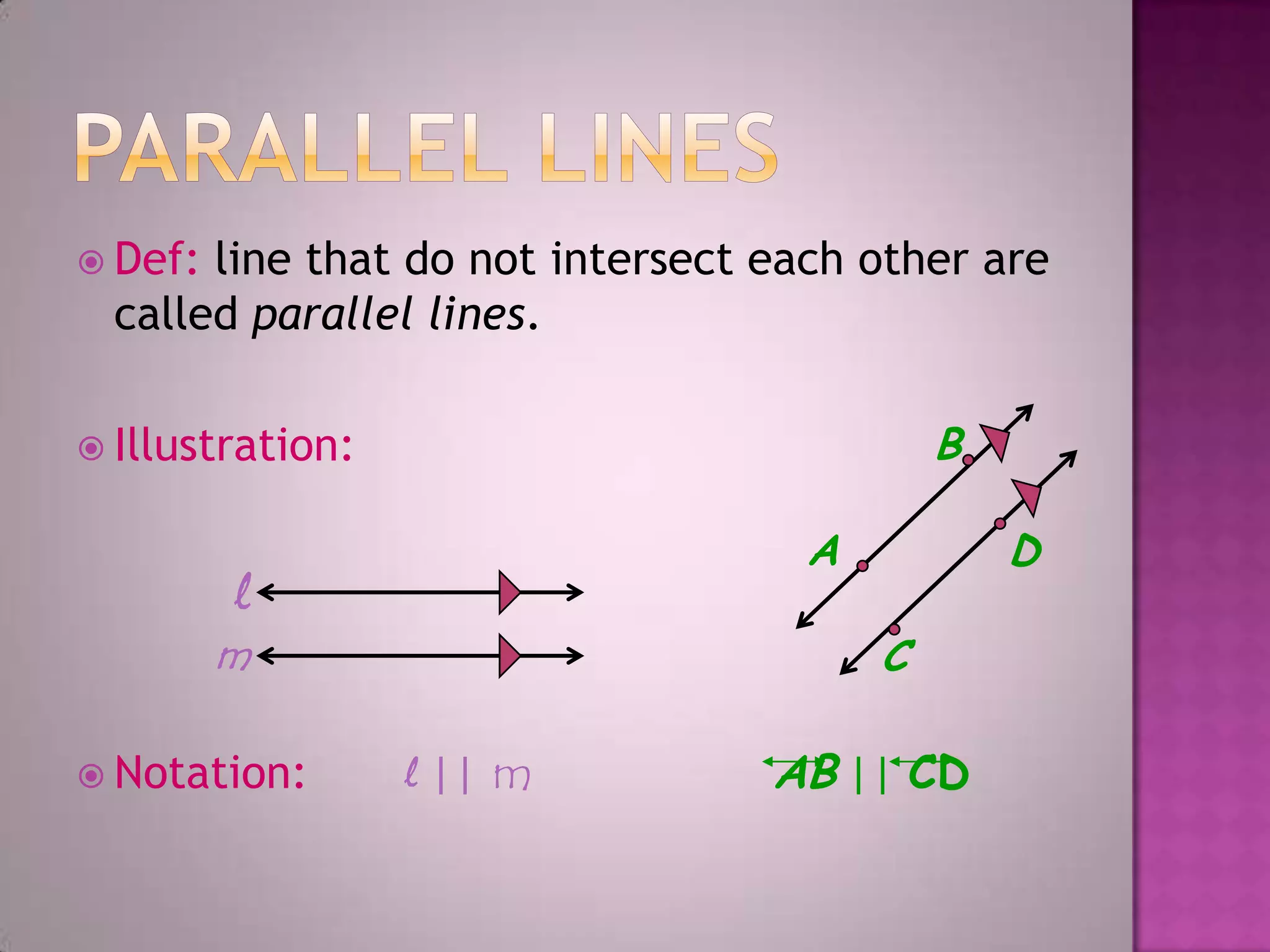
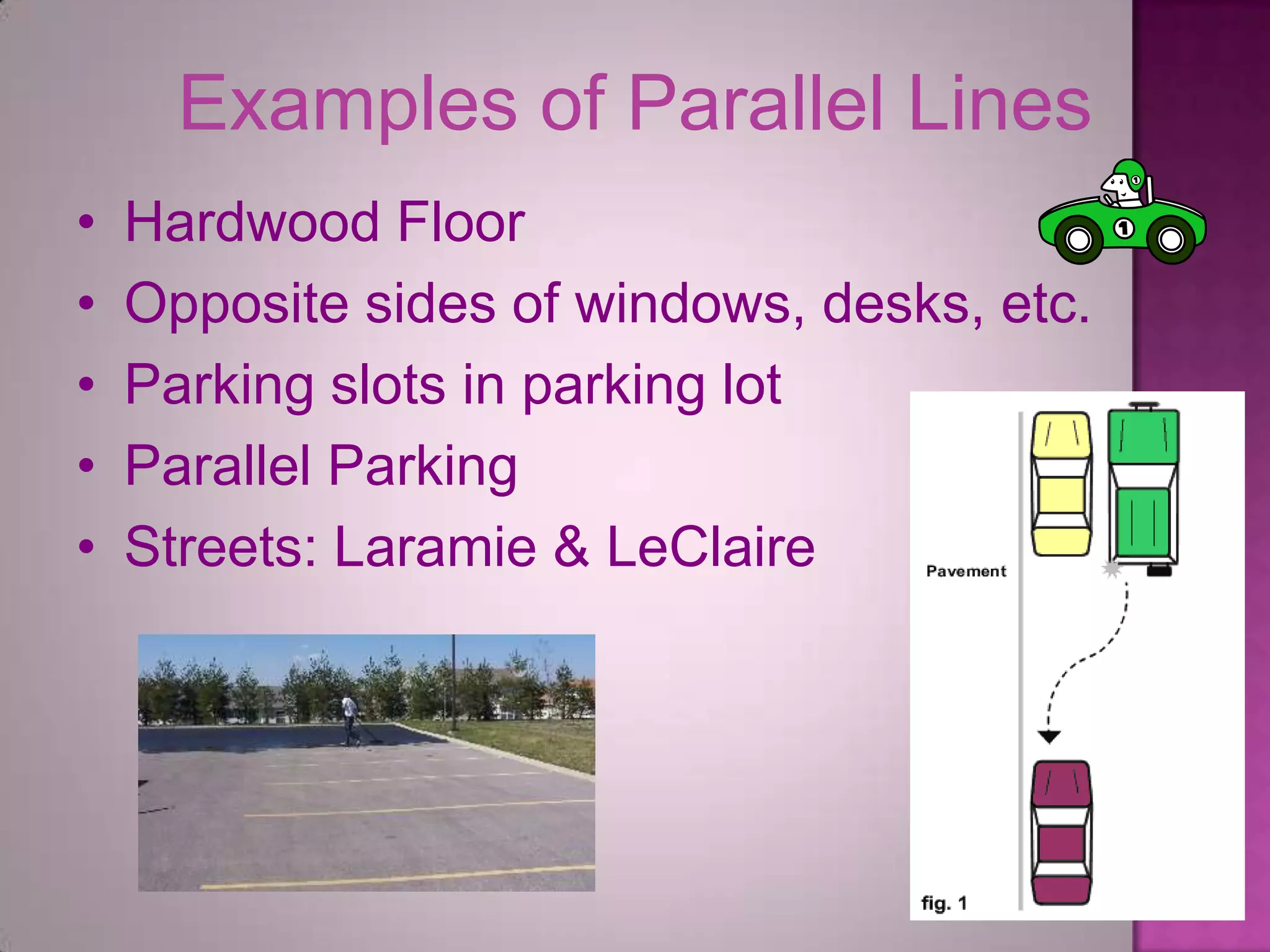
