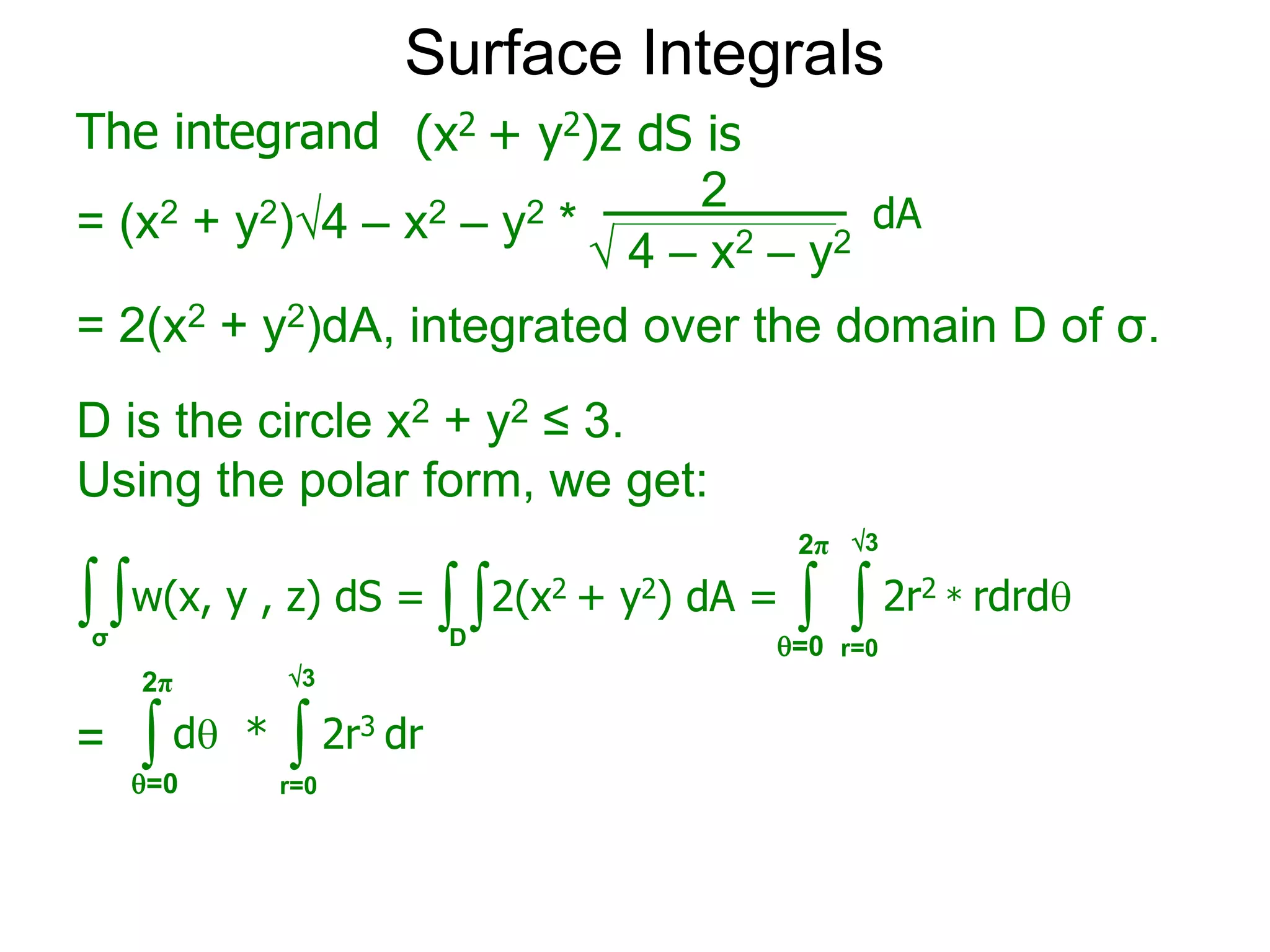
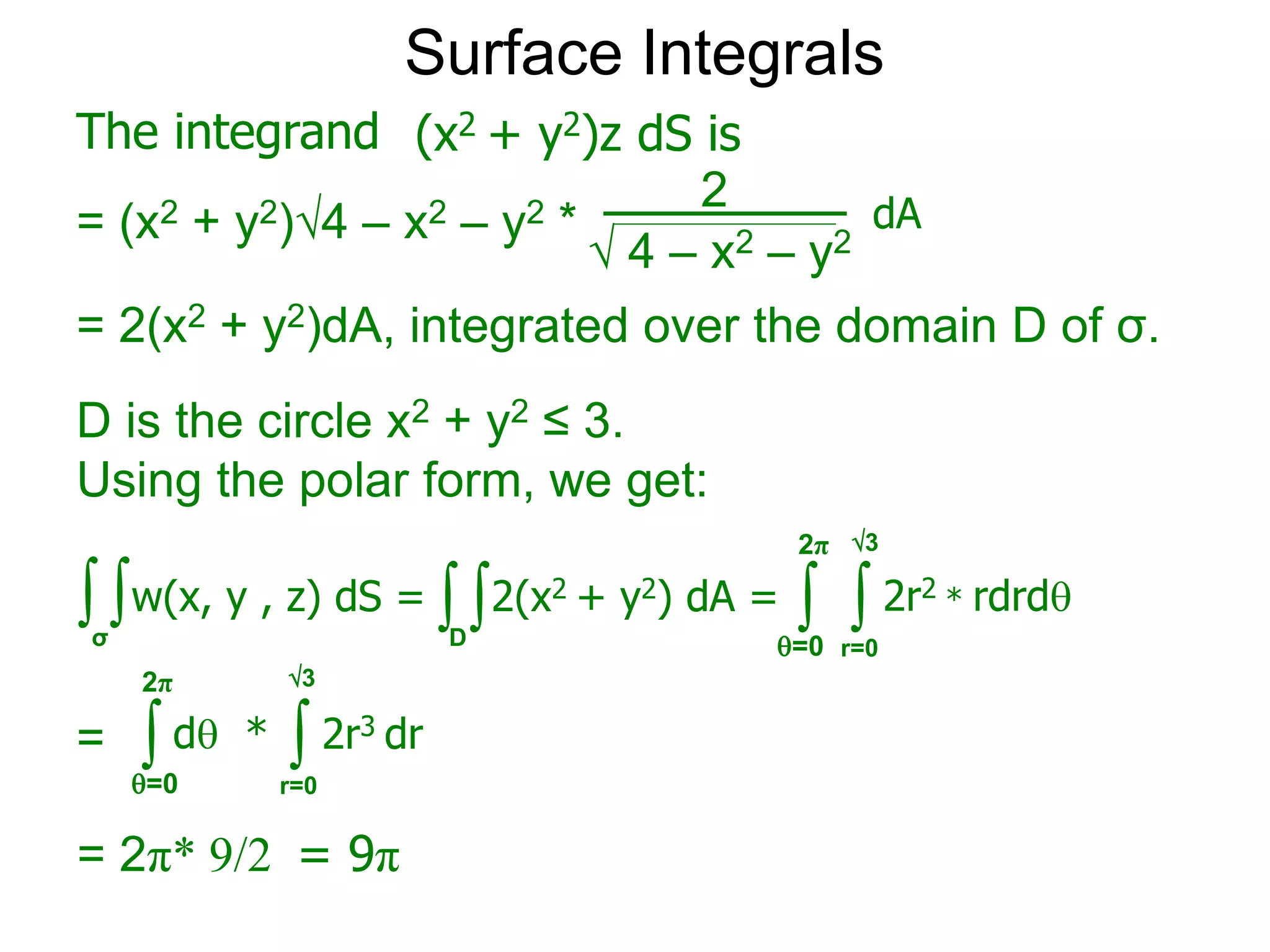
The document discusses surface integrals. It defines a surface σ as z=f(x,y) over a domain D. A density function w(x,y,z) gives the density at each point on σ. The surface is partitioned into small patches, and the area of each patch is approximated using the tangent plane at that point. The total mass of the surface is calculated as the integral of w over σ, with the surface differential dS representing the area of each small patch. An example calculates the mass of a surface in the first octant given a density function w(x,y,z)=xz.

![Surface Integrals
Fact: Given a tilted
parallelogram in 3D over the
domain [0,1] x [0, 1].
x
y
z
1
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30surfaceintegrals-211129003838/75/30-surface-integrals-2-2048.jpg)
![Surface Integrals
Fact: Given a tilted
parallelogram in 3D over the
domain [0,1] x [0, 1].
Let M and L be the slopes
in the x–direction and in the
y–direction respectively,
x
y
z
1
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30surfaceintegrals-211129003838/75/30-surface-integrals-3-2048.jpg)
![Surface Integrals
Fact: Given a tilted
parallelogram in 3D over the
domain [0,1] x [0, 1].
Let M and L be the slopes
in the x–direction and in the
y–direction respectively,
x
y
z
M
1
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30surfaceintegrals-211129003838/75/30-surface-integrals-4-2048.jpg)
![Surface Integrals
