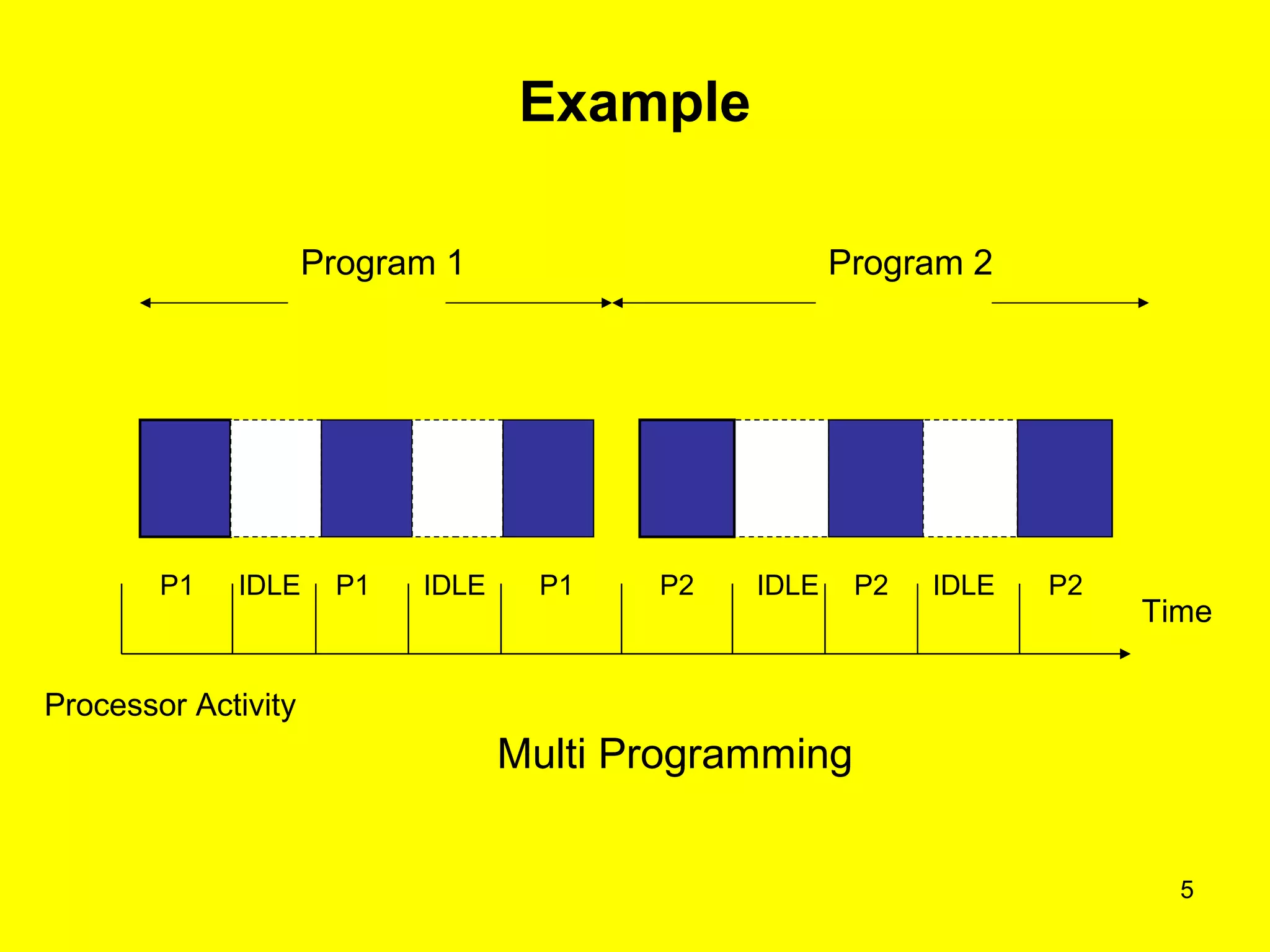
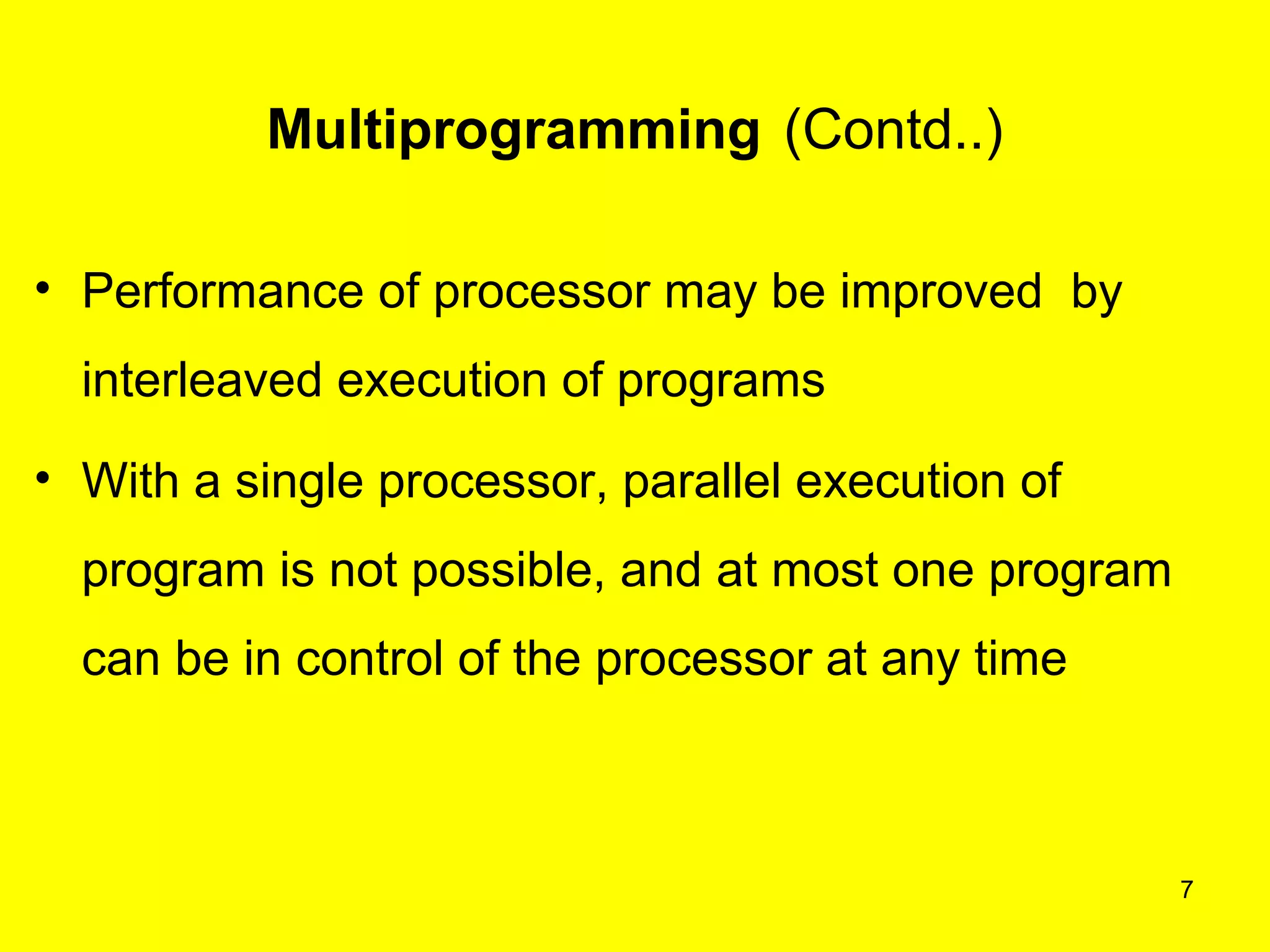
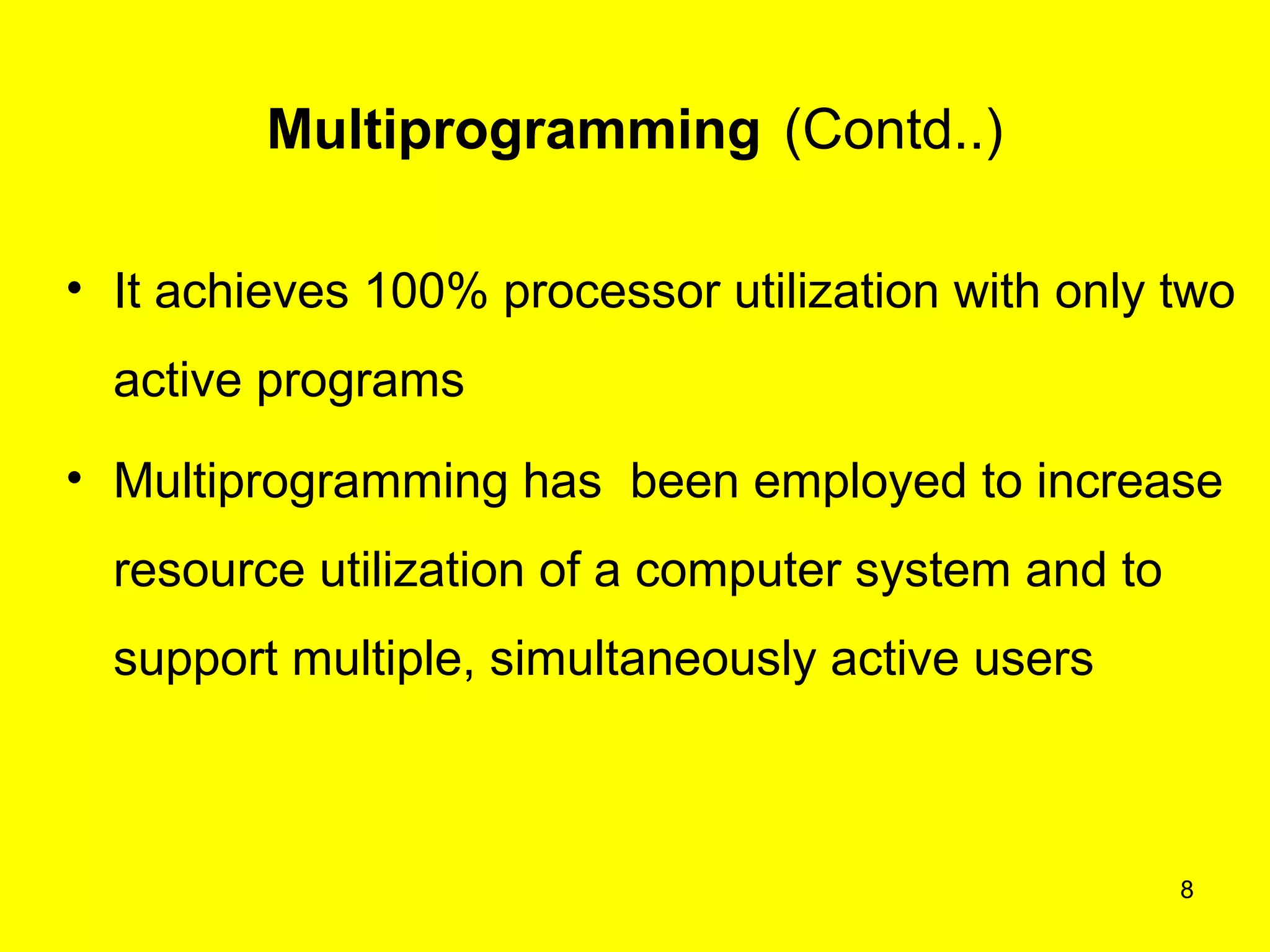