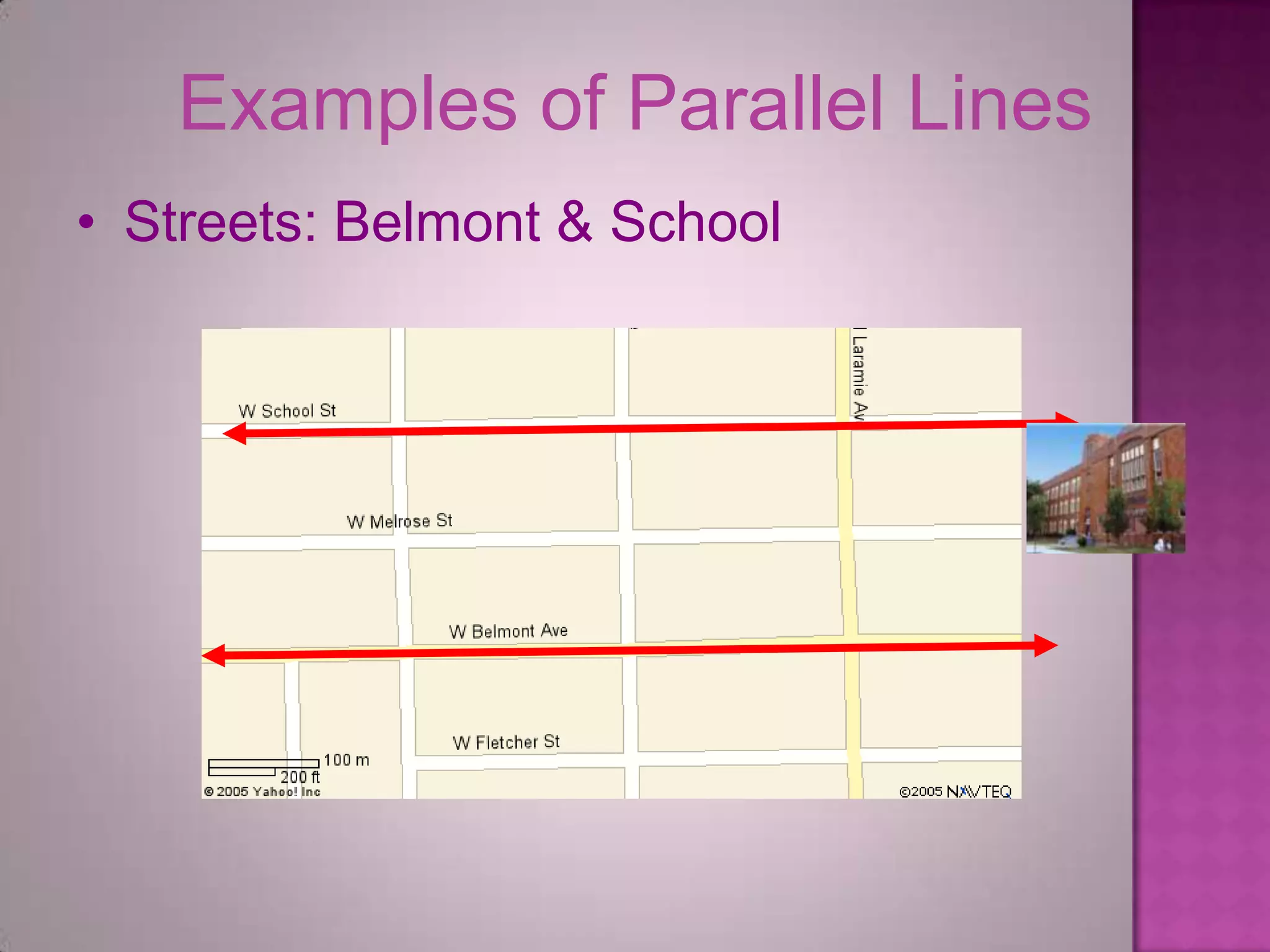
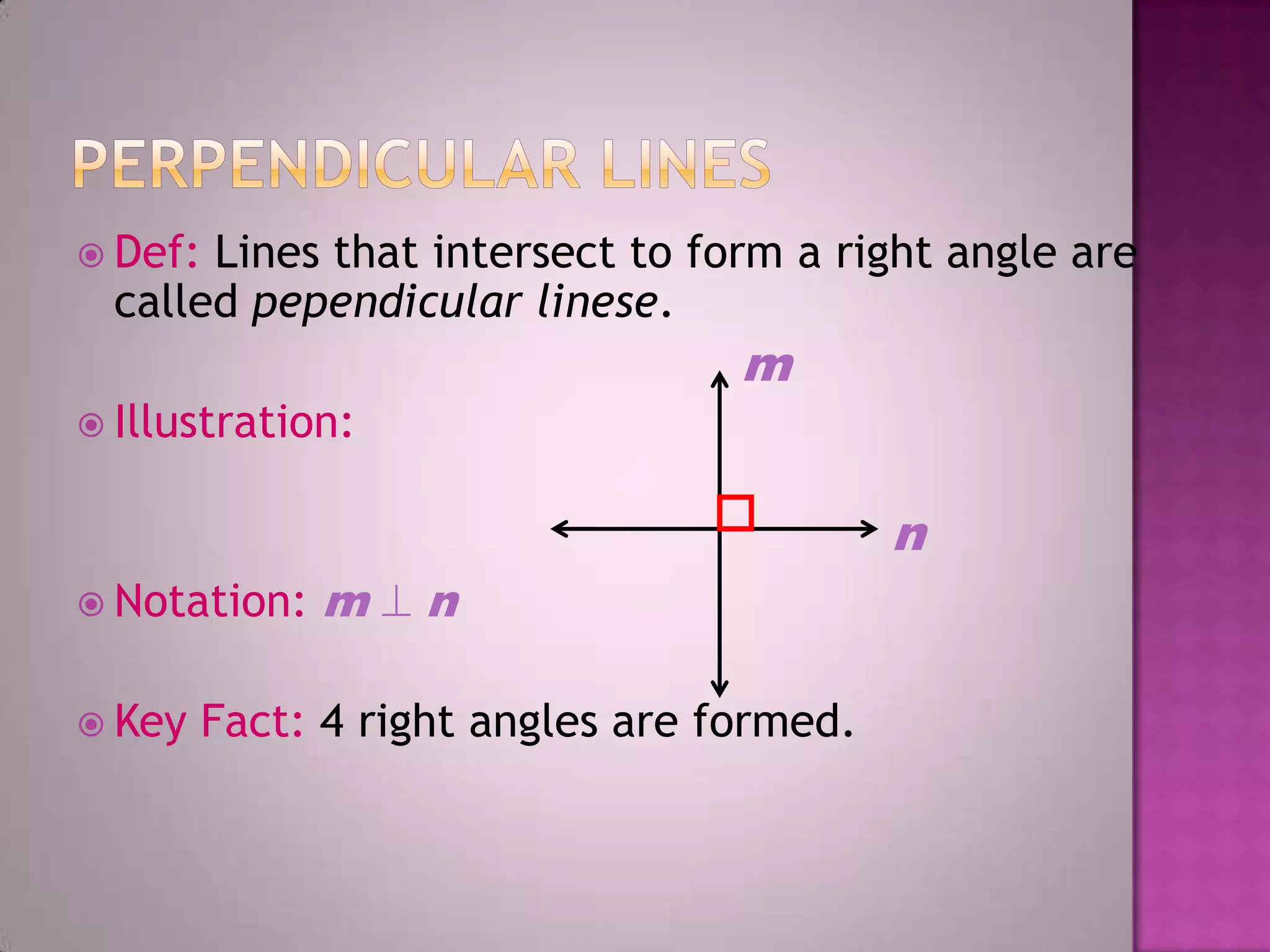
