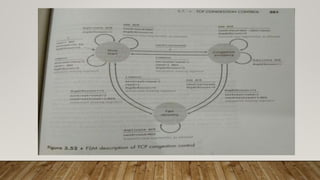
The document discusses congestion control mechanisms in computer networks. It defines congestion as occurring when a link or node carries more data than it can handle. Congestion can be caused by senders transmitting at rates higher than the router's capacity. TCP uses three components - slow start, congestion avoidance, and fast recovery - to control congestion. Slow start exponentially increases the congestion window when acknowledgments are received. Congestion avoidance linearly increases the window size when no packet loss is detected. Fast recovery allows rapid retransmission when packet loss is detected.