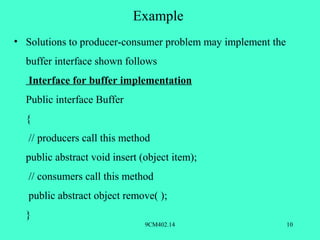
This document discusses process management and cooperation between processes. It defines independent and cooperating processes, with independent processes unable to affect or be affected by other processes, while cooperating processes can. Reasons for process cooperation include information sharing, speeding up computation by dividing tasks, modularity, and convenience. The producer-consumer problem is provided as an example of cooperating processes, where a producer process generates items for a consumer process to use.








![Example
• The producer process involves the insert( ) method when It
wishes to enter an item in the buffer
insert( ) method
Public void insert (object item){
While (count= = BUFFER SIZE)
; // do nothing - - no free buffers
+ + count;
buffer [in]=item;
in=(in+1) % BUFFER -SIZE;
}
9CM402.14 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14relationshipbetweenprocesses-130116081629-phpapp02/85/14-relationship-between-processes-11-320.jpg)
![Example
• The consumer calls the remove( ) method when it wants to consume an item
from the buffer
remove method
Public object remove ( ) {
Object item;
While (count= = 0)
; // do nothing - - nothing to consume
// remove an item from the buffer
--count;
item=buffer [out];
out=(out+1) % BUFFER _ SIZE;
return item; } 9CM402.14 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14relationshipbetweenprocesses-130116081629-phpapp02/85/14-relationship-between-processes-12-320.jpg)





