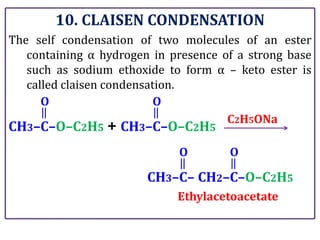
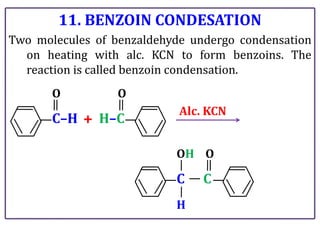
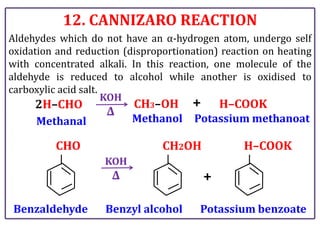
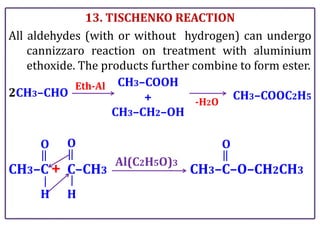
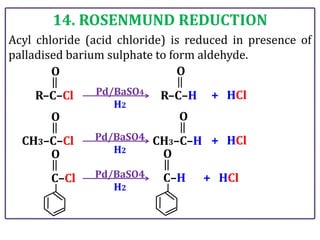
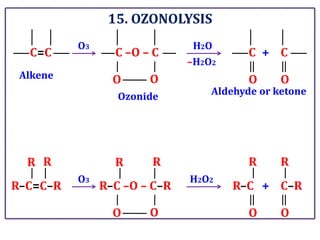
The document presents various chemical reactions involving aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids, including ozonolysis, aldol condensation, and Cannizzaro reaction. Each reaction is briefly explained, providing the reactants, conditions, and products involved. A total of 15 different reactions are outlined, demonstrating key organic chemistry concepts.






![9. CLEMENSON REDUCTION
The reduction of aldehyde or ketone (carbonyl CO group)
to alkane with amalgamated zinc and concentrated
hydrochloride acid.
R–C–H
O
+ 4[H]
Zn/Hg + Conc. HCl
R–CH3 + H2O
R–C–R
O
+ 4[H]
Zn/Hg + Conc. HCl
R–CH2–R + H2O
Ar–C–H
O
+ 4[H]
Zn/Hg + Conc. HCl
Ar–CH2–R + H2O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12-221223034300-f11da7a9/85/12-ALDEHYDE-pptx-12-320.jpg)