Fact: Given a tilted
parallelogram in 3D over the
domain [0,1] x [0, 1].
Let M and L be the slopes
in the x–direction and in the
y–direction respectively,
1
1
x
y
z
M
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30surfaceintegrals-211129003838/75/30-surface-integrals-5-2048.jpg)
![Surface Integrals
Fact: Given a tilted
parallelogram in 3D over the
domain [0,1] x [0, 1].
Let M and L be the slopes
in the x–direction and in the
y–direction respectively,
1
1
x
y
z
M
L
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30surfaceintegrals-211129003838/75/30-surface-integrals-6-2048.jpg)
![Surface Integrals
Fact: Given a tilted
parallelogram in 3D over the
domain [0,1] x [0, 1].
Let M and L be the slopes
in the x–direction and in the
y–direction respectively,
by cross product, the area of
the parallelogram is M2 + L2 + 1.
1
1
x
y
z
M
L
L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30surfaceintegrals-211129003838/75/30-surface-integrals-7-2048.jpg)
![Surface Integrals
1
1
x
y
z
M
L
L
In general, if the domain is
[0,Δx] x [0, Δy] instead,
then its area is
M2 + L2 + 1 ΔxΔy
Δx
Δy
x
y
z
MΔx
LΔy
LΔy
MΔx
Fact: Given a tilted
parallelogram in 3D over the
domain [0,1] x [0, 1].
Let M and L be the slopes
in the x–direction and in the
y–direction respectively,
by cross product, the area of
the parallelogram is M2 + L2 + 1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/30surfaceintegrals-211129003838/75/30-surface-integrals-8-2048.jpg)