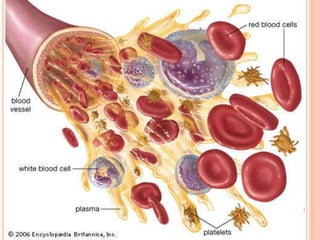
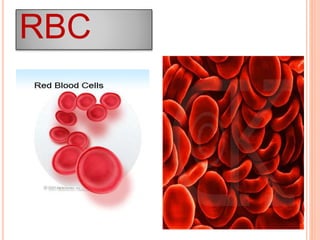
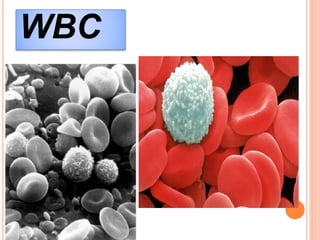
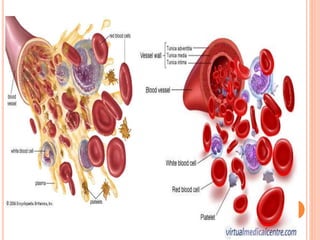
This document is a PowerPoint presentation on blood cells submitted by Anusree.C to her lecturer Smt.Soya.P. It introduces the three main types of blood cells - erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells), and platelets. It describes the functions of each cell type, including that red blood cells transport oxygen, white blood cells protect against infection, and platelets help the blood clotting process. Diagrams and details are provided about the shape and components of red blood cells and the different types of white blood cells.