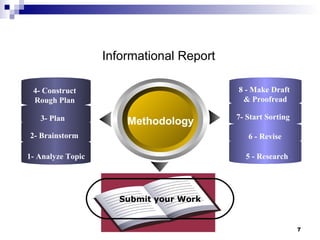
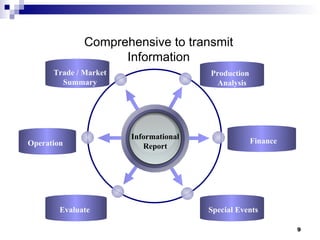
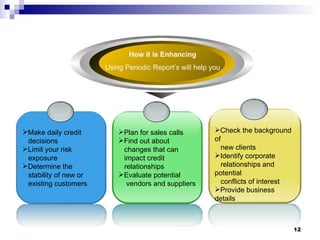
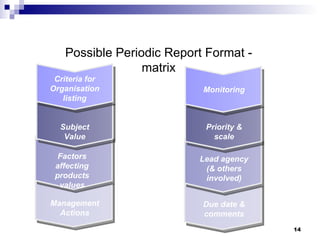
The document discusses different types of typical business reports including periodic reports, situational reports, investigative reports, compliance reports, analytical reports, justification/recommendation reports, and feasibility reports. It provides examples of each type of report and discusses their purpose, format, and key elements. The document aims to provide guidance on writing different business reports for various audiences and situations.