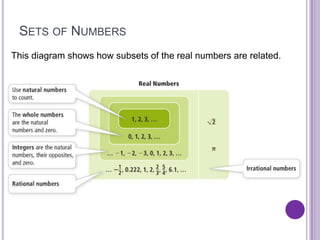
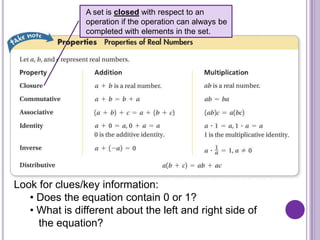
This document defines key concepts in algebra including variables, expressions, real numbers and their subsets. It discusses properties of real numbers such as additive inverses where the sum of a number and its opposite is 0, and multiplicative inverses where the product of a number and its reciprocal is 1. Examples are provided to illustrate these concepts and properties.