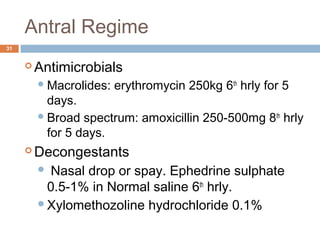
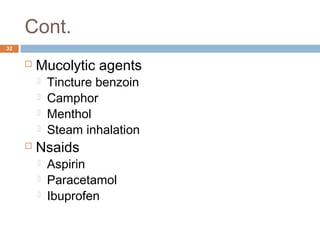
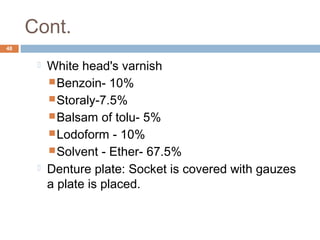
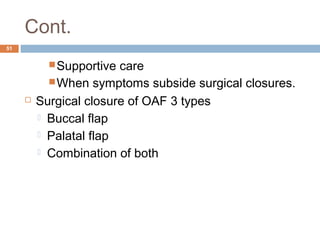
The document discusses the anatomy, physiology, and clinical aspects of the maxillary sinus. Key points include:
- The maxillary sinus is the largest paranasal sinus located within the maxilla. It communicates with the nasal cavity and has a volume of 15-30ml in adults.
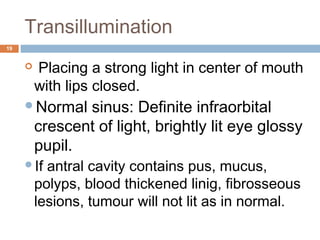
- Infections of the maxillary sinus can be odontogenic (caused by dental infections), acute or chronic maxillary sinusitis. Symptoms include pain, nasal congestion, and purulent drainage.
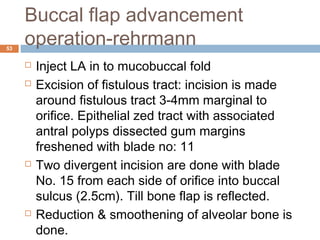
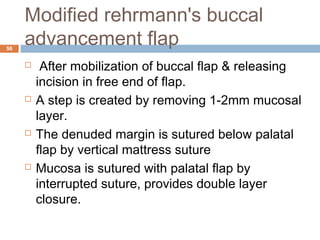
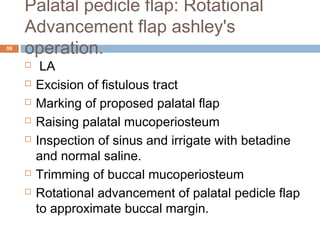
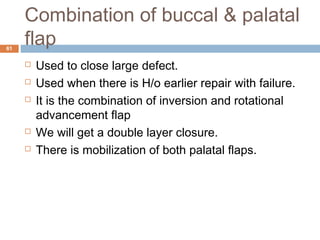
- Oroantral communications and fistulas can form between the oral cavity and maxillary sinus due to tooth extractions or other trauma/surgery. They may cause pain, nasal discharge,