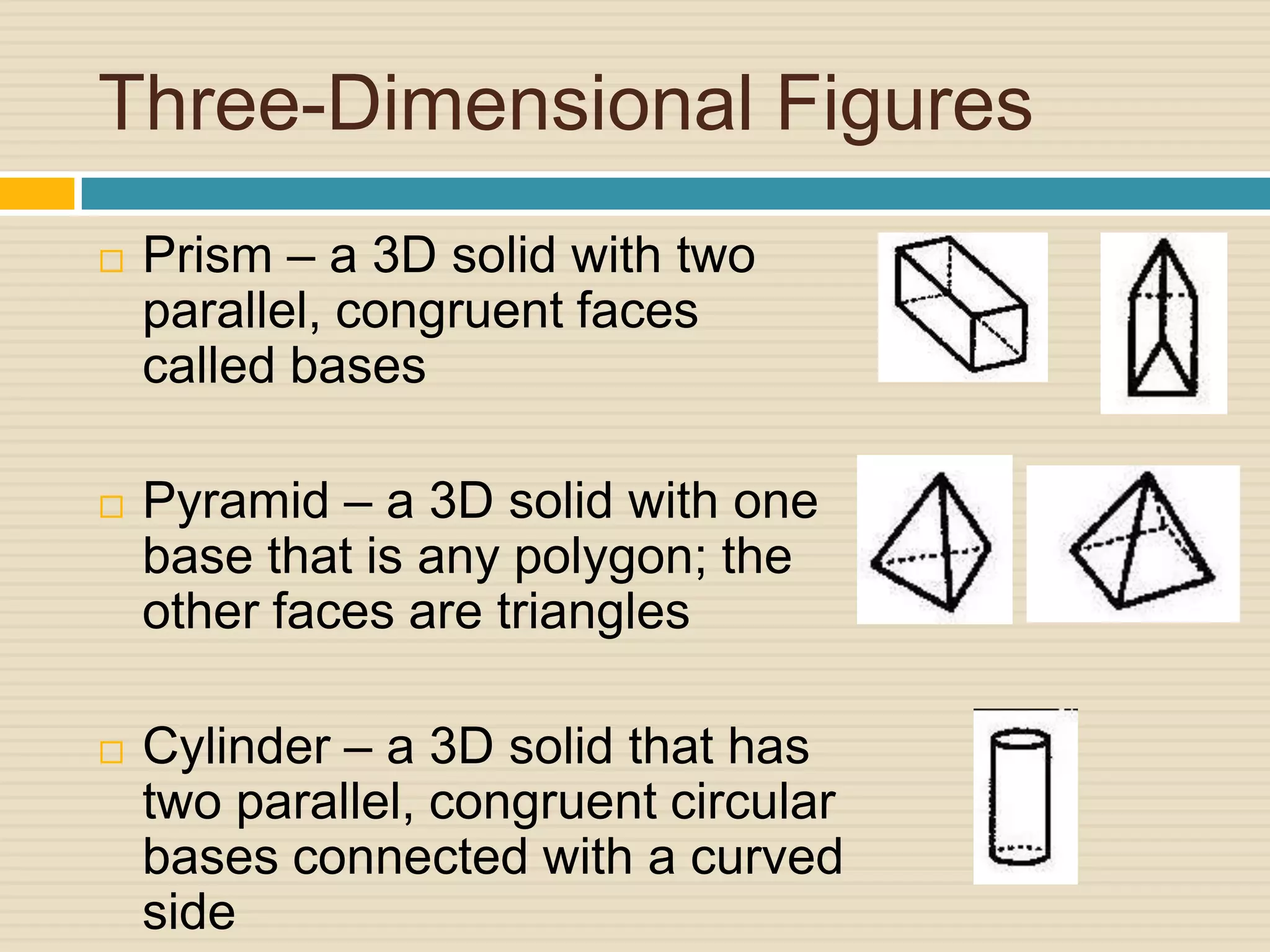
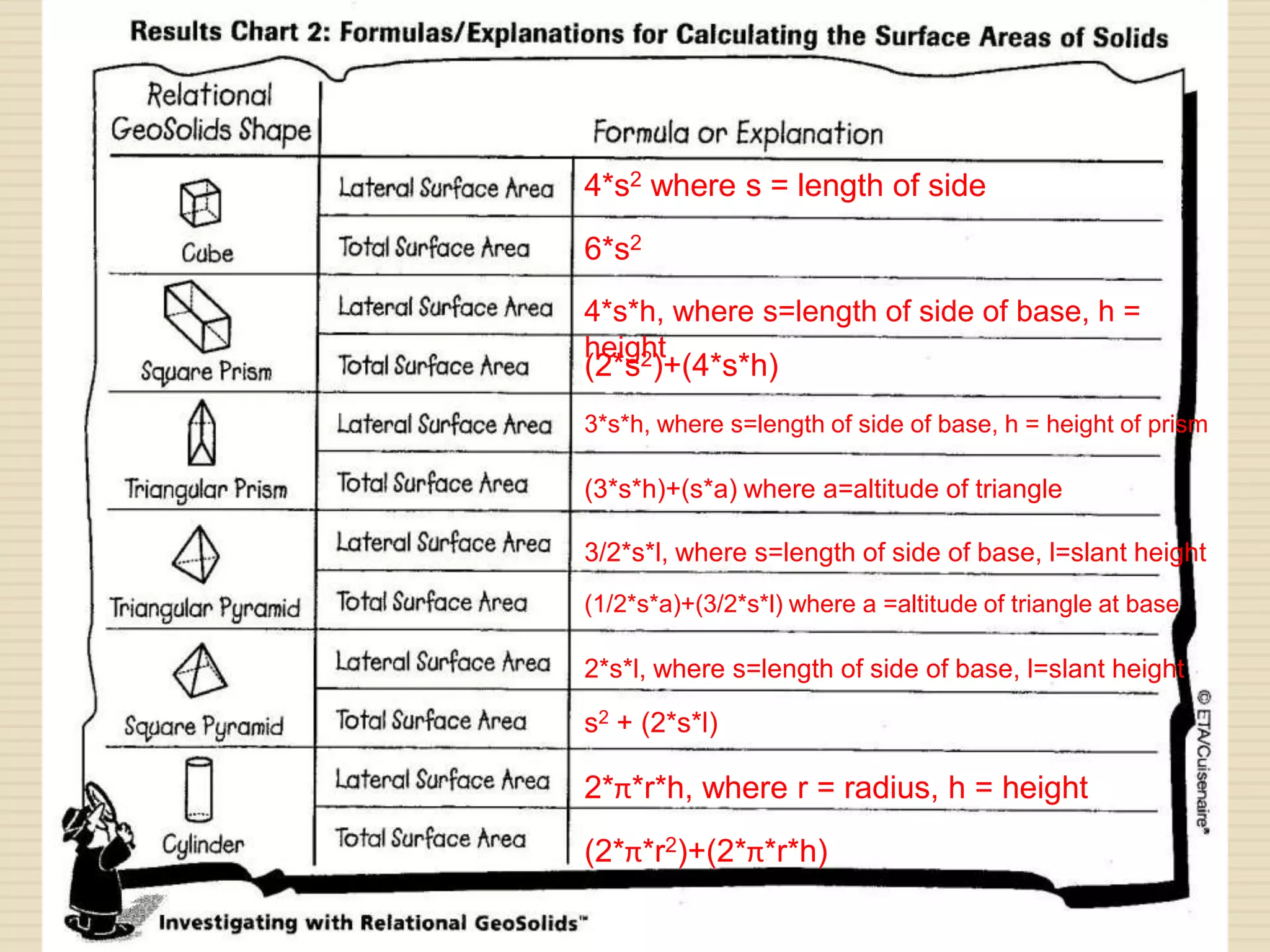
The document discusses surface area of three-dimensional geometric solids including prisms, pyramids, and cylinders. It defines surface area as the sum of the areas of all surfaces, and lateral surface area as excluding the base(s). Formulas are provided to calculate the surface area of various solids using measurements like side length, height, radius, and slant height.