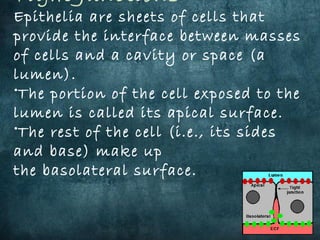
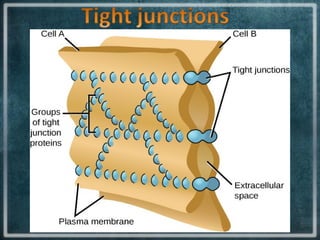
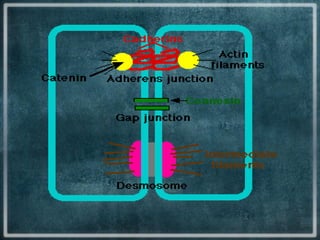
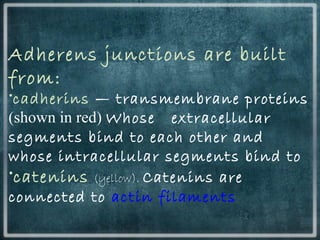
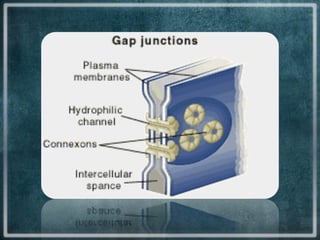
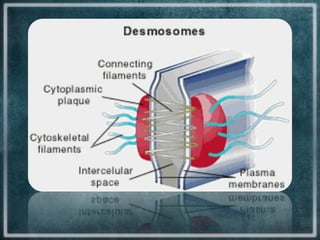
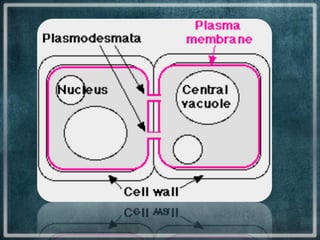
This document discusses different types of cell junctions that allow communication between animal and plant cells. There are four main types of junctions in animal tissues: tight junctions, adherens junctions, gap junctions, and desmosomes. Tight junctions seal adjacent epithelial cells and control molecular passage. Adherens junctions provide strong mechanical attachment between cells. Gap junctions allow small molecules and ions to pass directly between cells. Desmosomes strongly attach epithelial cells, and hemidesmosomes attach epithelial cells to the basal lamina. In plant tissues, plasmodesmata connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells through pores in the cell wall, providing an easy route for communication.