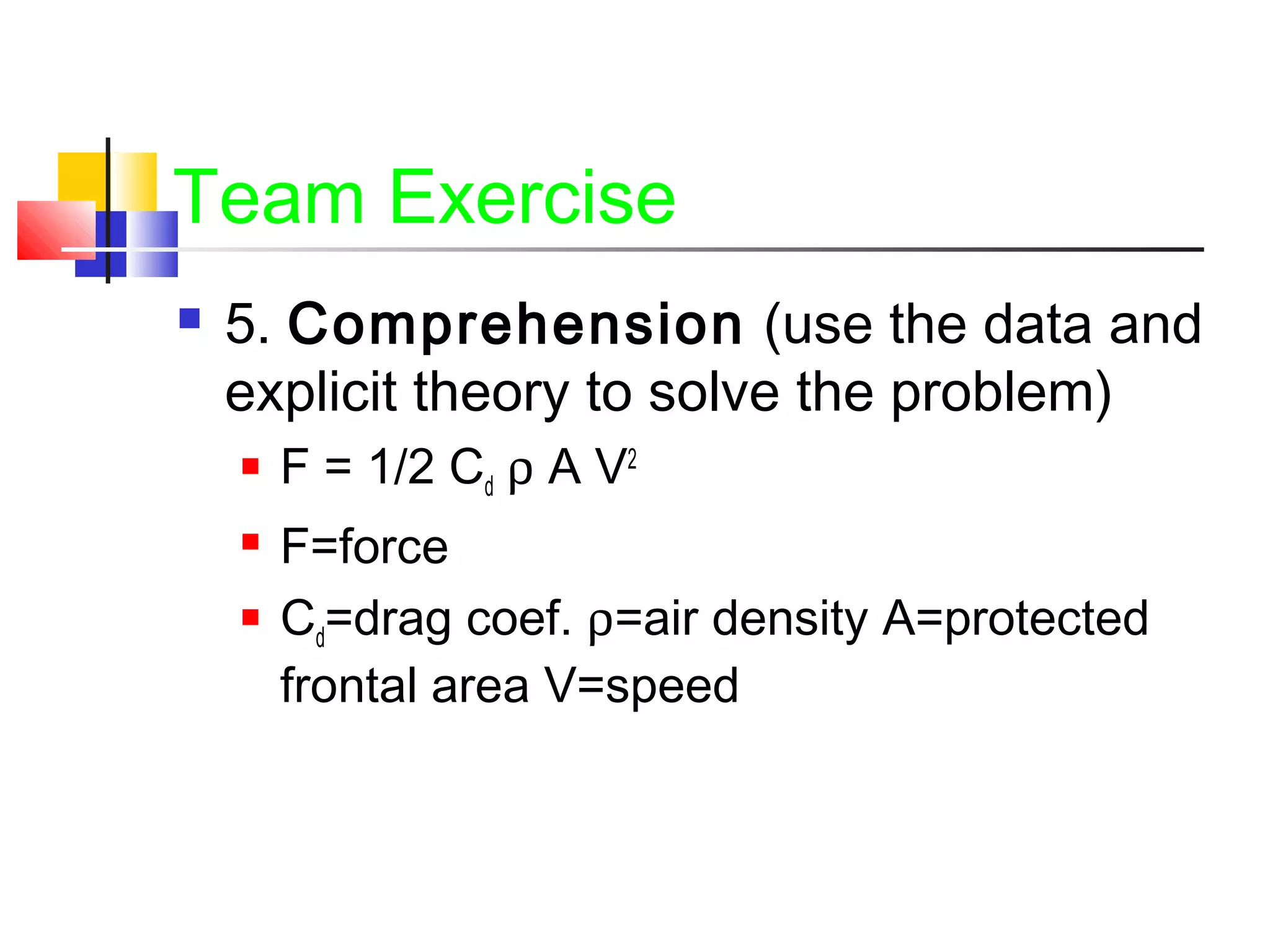
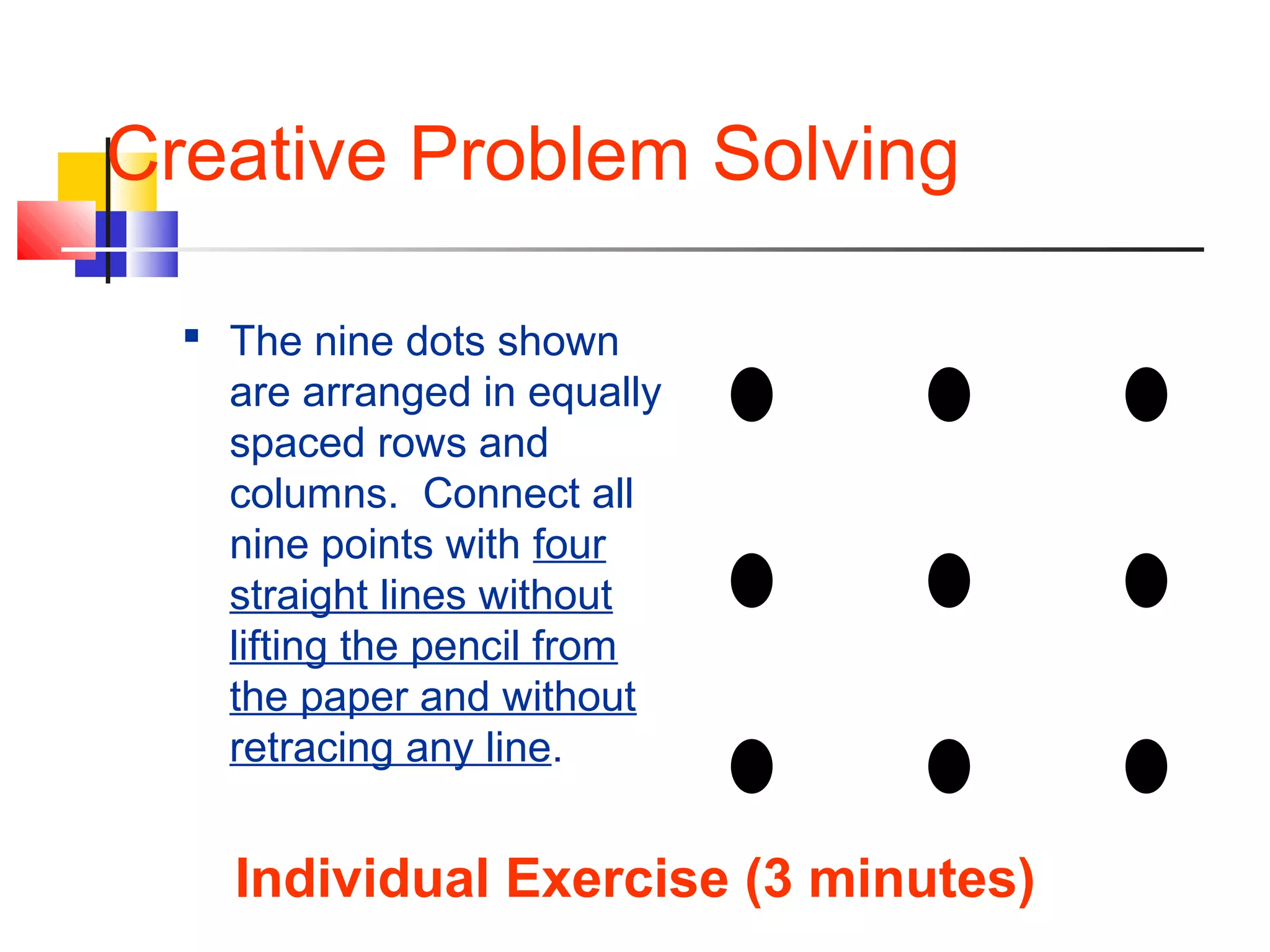
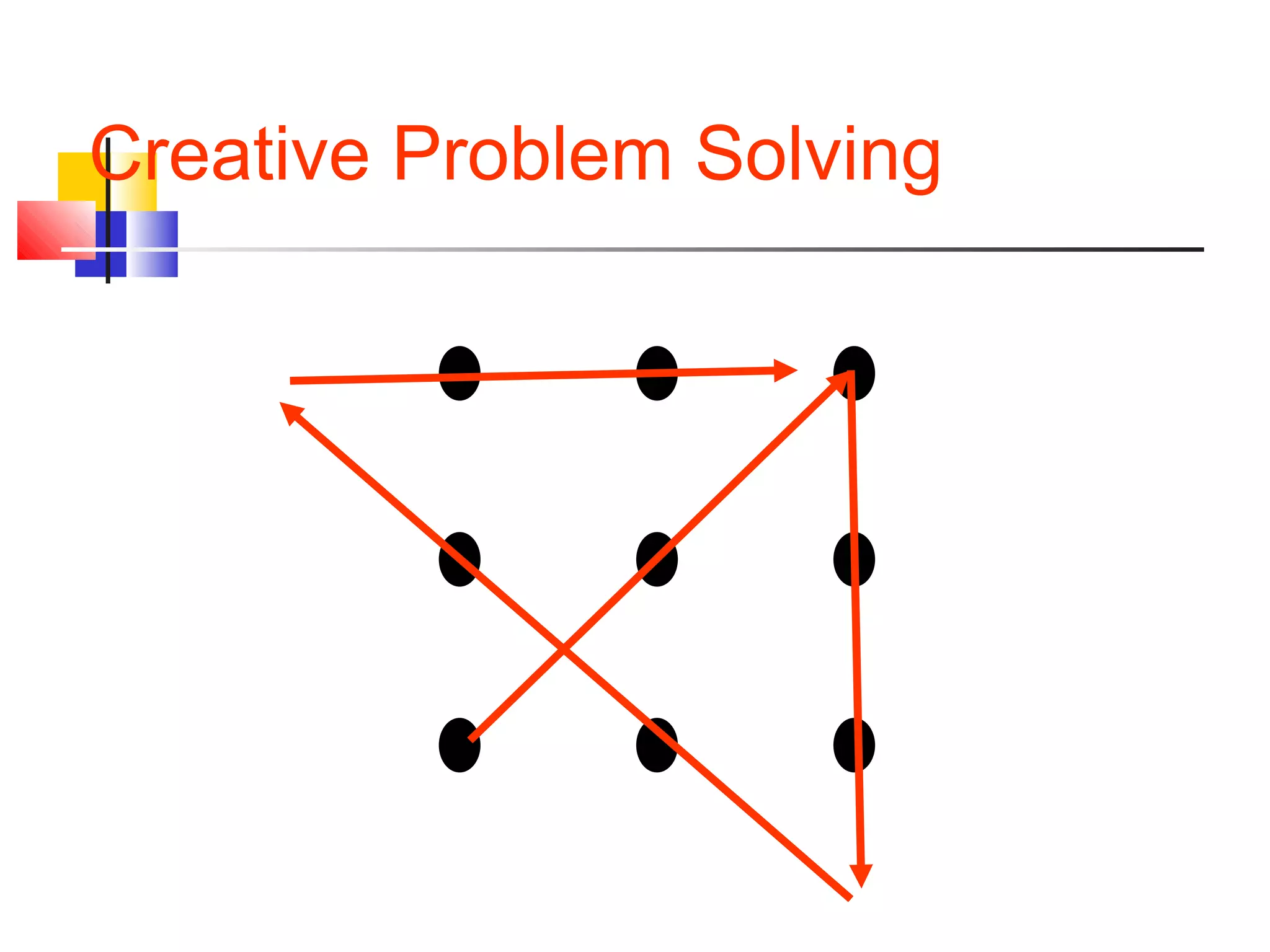
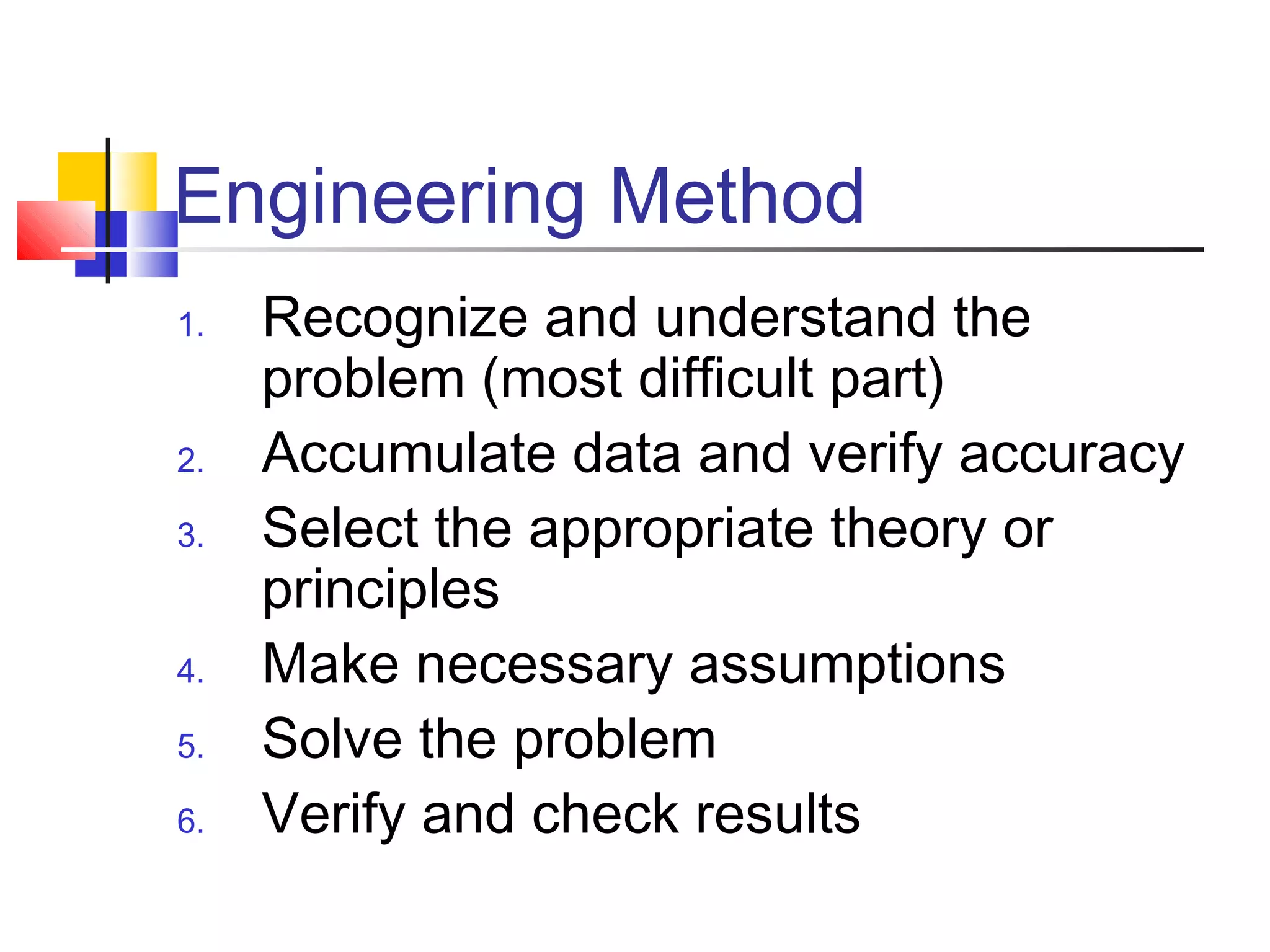