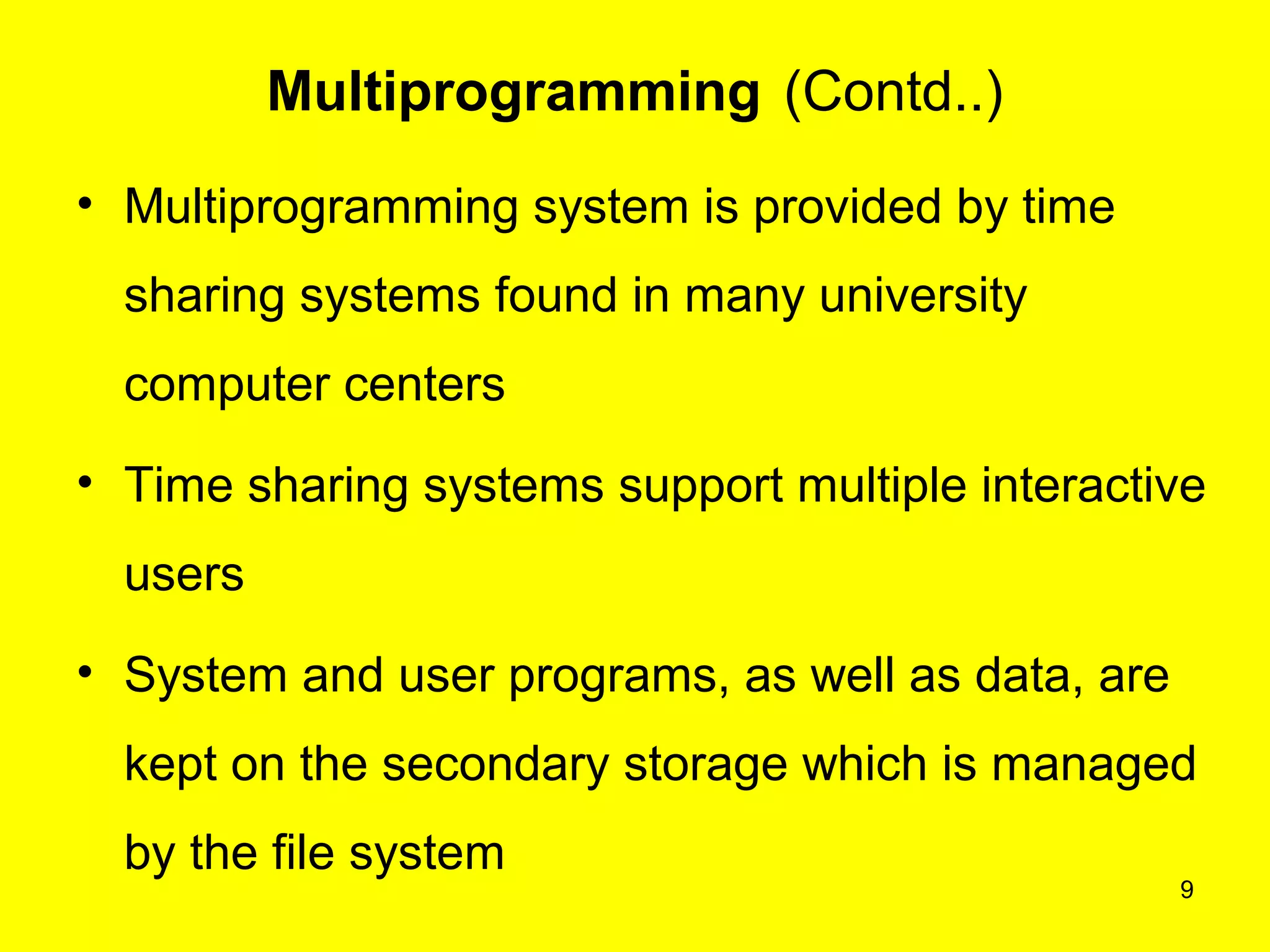
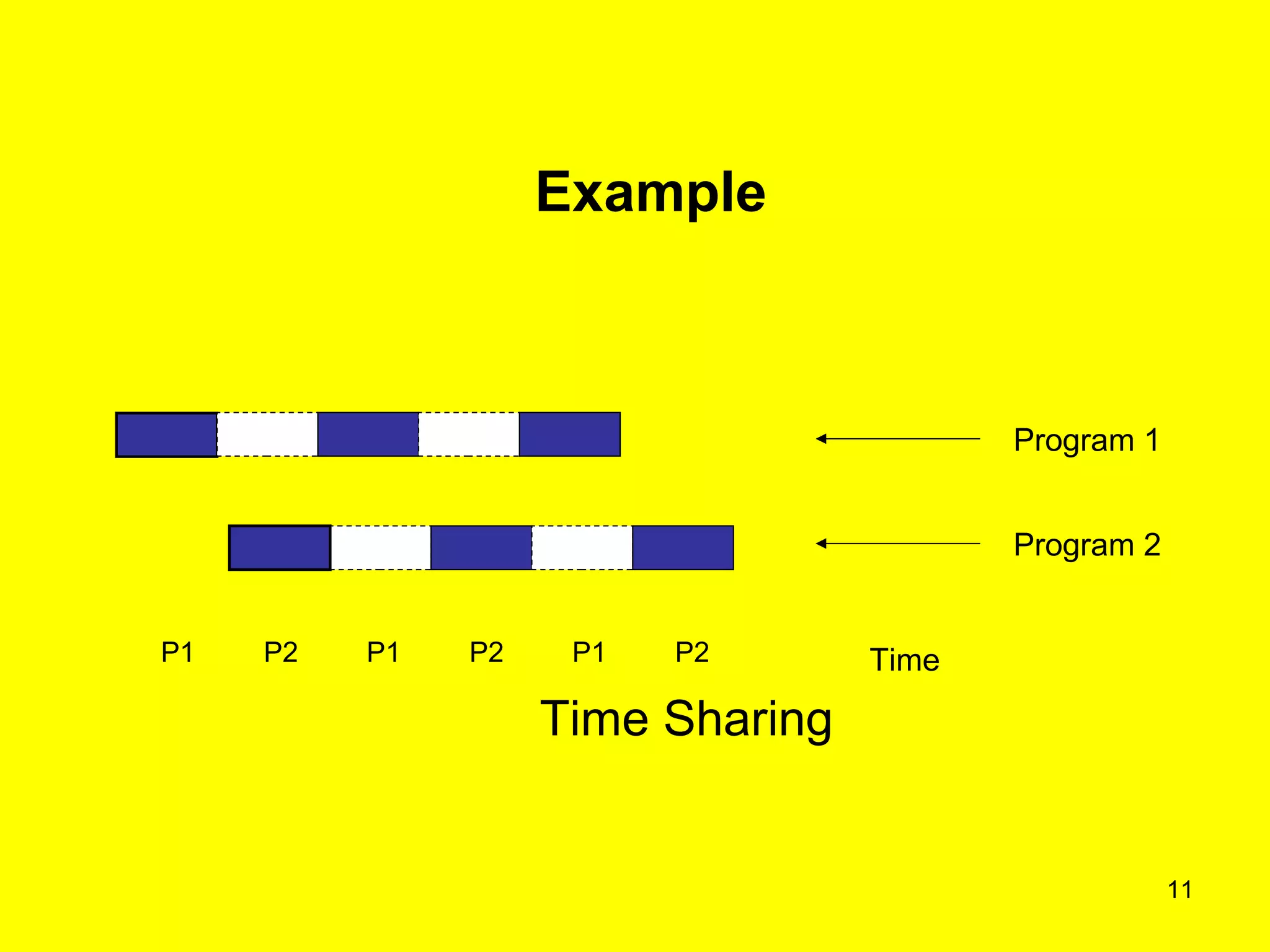
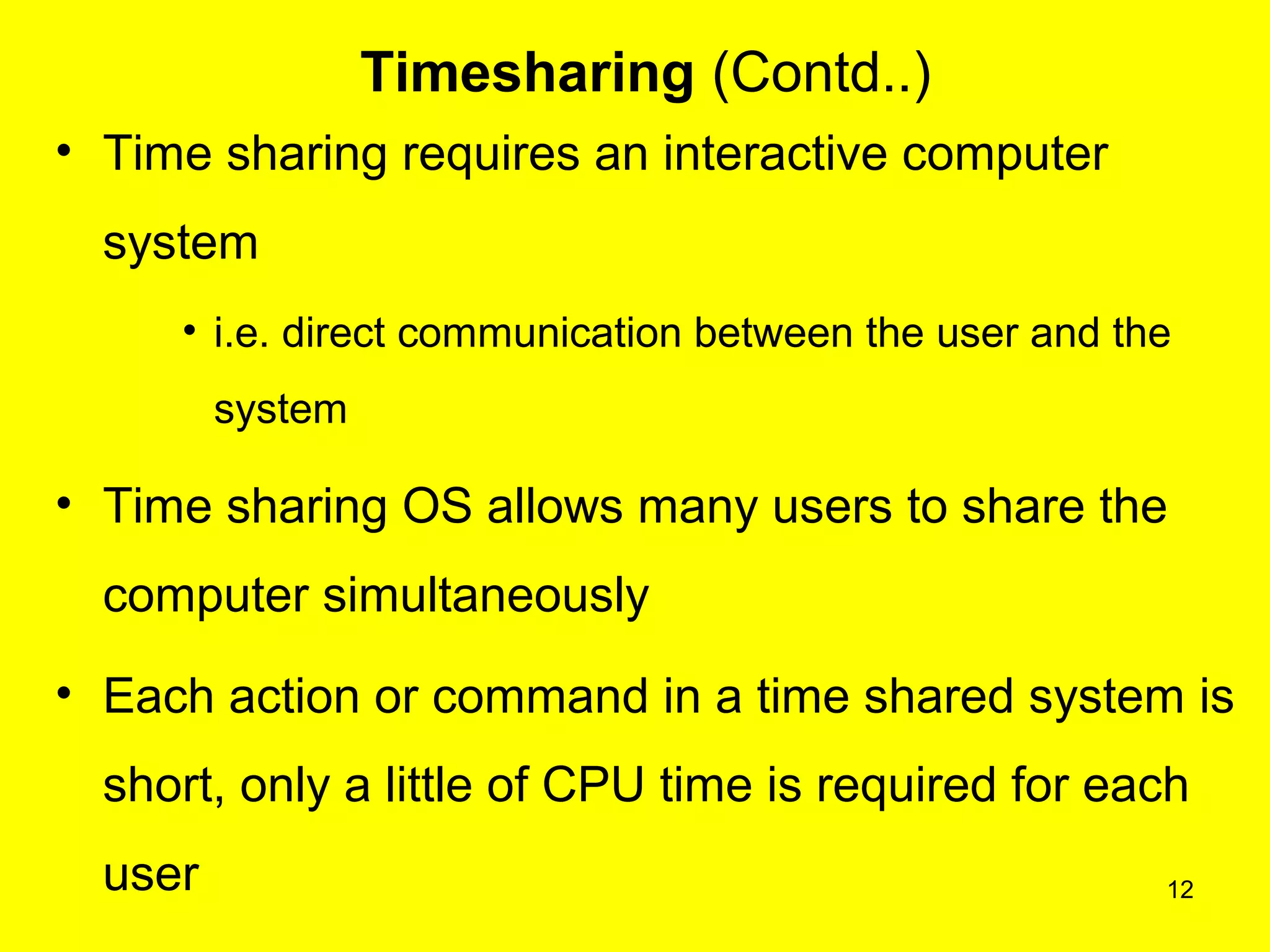
