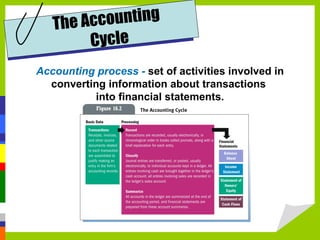
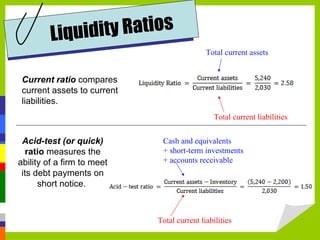
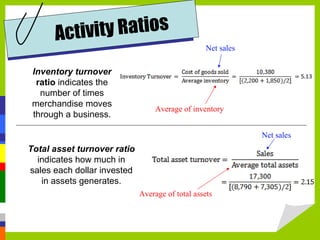
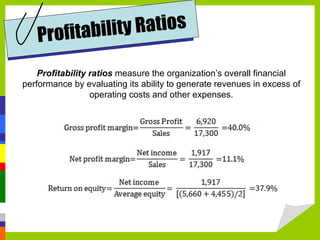
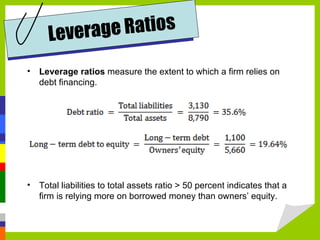
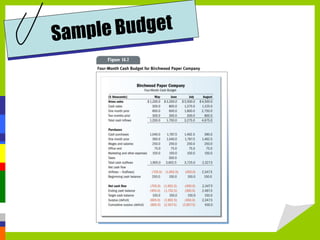
Accounting measures, communicates, and supports business decision making with financial information. The four main financial statements are the balance sheet, income statement, statement of owner's equity, and statement of cash flows. Financial ratios analyze strengths and weaknesses by measuring liquidity, profitability, leverage, and activity. Budgets and international standards aim to improve financial reporting consistency.