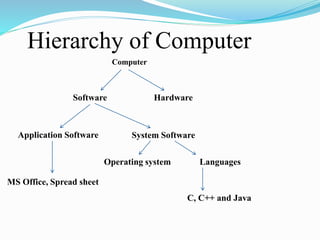
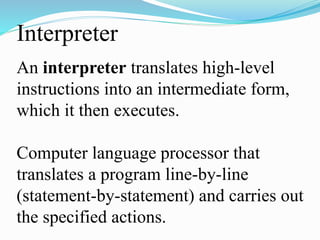
The document introduces computer programming concepts including the hierarchy of computers, programming languages, and specific characteristics of the C language. It explains the roles of compilers and interpreters, and highlights the differences between structured and object-oriented programming. Additionally, it emphasizes the advantages of learning C for its speed, portability, and support for modular programming.