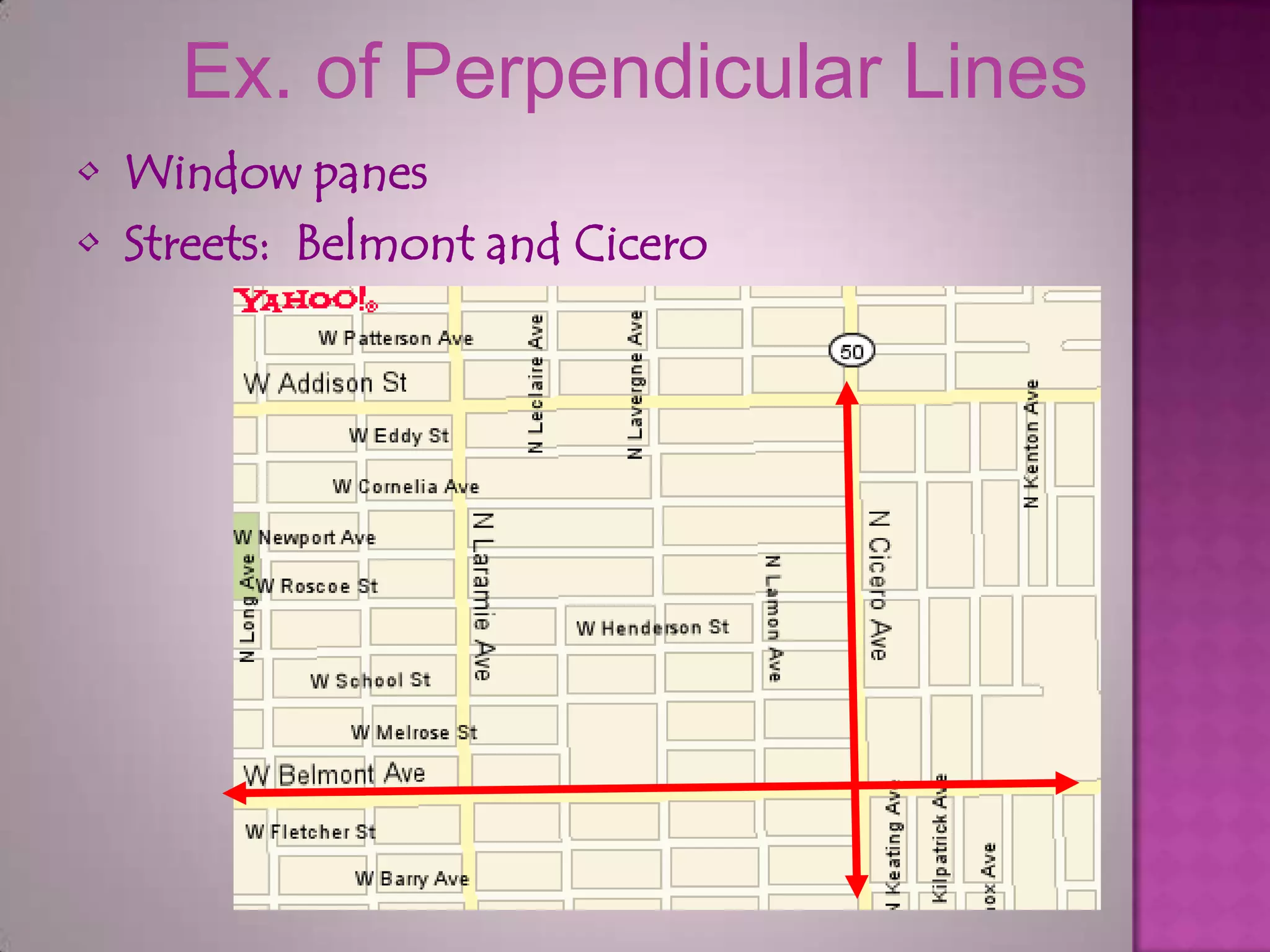
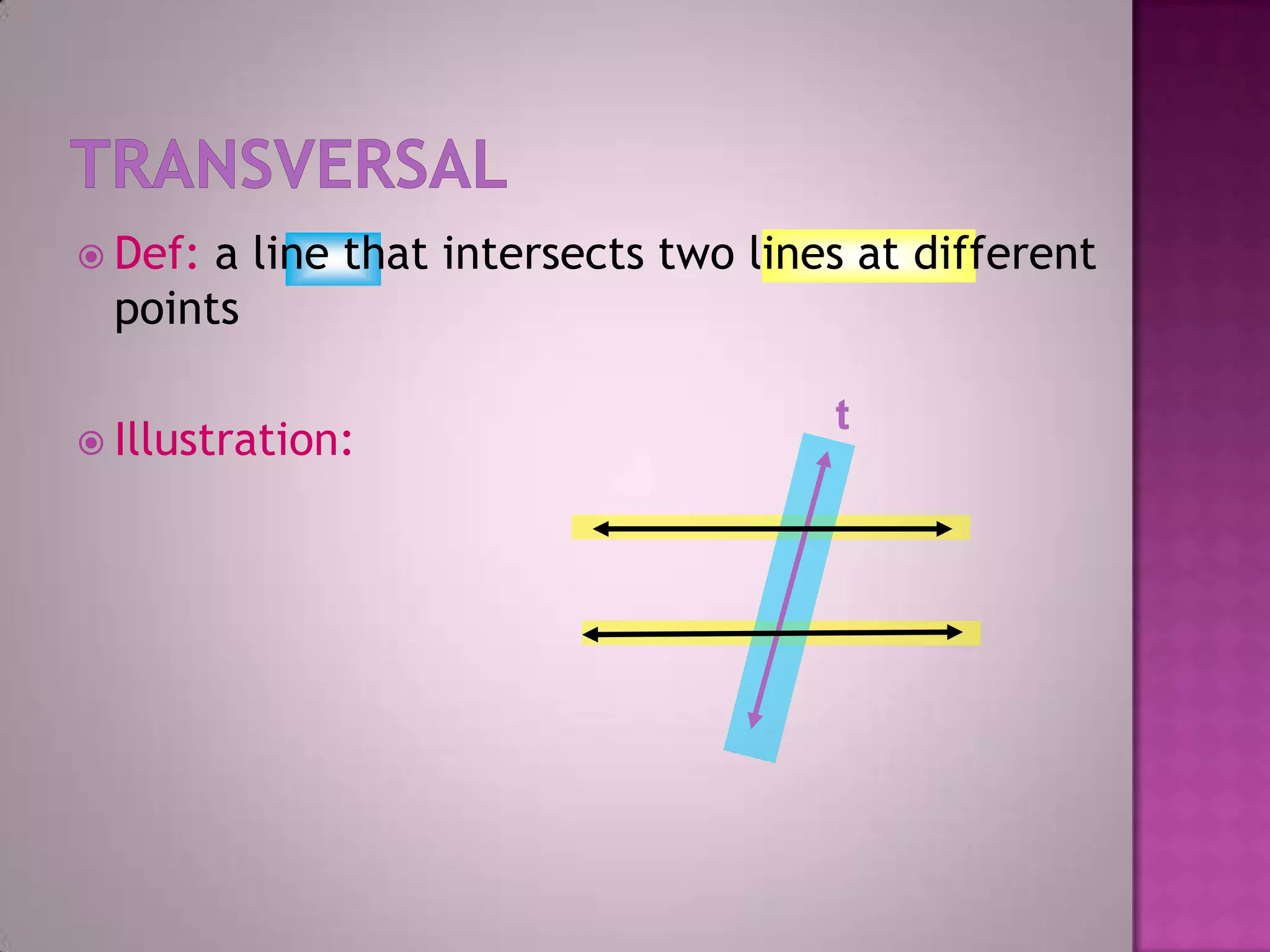
