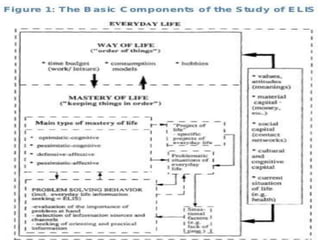
The document discusses everyday life information seeking (ELIS). It defines ELIS as focusing on how social and cultural factors influence how people acquire information to solve daily problems. It notes two main reasons for seeking information: for orientation and for solving specific problems. The document also discusses who seeks information, usually people in problematic situations, and how they seek it through information sharing with others or exploring different information source horizons based on content and accessibility.