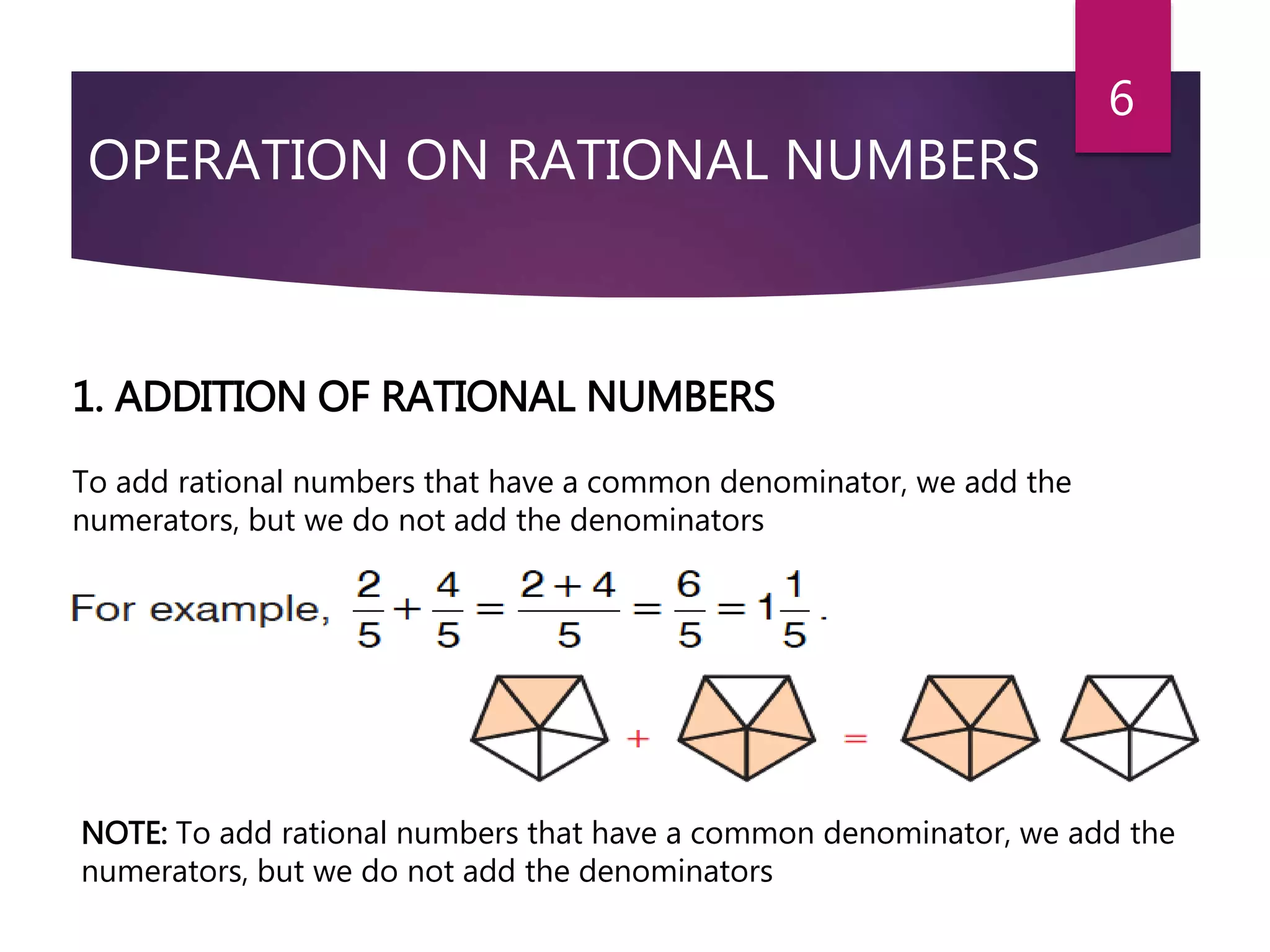
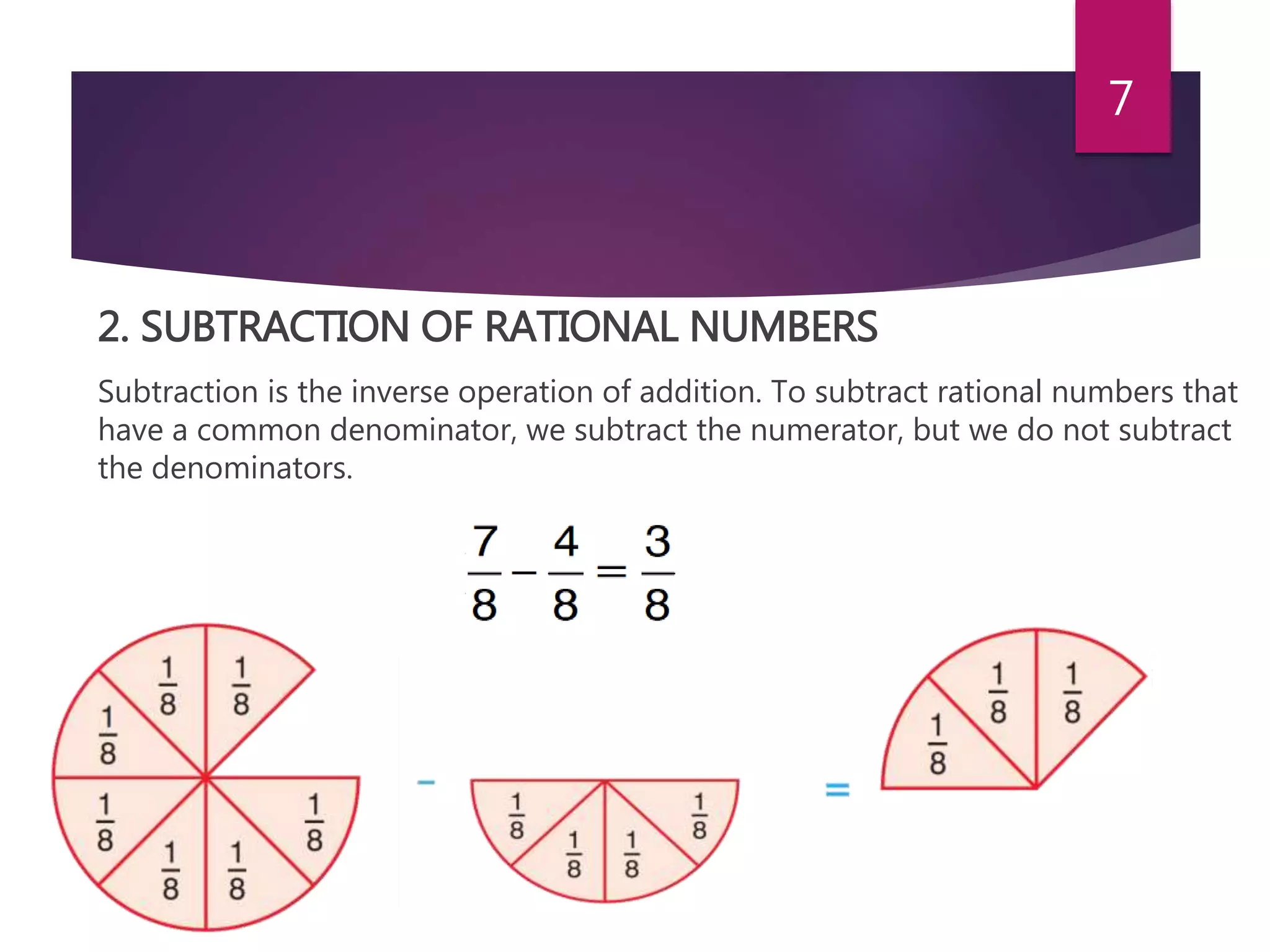
This document discusses rational and irrational numbers. It defines rational numbers as numbers that can be written as p/q where p and q are integers and q is not equal to 0. Rational numbers include fractions, integers, and natural numbers. The document describes the different types of rational numbers such as positive, negative, and in standard form. It also discusses how to perform operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division on rational numbers. Irrational numbers are defined as real numbers that cannot be expressed as a ratio of integers like the roots of prime numbers or pi.