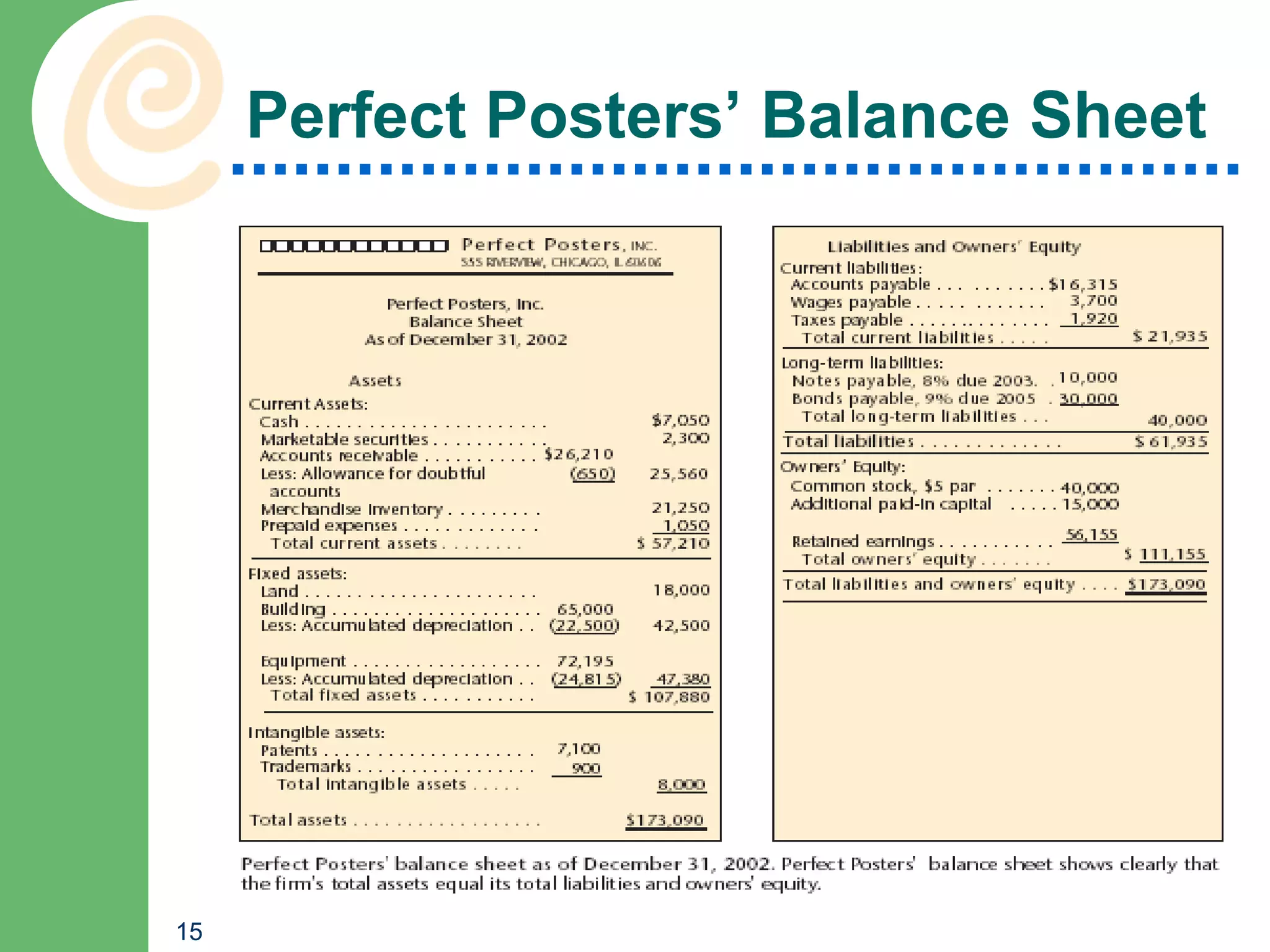
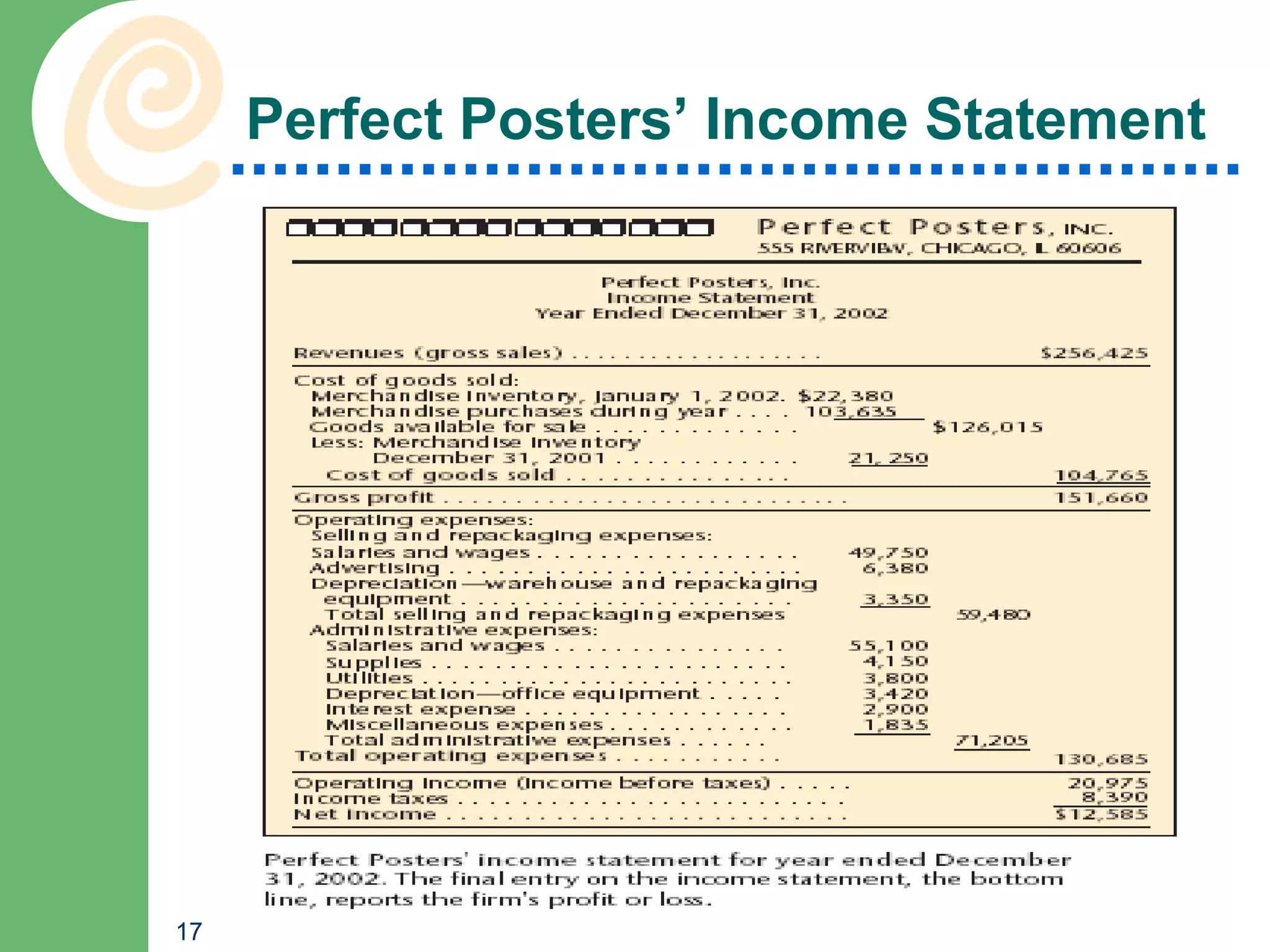
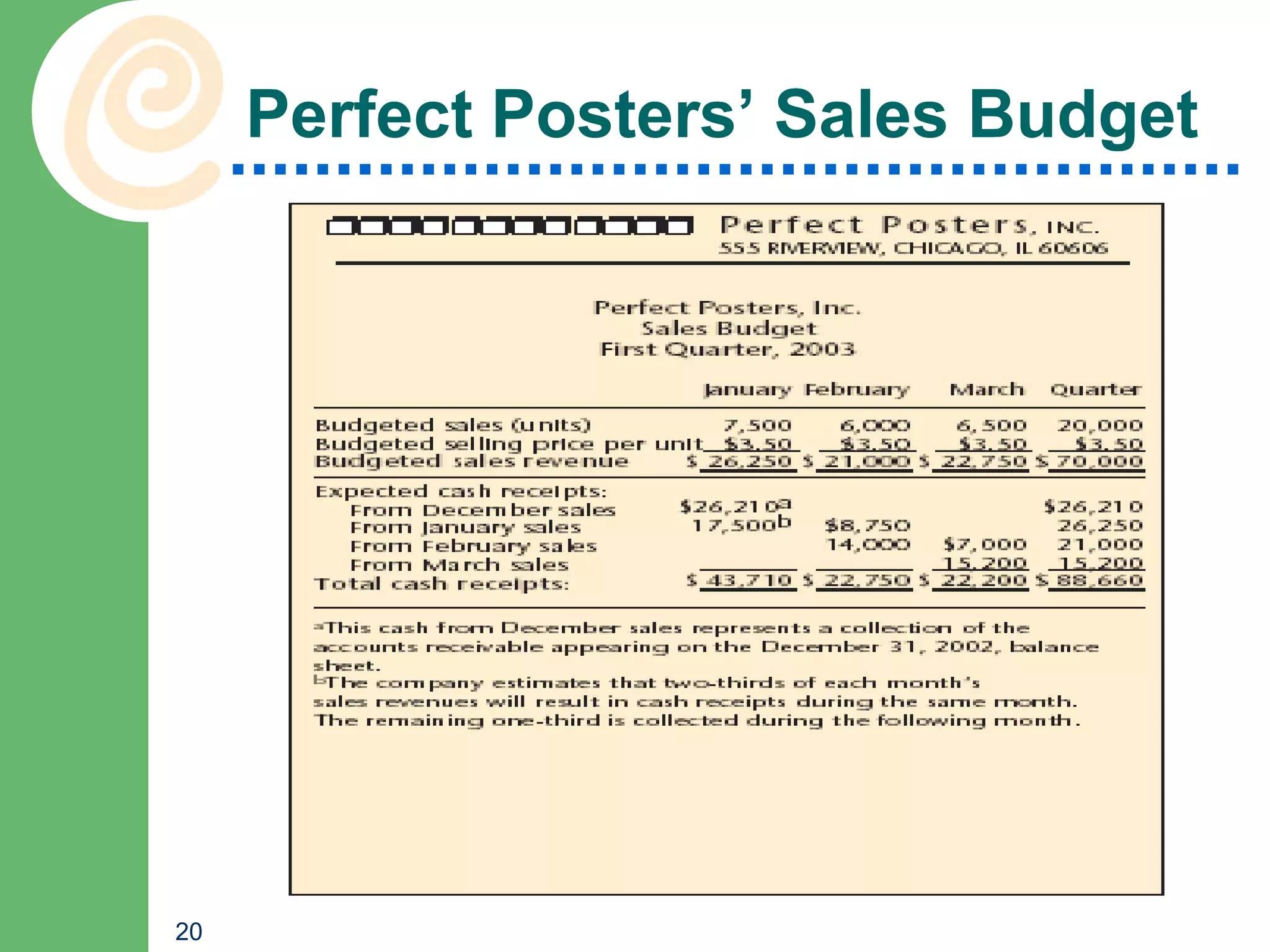
