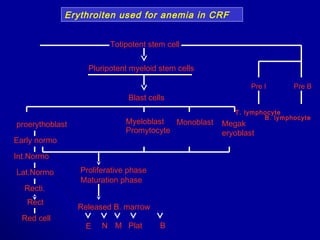
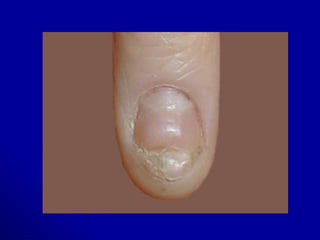
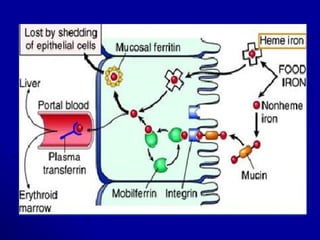
This document discusses blood formation and types of anemia. It explains that blood is composed of red cells, white cells, platelets, and plasma. Blood formation begins in the yolk sac in the 2nd week and later occurs chiefly in the liver and spleen, then the bone marrow. The bone marrow contains stem cells that can differentiate into mature blood cells. Various growth factors are involved in blood formation. The document also classifies and describes different types of anemia, including iron deficiency anemia, and lists causes and treatment for anemia.