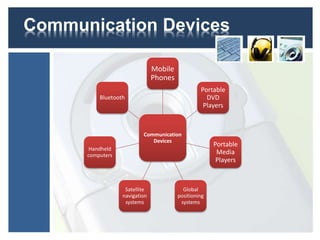
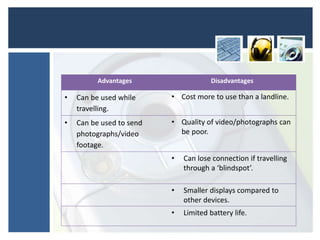
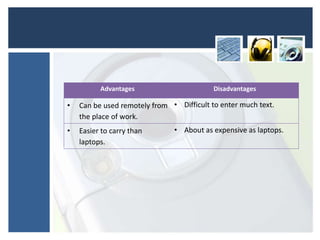
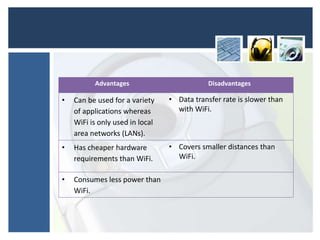
This document discusses various portable communication devices including mobile phones, portable DVD players, portable media players, global positioning systems, satellite navigation systems, handheld computers, and Bluetooth. Mobile phones can be used for calls and messages while traveling but have limited battery life and displays. Portable DVD and media players allow compact playback of music and videos but have small screens. GPS and satellite navigation provide positioning and routing assistance but require expensive devices. Handheld computers allow remote work but are difficult for text entry. Bluetooth enables wireless connection of devices like headsets, mice, and printers and has cheaper hardware than WiFi.