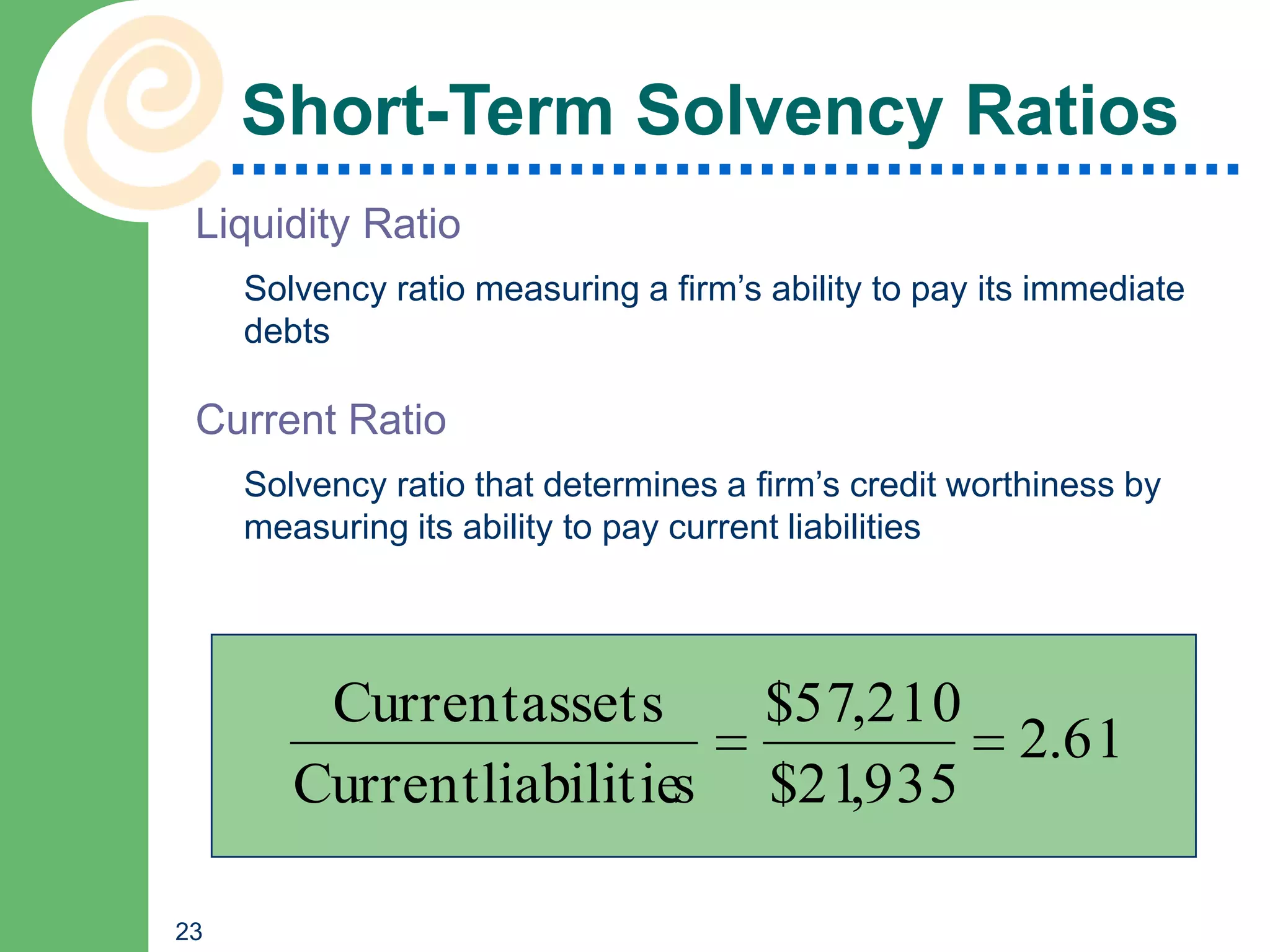
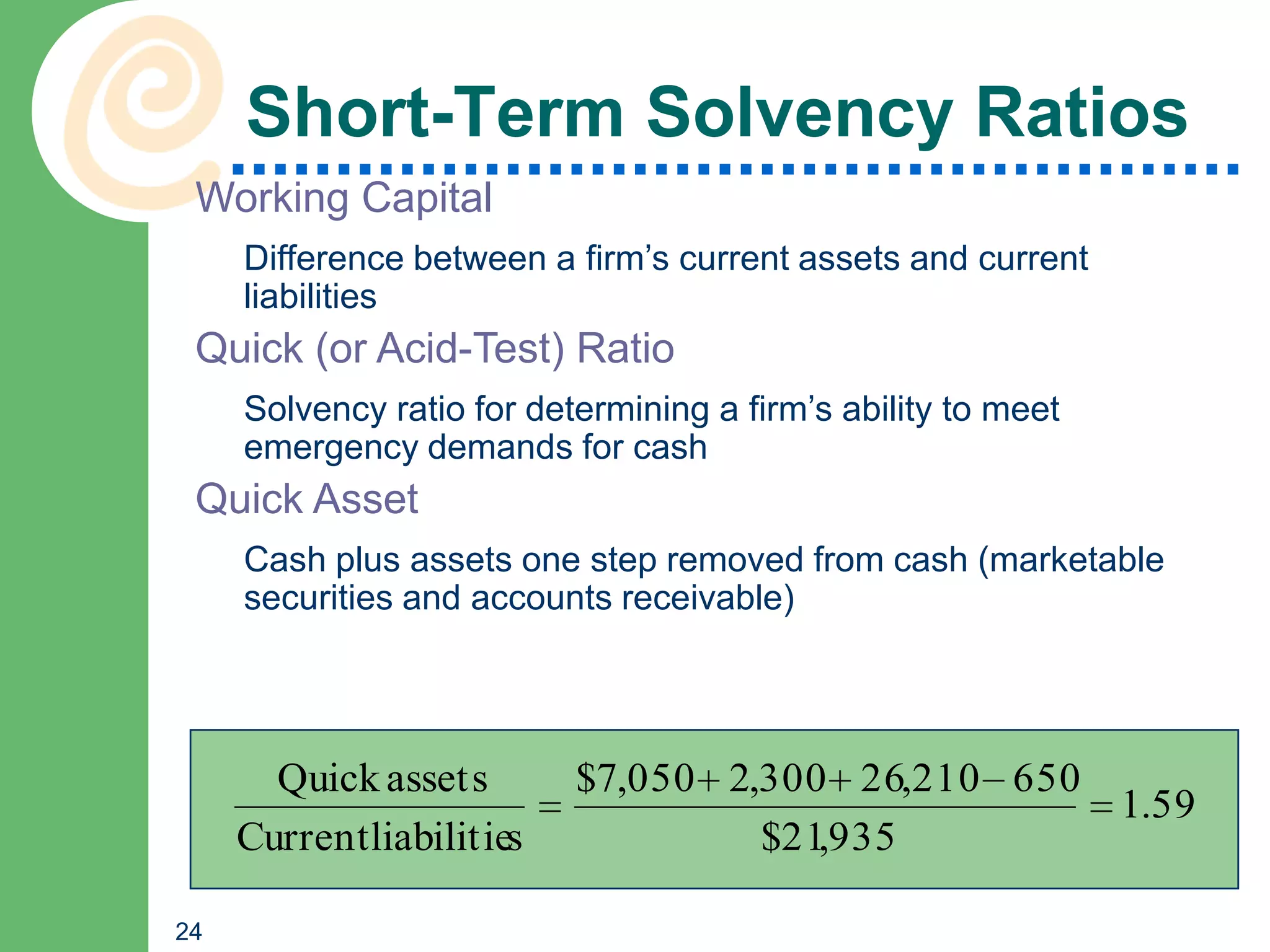
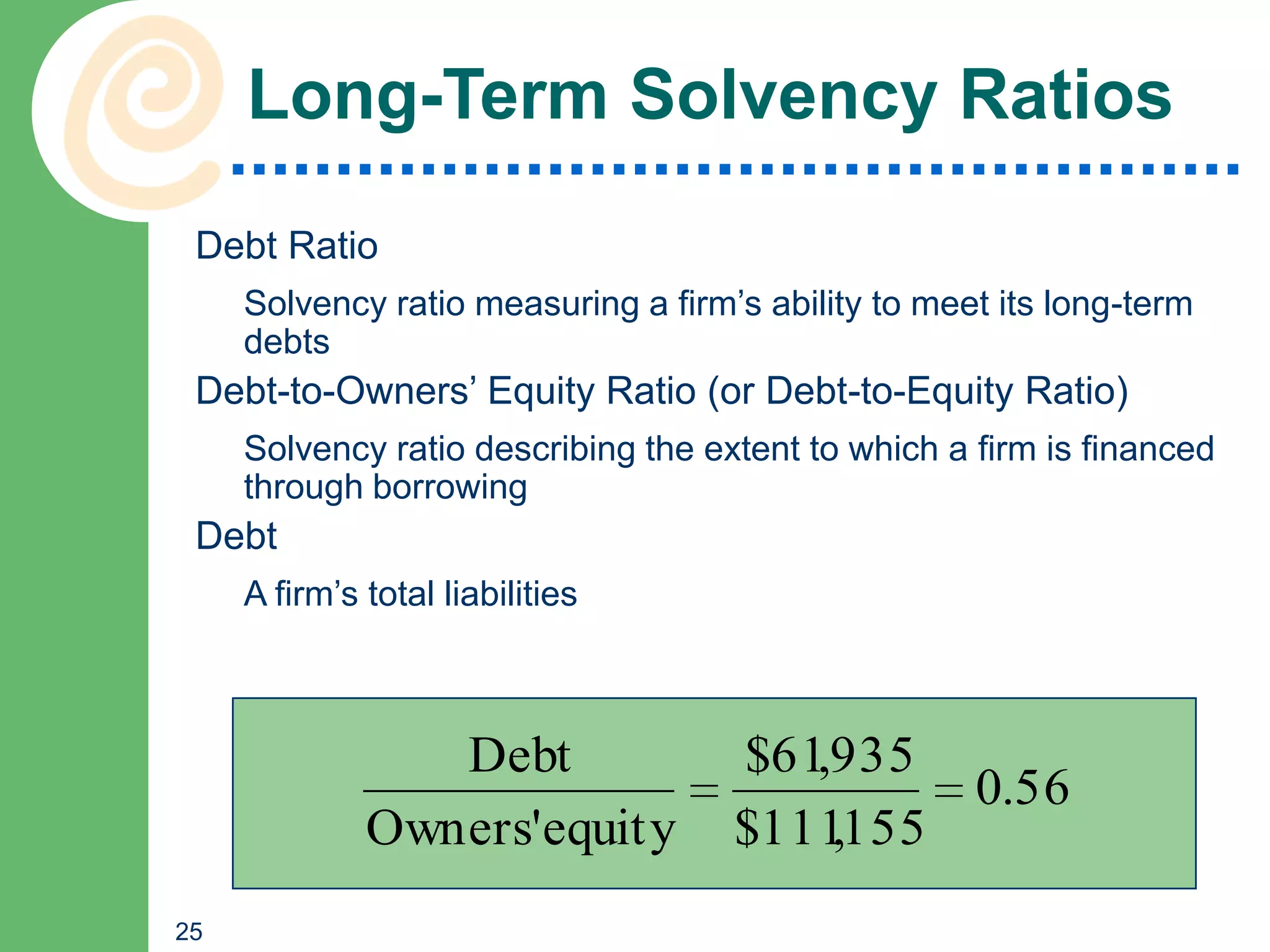