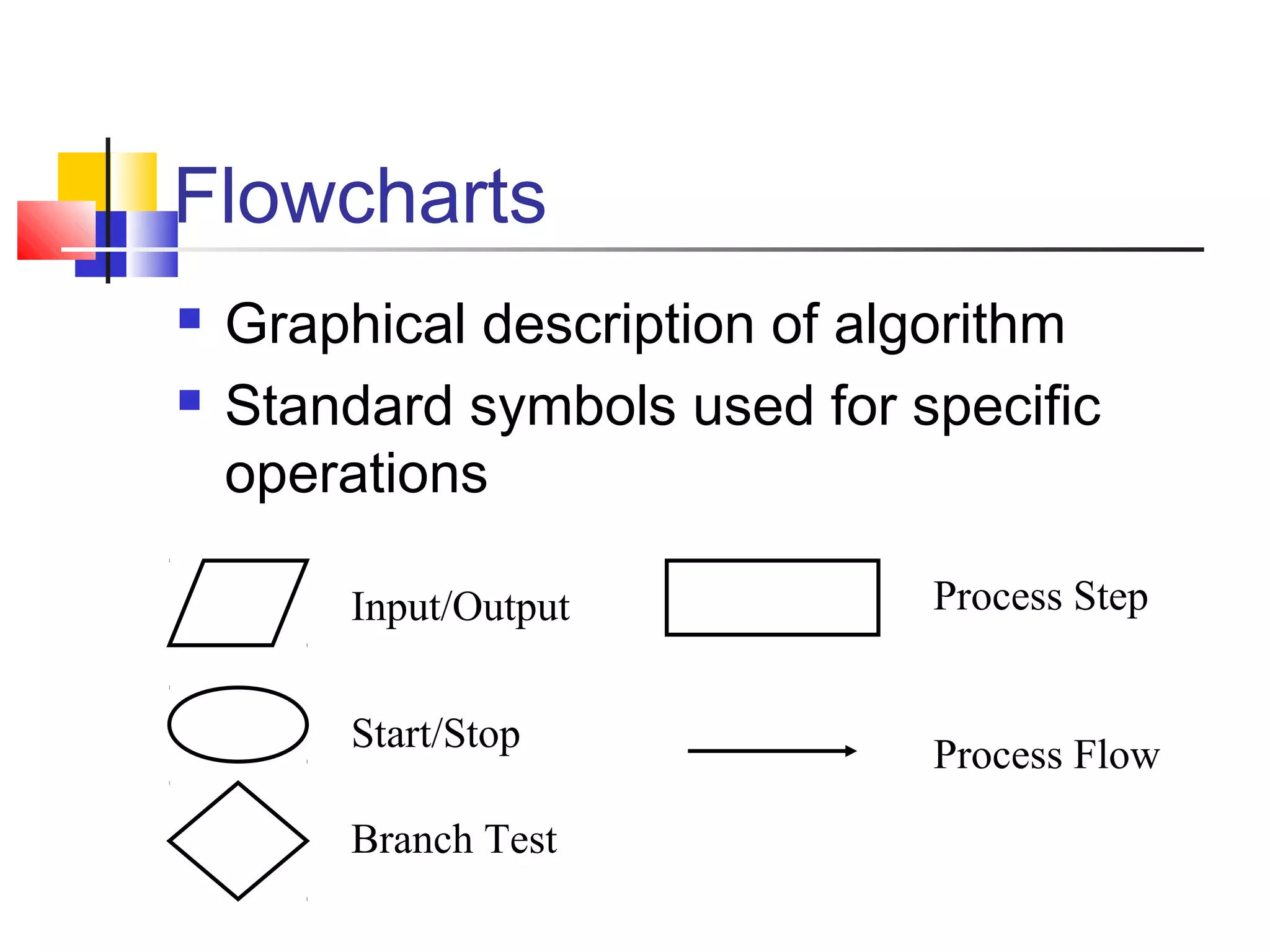
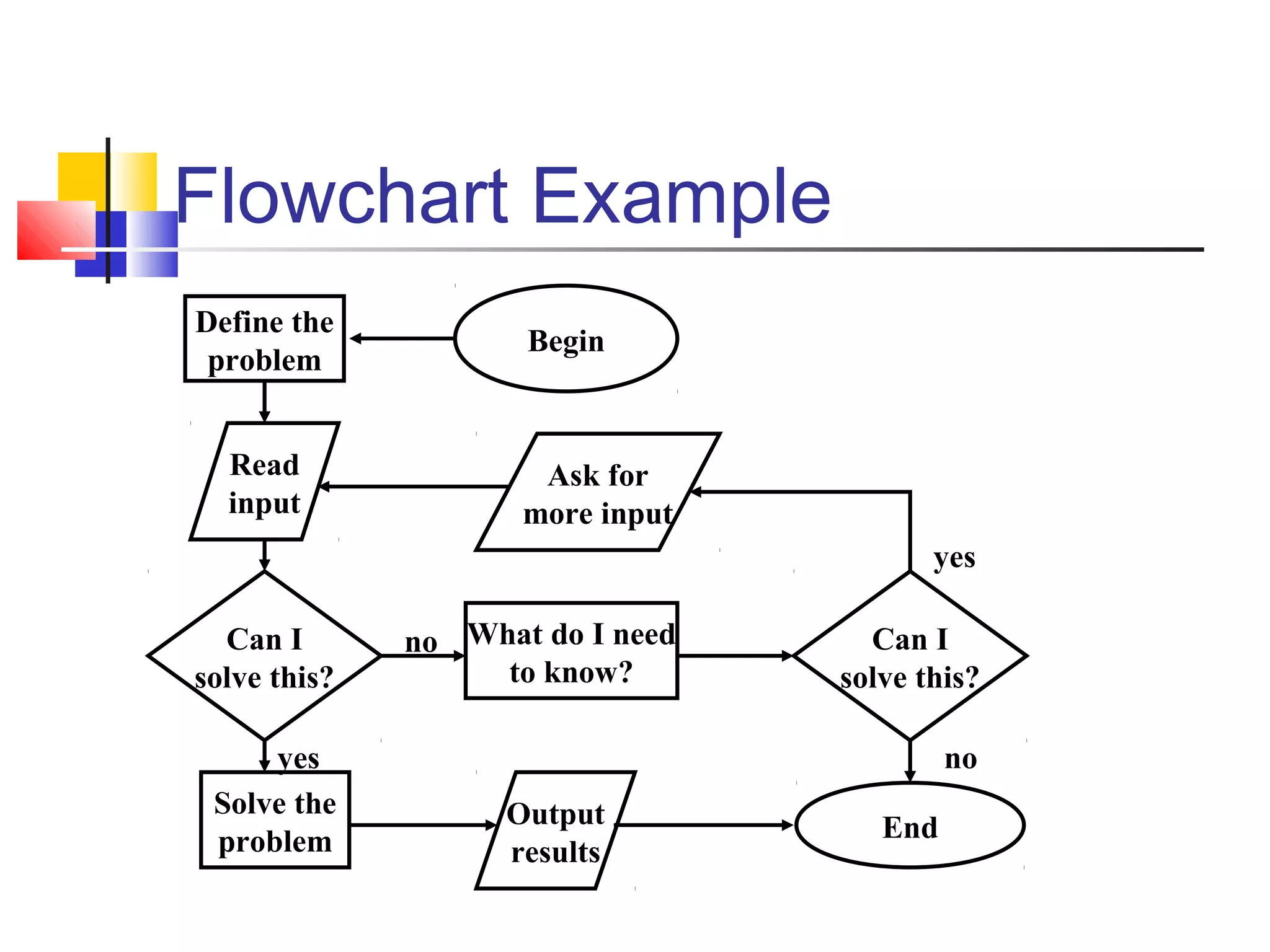
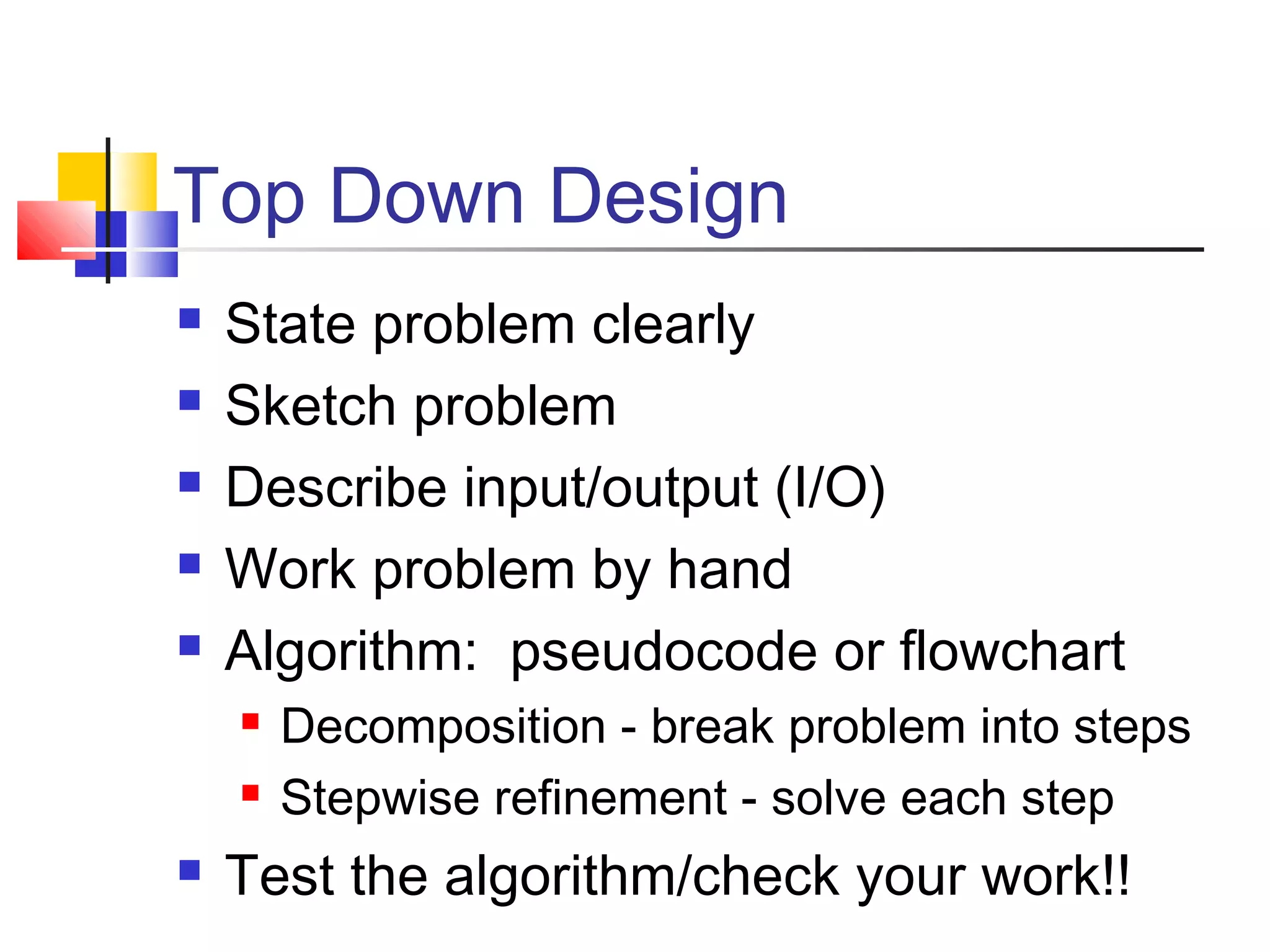
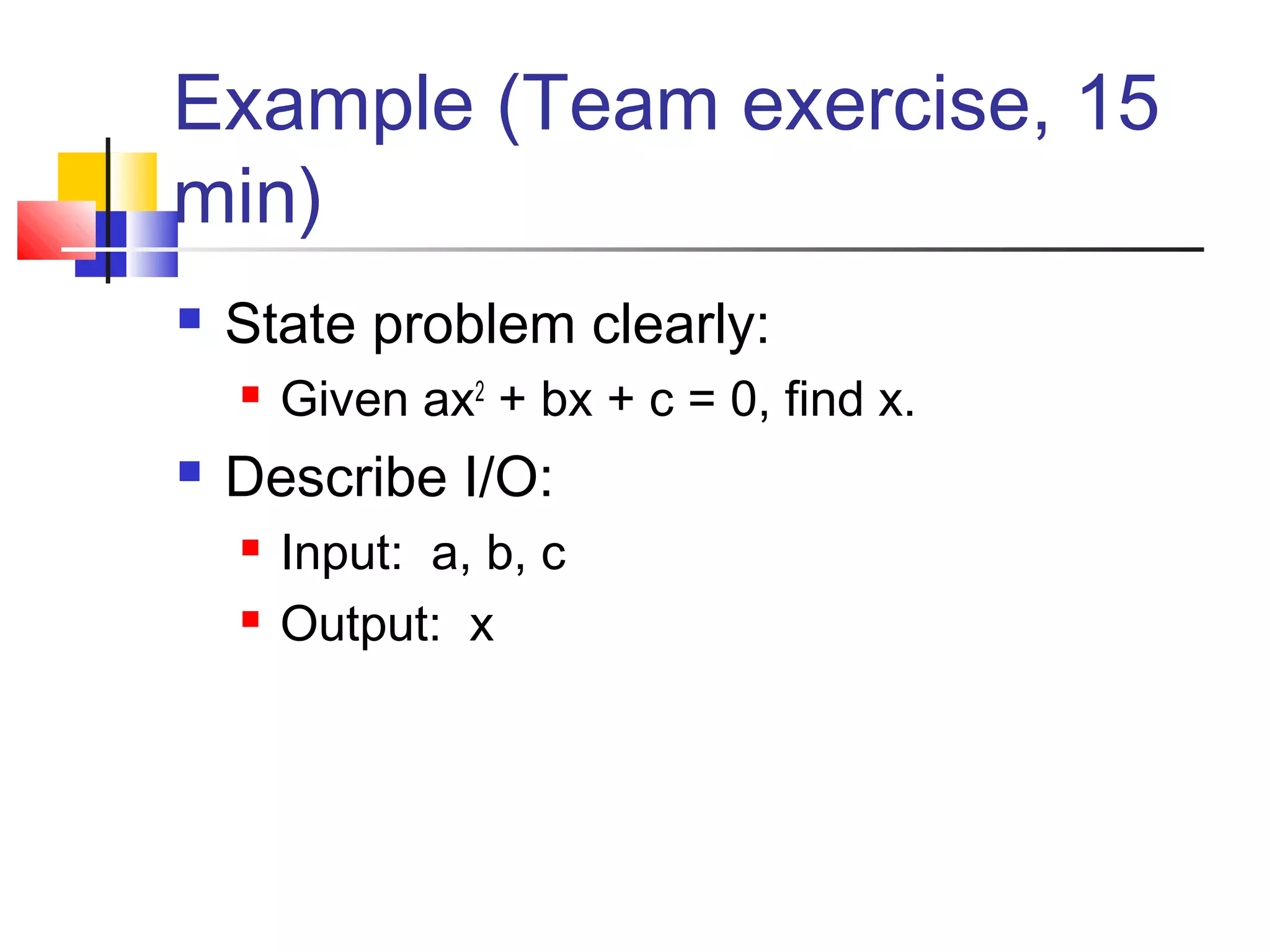
