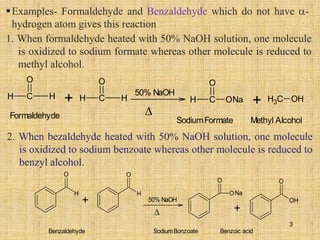
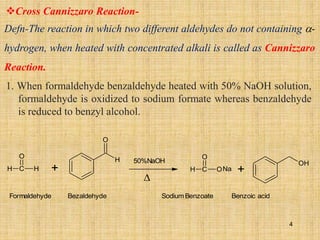
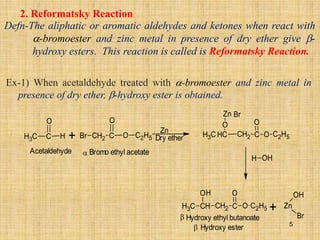
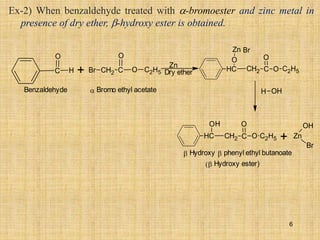
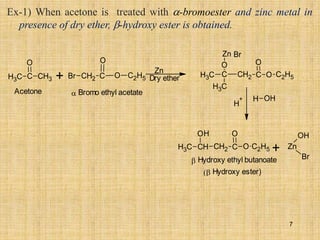
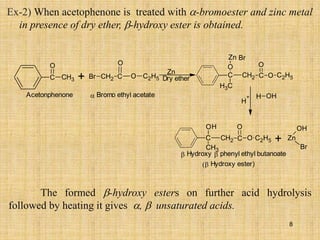
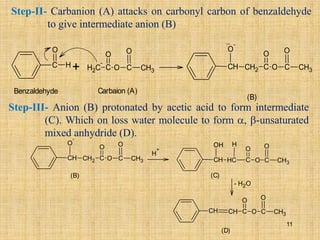
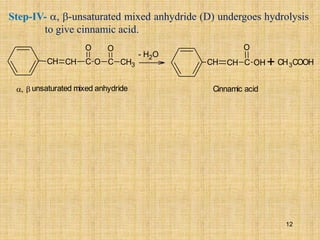
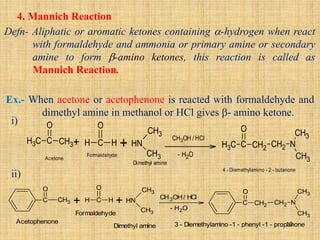
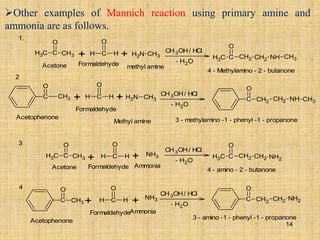
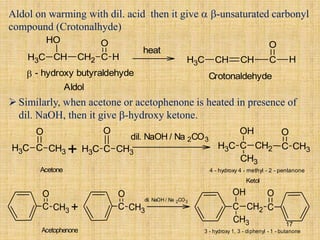
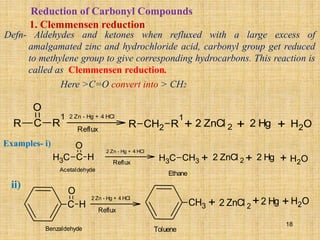
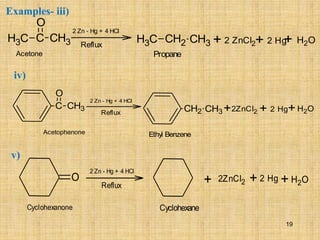
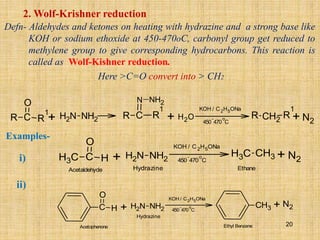
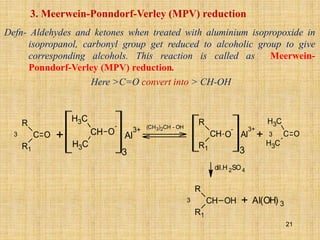
The document outlines various chemical reactions involving aldehydes and ketones, including the Cannizzaro reaction, Reformatsky reaction, Perkin reaction, Mannich reaction, and others. It describes the conditions and mechanisms for these reactions, providing examples and the products formed, such as sodium salts, hydroxy esters, and unsaturated acids. Additionally, it covers reduction methods such as Clemmensen, Wolf-Kishner, and Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reductions.






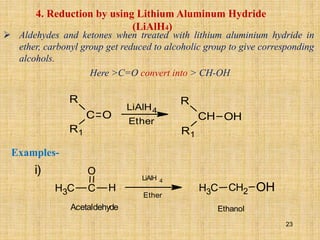
![Examples-
C
H3 C H
O
[(CH 3)2CHO] 3Al
Acetaldehyde Ethanol
(CH3)2 -CH - OH
C
H3 CH2 OH
C H
O
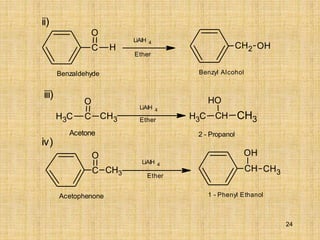
CH2 OH
[(CH 3)2CHO] 3Al
(CH3)2 -CH - OH
Benzaldehyde Benzyl Alcohol
C
H3
C CH3
O
[(CH 3)2CHO] 3Al
Acetone 2 - Propanol
(CH3)2 -CH - OH
C
H3 CH CH3
O
H
C CH3
O
CH
OH
CH3
[(CH 3)2CHO] 3Al
(CH3)2 -CH - OH
Acetophenone 1 - Phenyl Ethanol
i)
ii)
iii)
iv)
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemsem-iiiunit-iii-aldehydepart-ii-210218095438/85/Aldehyde-Ketone-22-320.jpg)