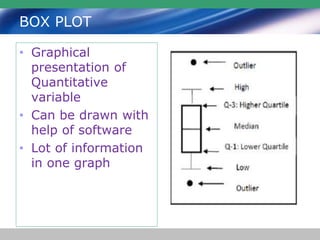
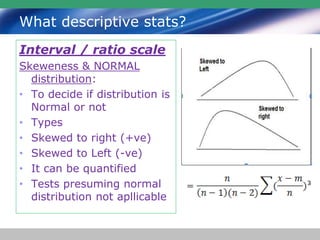
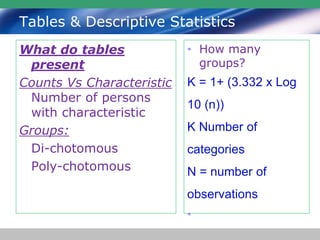
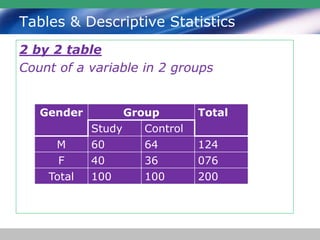
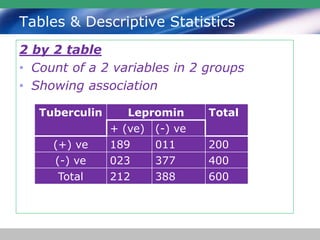
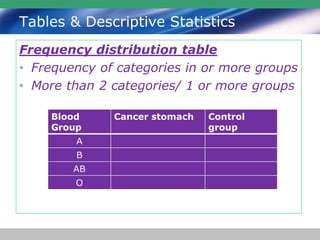
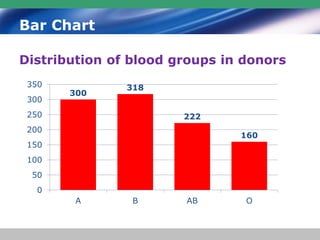
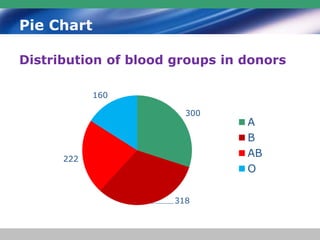
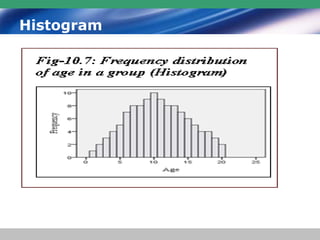
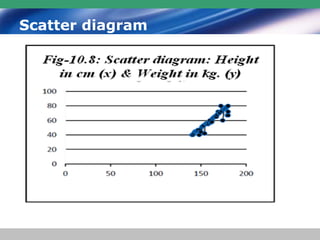
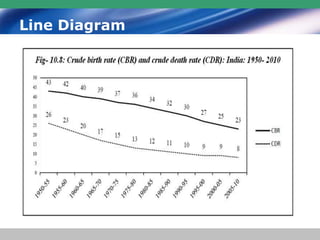
This document discusses descriptive statistics and how they are used to summarize raw data. Descriptive statistics include rates, ratios, proportions, measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), variation (standard deviation), and position (percentiles, quartiles). These statistics can be presented numerically and graphically using tables, bar charts, pie charts, histograms, box plots, and scatter plots. Software like MS Excel is commonly used to calculate descriptive statistics and generate graphs to meaningfully reduce and present large amounts of raw data.