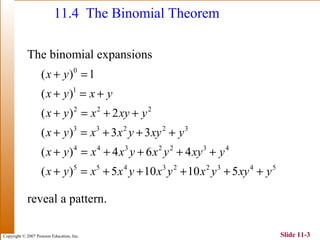
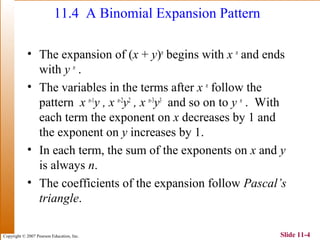
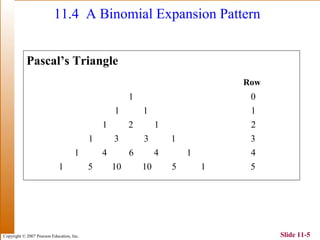
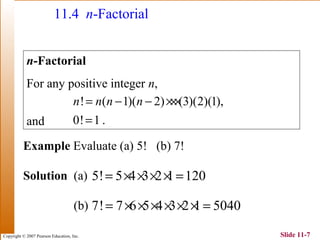
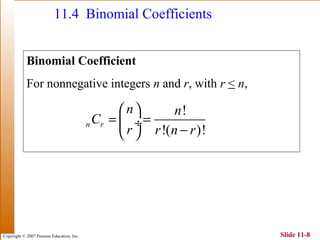
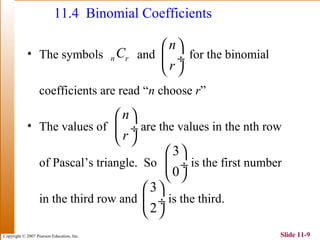
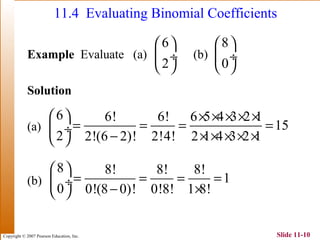
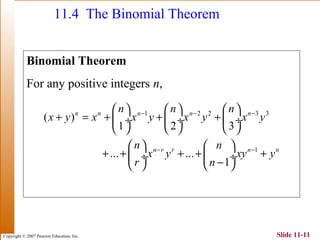
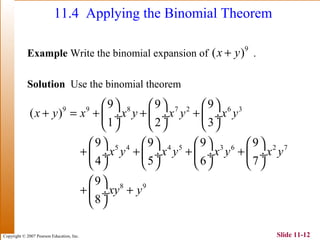
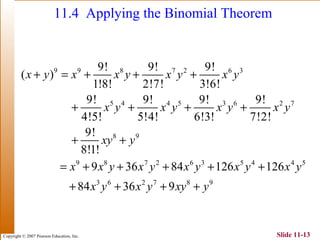
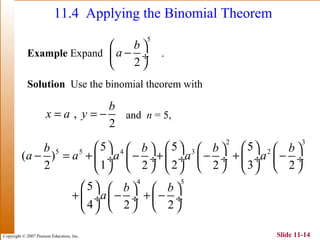
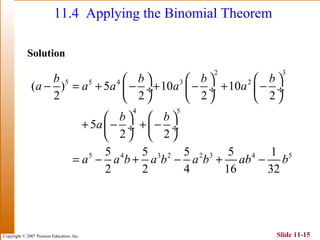
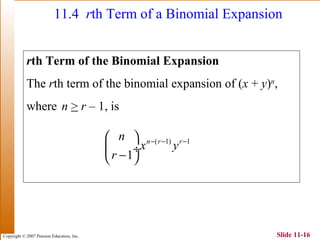
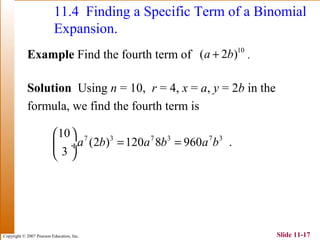
This document summarizes key topics in algebra including sequences, series, the binomial theorem, and probability. It provides examples and explanations of arithmetic and geometric sequences and series. The binomial theorem section explains the pattern in binomial expansions and uses Pascal's triangle to determine the coefficients. It provides the formula for the general term in a binomial expansion and works through examples of applying the binomial theorem.