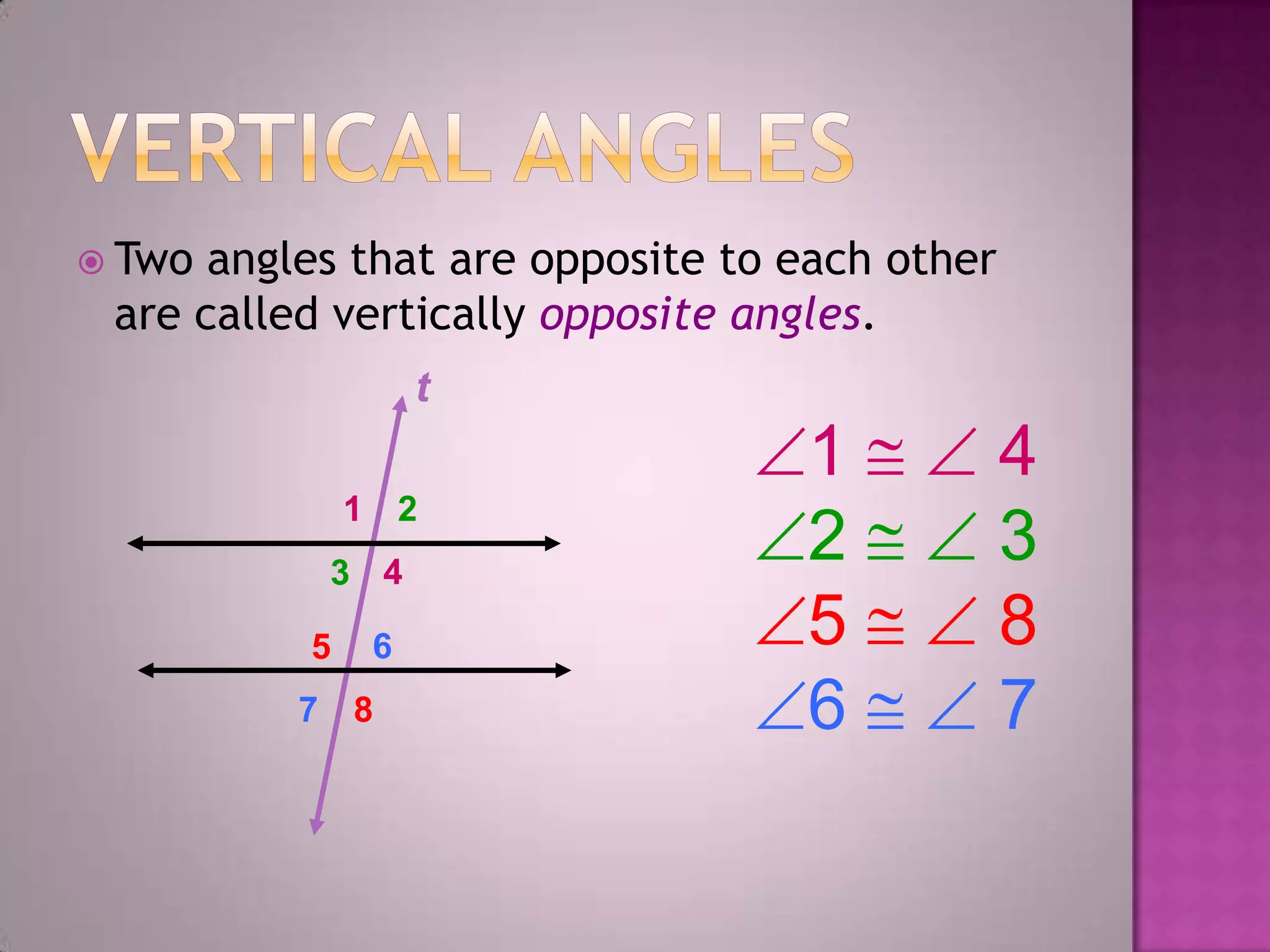
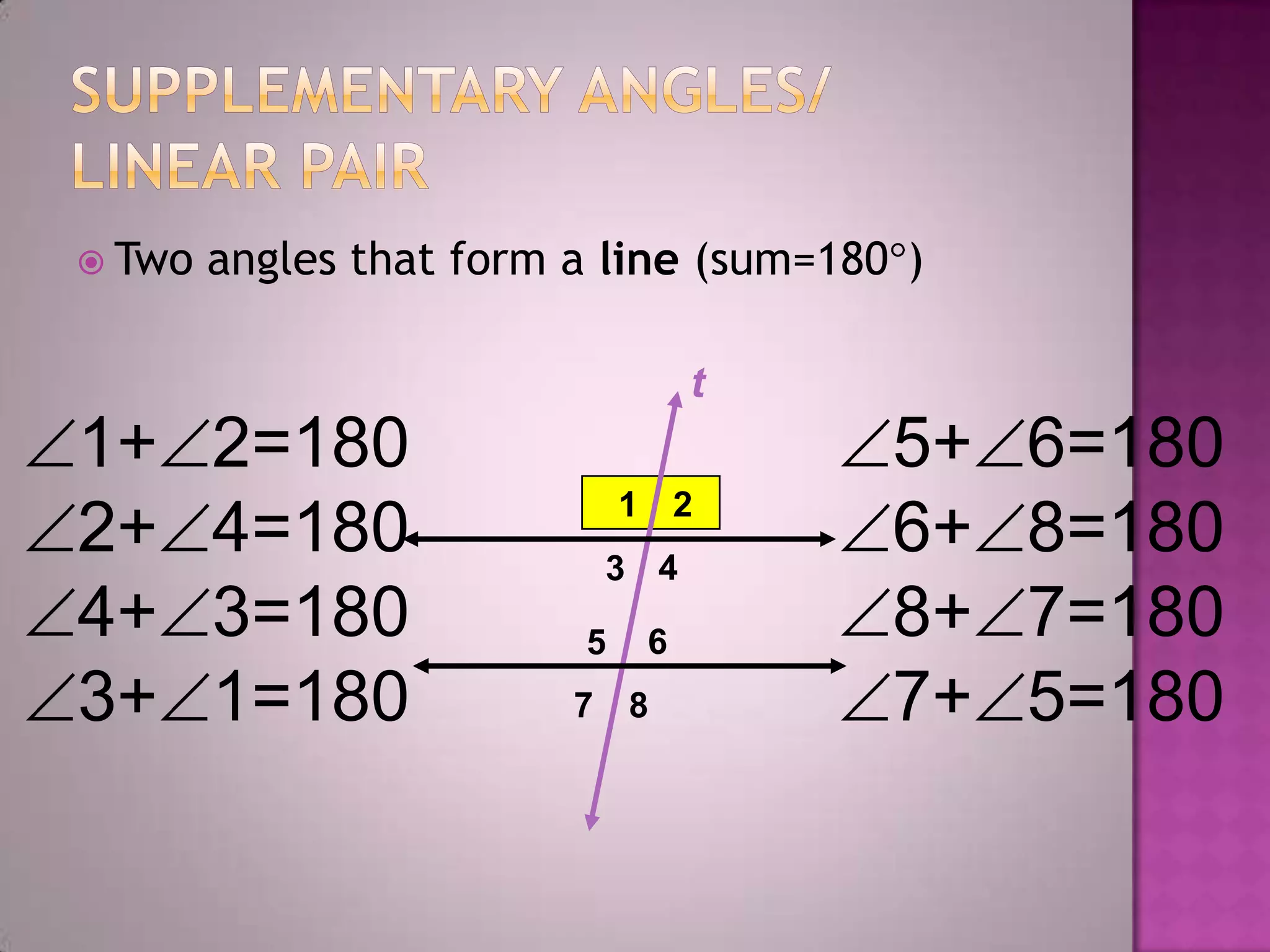
Parallel lines are lines that do not intersect. They are shown as lines AB and CD that never meet. Perpendicular lines intersect to form a right angle, as shown with lines m and n. Angles that are opposite each other across a straight line, like angles 1 and 4, are called vertically opposite angles and are equal.