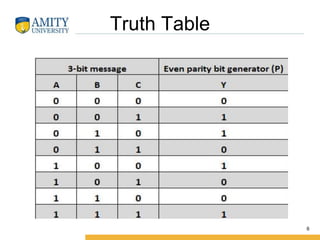
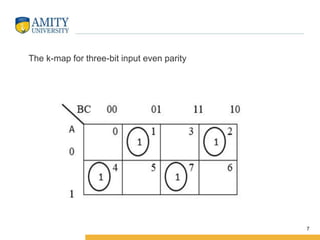
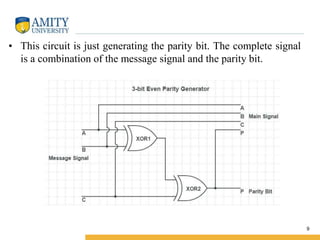
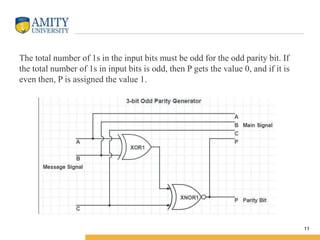
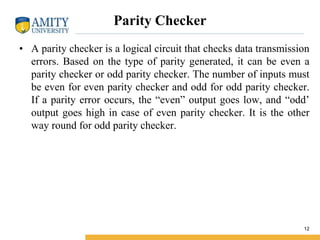
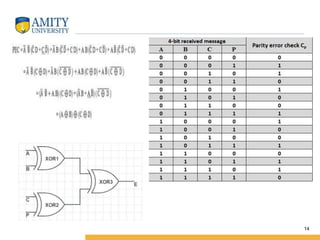
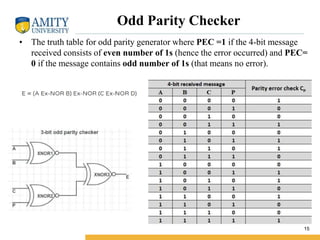
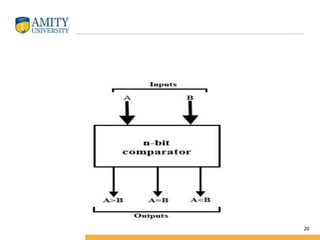
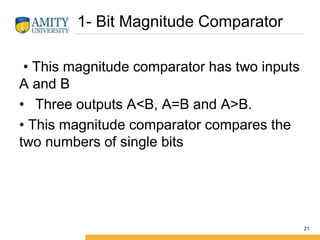
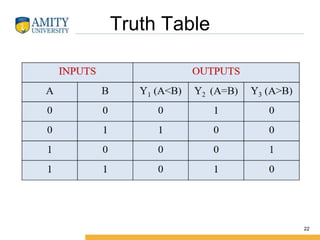
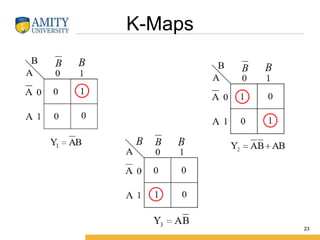
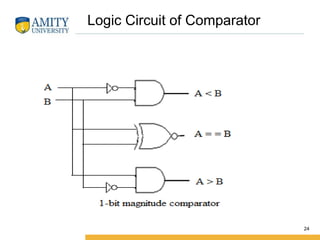
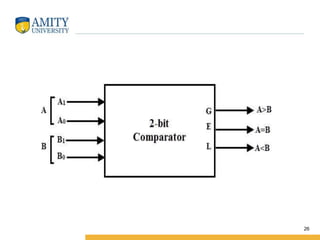
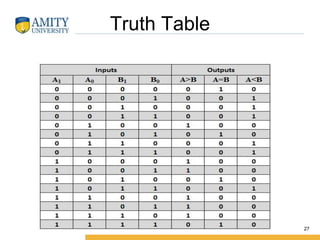
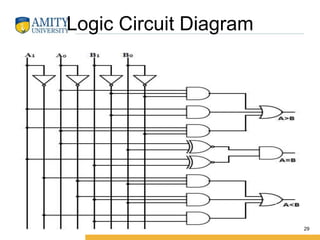
This document discusses parity circuits and comparators in digital electronics. It describes how parity bits are used to detect errors during data transmission by making the total number of 1s in a message either even or odd. Parity generators add the parity bit and parity checkers detect errors by checking the parity. Even and odd parity circuits are explained along with examples of 3-bit generators and 4-bit checkers. The document also describes how magnitude comparators work by taking two binary numbers as input and determining if one is greater than, less than, or equal to the other. Examples of 1-bit and 2-bit comparators are presented along with their truth tables, K-maps, and logic circuits.