1) Malpresentations occur when the fetus is positioned abnormally during delivery, with the most common normal positions being left or right occiput anterior. Malpositions involve a normal presentation (vertex) but abnormal positioning of the occiput.
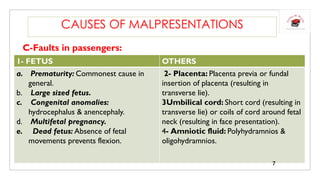
2) Causes of malpresentations can include faults in the powers (weak uterine contractions), faults in the passages (abnormal pelvis), or faults in the passenger (fetal anomalies). Specific causes mentioned include contracted pelvis, uterine anomalies, large fetus size, and placenta previa.
3) Diagnosis involves history of abnormal fetal movements, abdominal exam findings like non-engaged head, and vaginal exam finding anything other than vertex. Comp