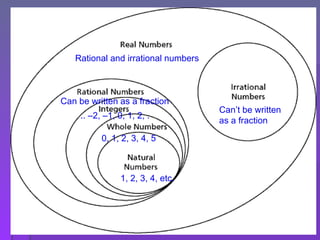
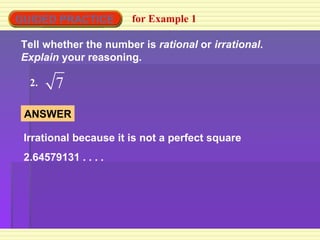
This document discusses rational and irrational numbers. It defines rational numbers as numbers that can be written as fractions or ratios, including integers, terminating decimals, and repeating decimals. Irrational numbers are defined as numbers that cannot be written as fractions or repeating/terminating decimals, such as the square root of a non-perfect square. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to determine if a number is rational or irrational based on its decimal representation.