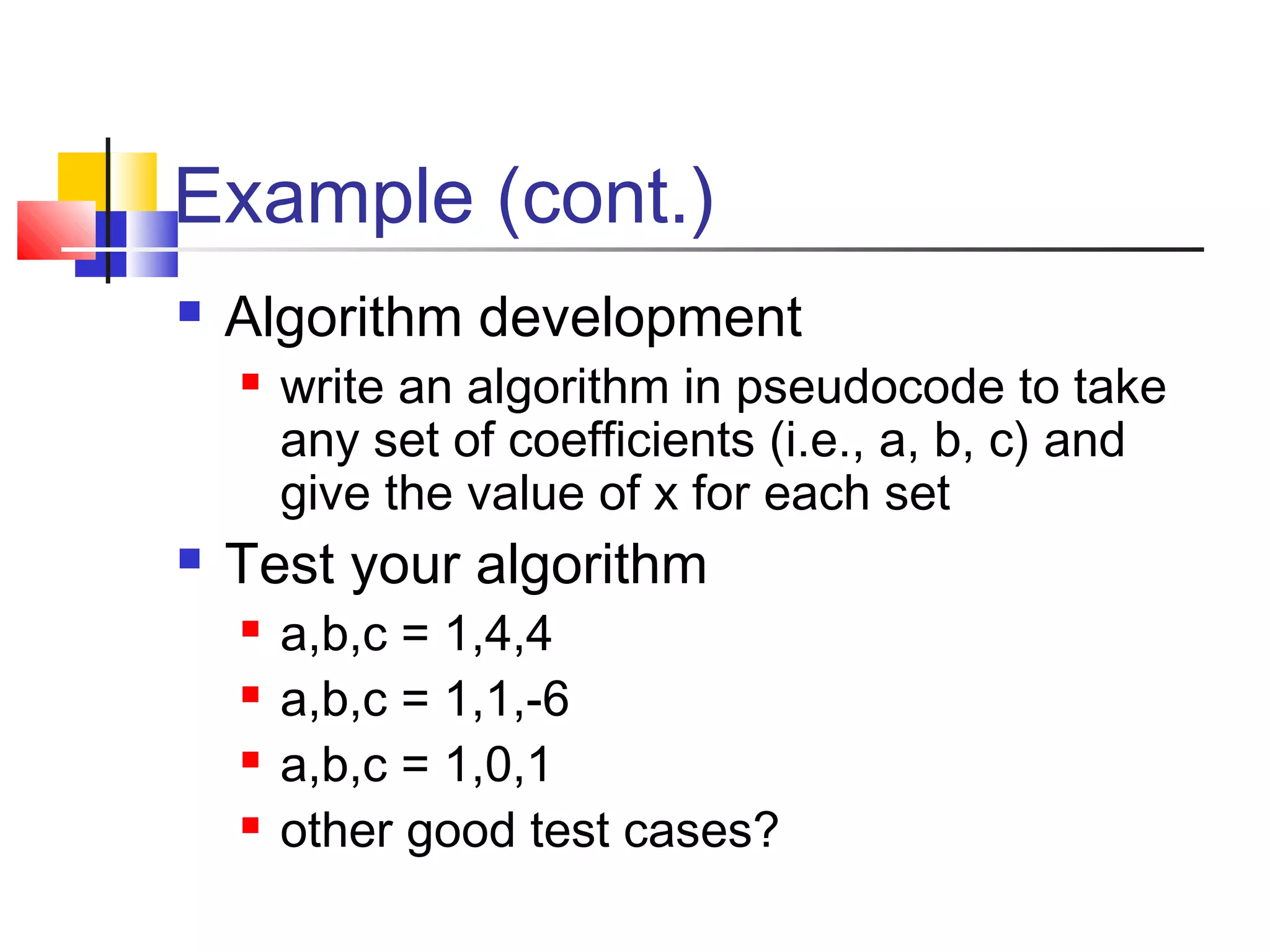
This document provides information on problem solving methods used by engineers. It discusses that problem solving involves a combination of experience, knowledge, process, and art. The design process involves a series of logical steps to produce an optimal solution given constraints of time and resources. A problem is defined as a situation that requires resolution where the individual sees no apparent solution. Problem solving is described as a process used to determine the best value for an unknown subject to specific conditions using previously acquired skills and knowledge. The document outlines various problem solving techniques including drawing pictures, stating assumptions, writing equations, and checking work. It also discusses different types of problems, skills used in problem solving, difficulties that can arise, and general problem solving methods.