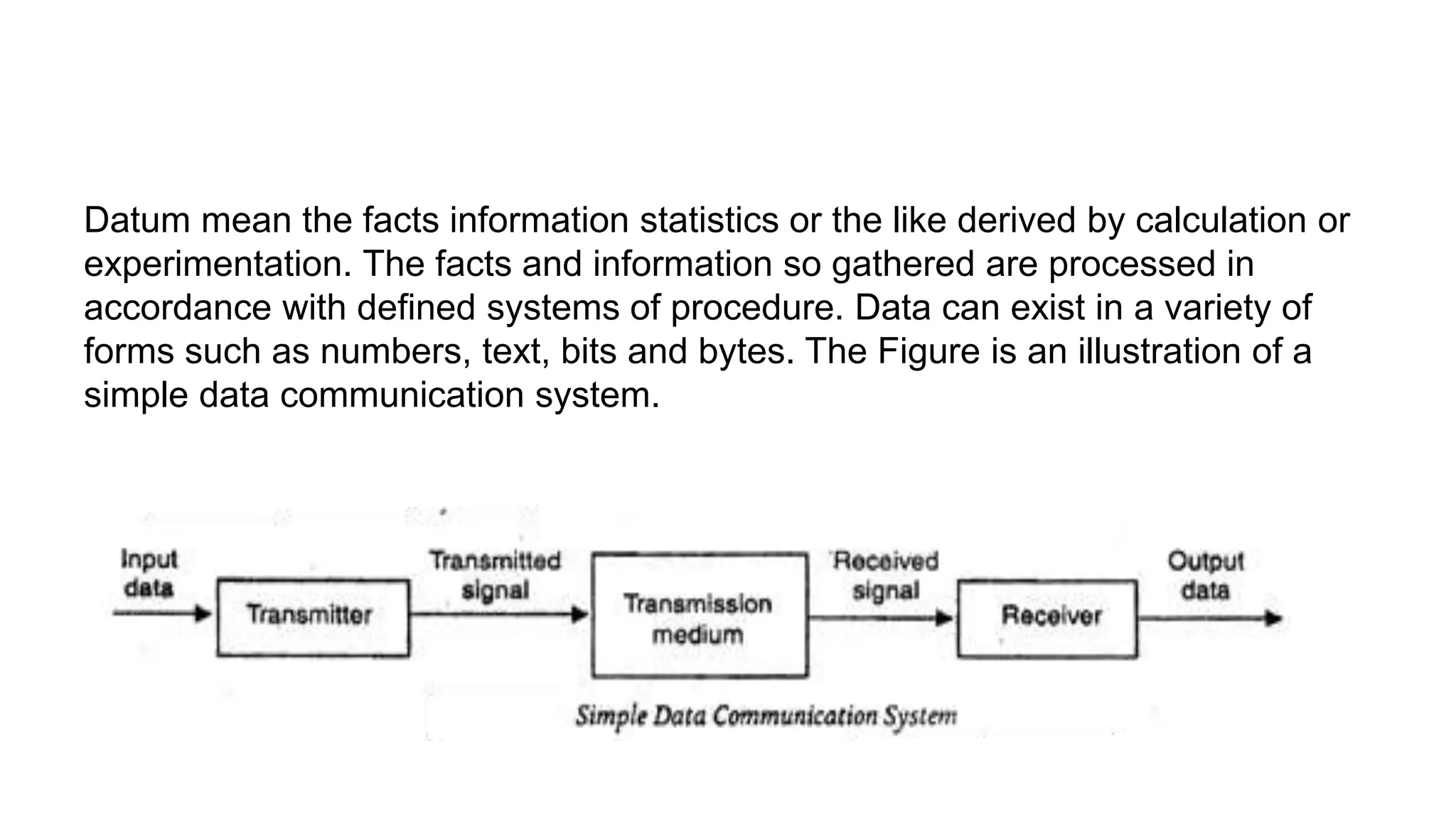
Data communication refers to the exchange of data between a source and receiver. It can be local, occurring within the same building, or remote, occurring over data transmission circuits. A data communication system collects data from remote locations and outputs processed results remotely. It consists of a message, sender, receiver, medium like wired or wireless networks, and protocols that govern communication between devices by sequencing data, routing, formatting, controlling flow, and detecting and correcting errors. Protocols also determine precedence, connection establishment, and termination.