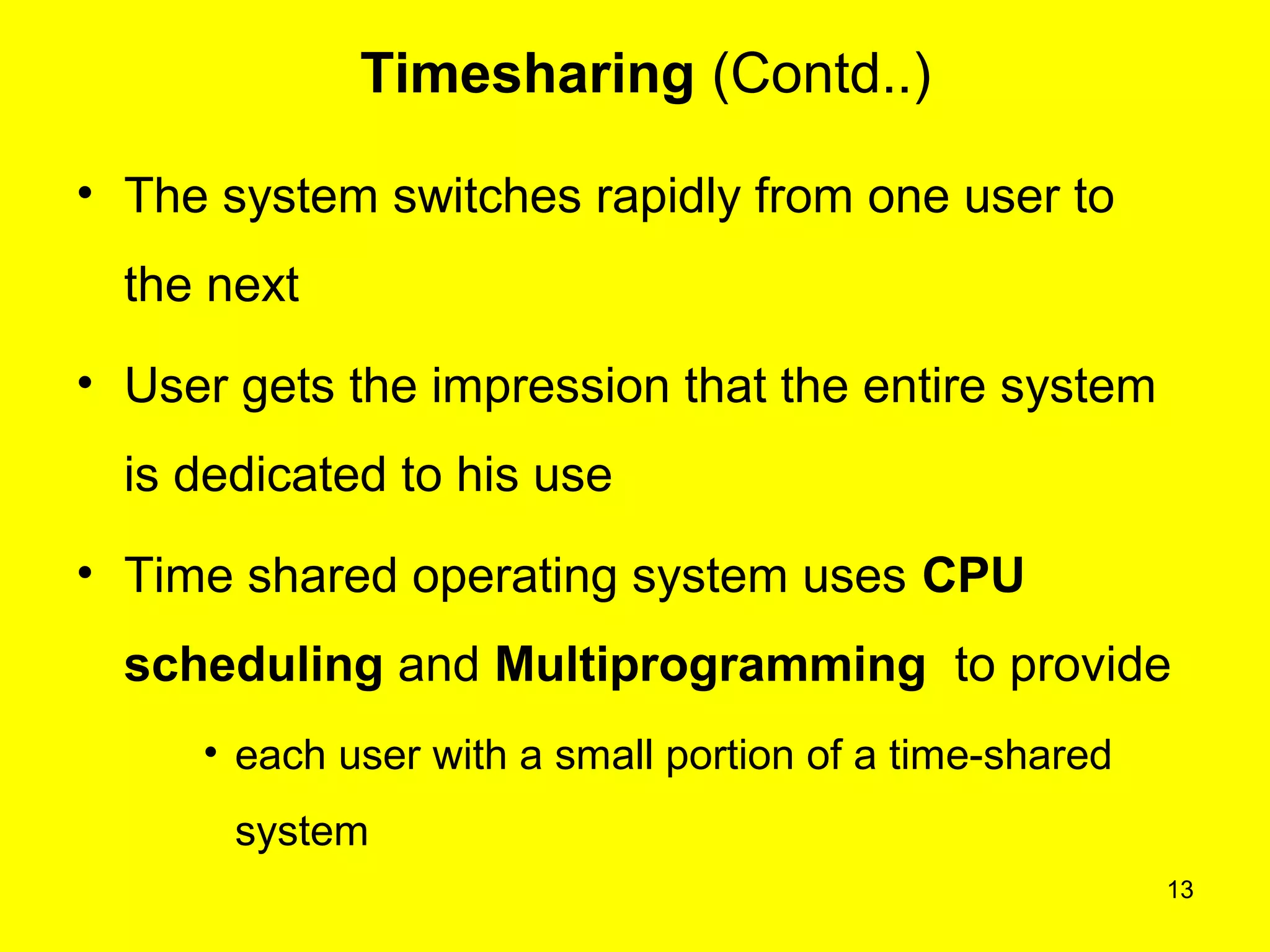
This document discusses multiprogramming and time sharing in operating systems. It defines multiprogramming as allowing multiple programs to execute concurrently by assigning pending work to underutilized components like processors and I/O devices. Time sharing extends this by rapidly switching between programs so that each user experiences dedicated access, while programs only execute briefly in time quanta. The key aspects of both techniques are explained with examples to improve processor utilization and support interactive, simultaneous multi-user systems.