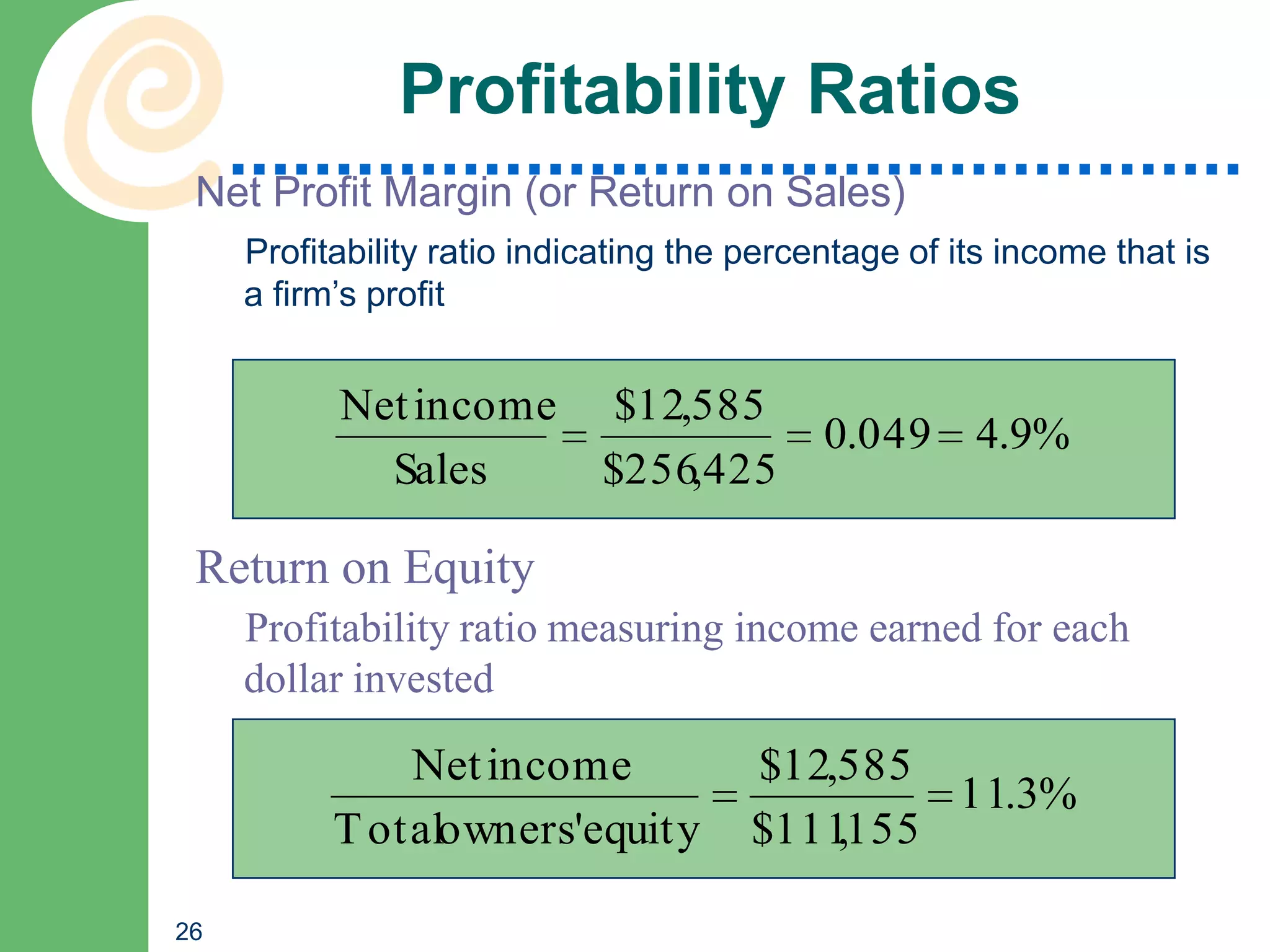
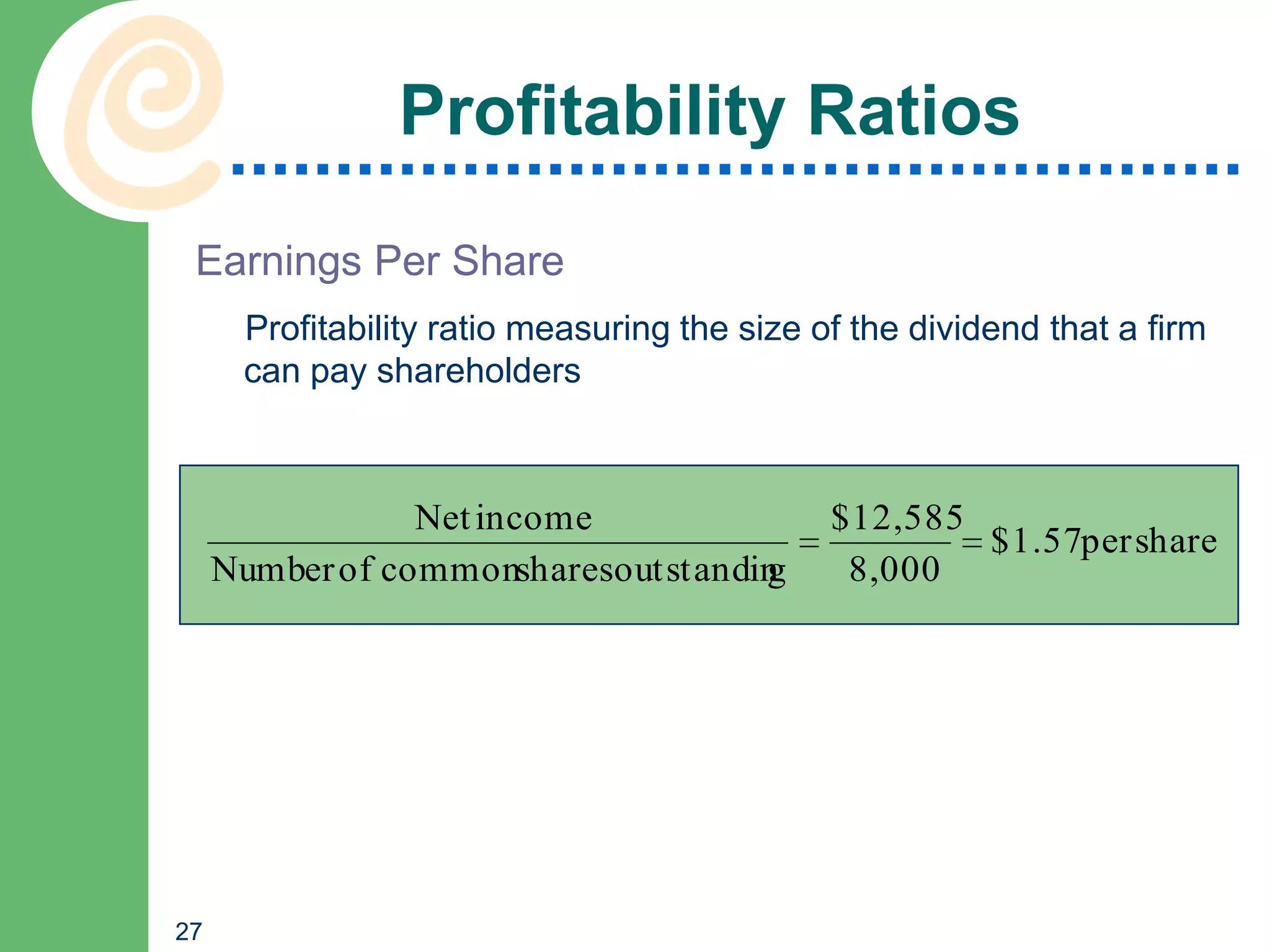
This chapter discusses key accounting concepts such as the accounting equation, financial statements, and ratio analysis. It explains that accounting is used to collect, analyze, and communicate financial information to both internal and external users. The chapter outlines the main financial statements - the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. It also describes how ratio analysis can be used to evaluate a company's solvency, profitability, and operational efficiency. Common ratios discussed include the current ratio, debt ratio, net profit margin, and inventory turnover ratio.