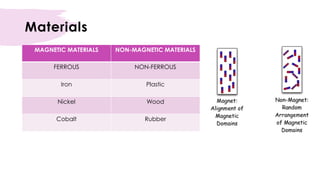
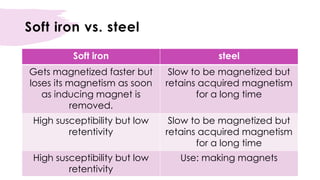
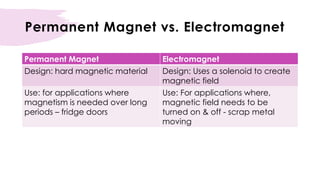
An induced magnet only becomes magnetic when placed within a magnetic field, such as near a permanent magnet. The induced magnetism is temporary and lost when removed from the magnetic field. The most effective way to induce magnetism is by passing a direct current through a solenoid coil containing the material. Materials can also be demagnetized by heating, hammering, or exposing to an alternating current within a solenoid coil. Soft iron is easily magnetized but loses magnetism quickly, while steel is harder to magnetize but retains magnetism longer.