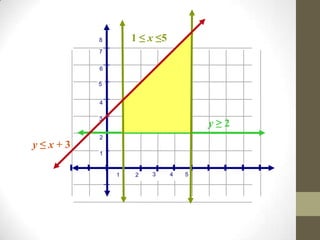
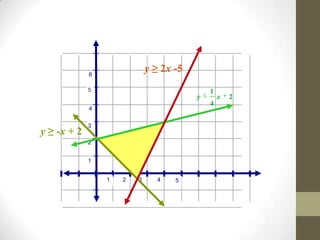
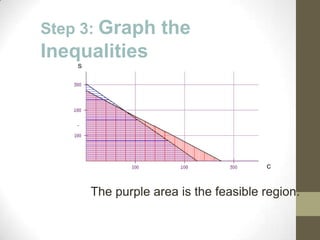
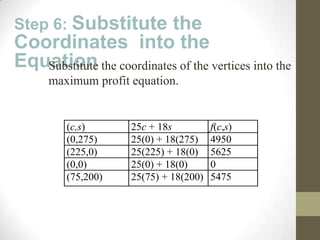
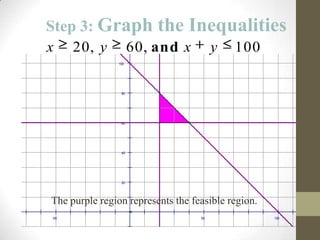
The document discusses the process of linear programming which involves defining variables, writing constraints as inequalities, graphing the feasible region, finding the vertices, writing an objective function, substituting the vertices into the function, and determining the maximum or minimum value. It provides two examples of using linear programming to maximize profits by determining the optimal number of acres to plant different crops or units of steel to produce.