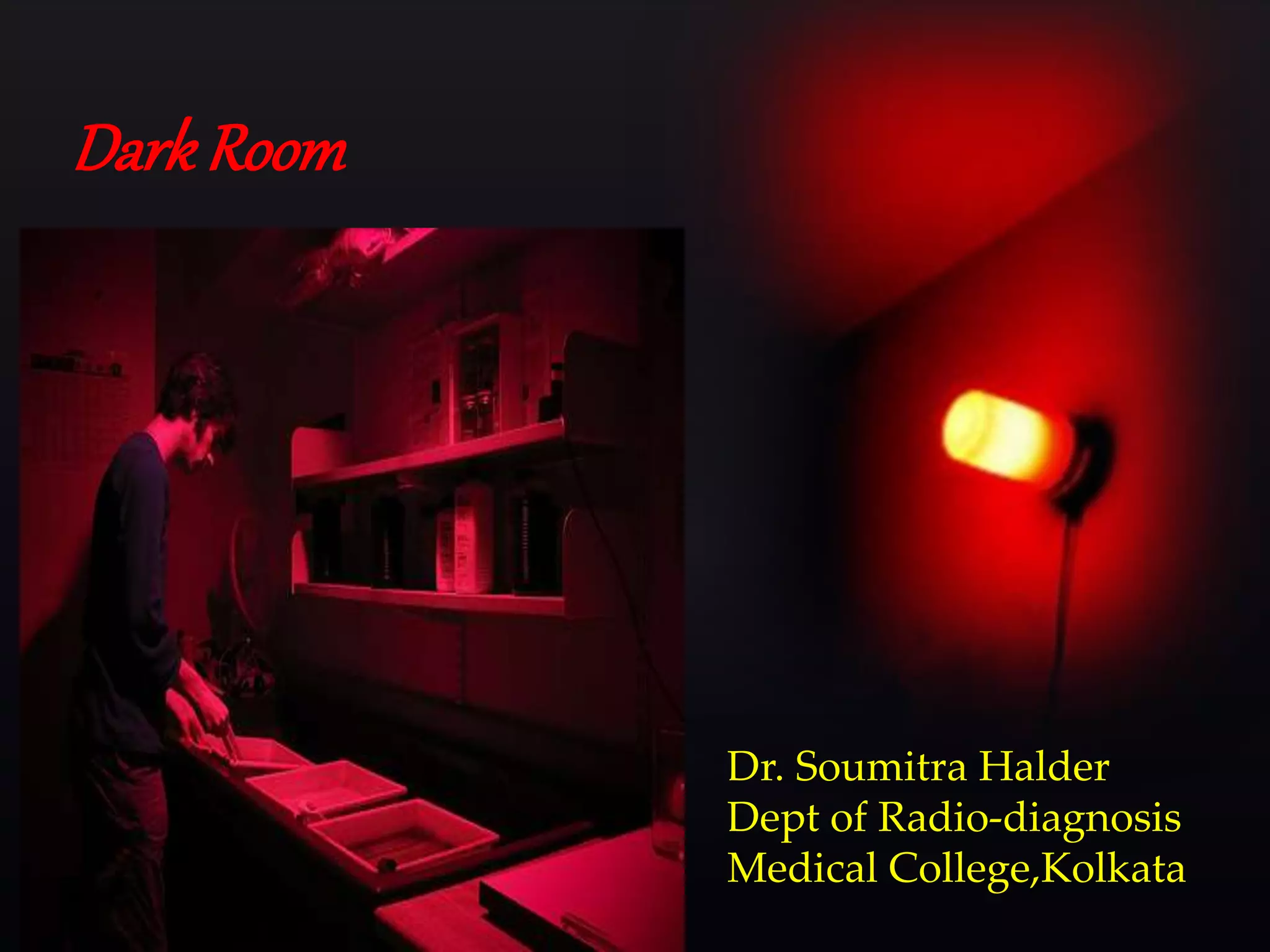
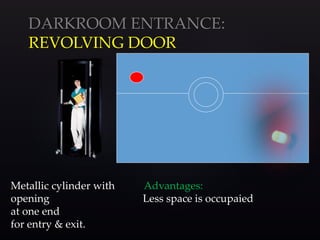
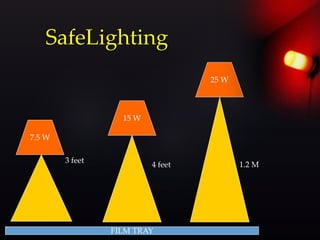
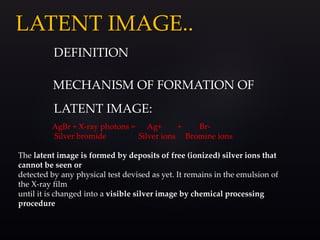
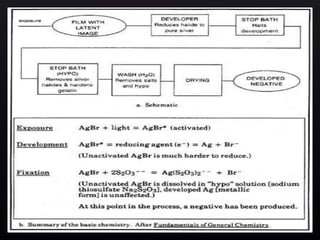
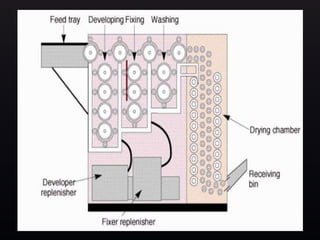
This document provides information about the components and operation of a darkroom for processing radiographic films. It discusses that a darkroom is needed to safely handle films without light exposure. The key components of a darkroom include storage shelves, workbenches, processing tanks, lights, and ventilation. Different types of entrances like single door, double door, and revolving doors are described. The document also explains the principles and proper use of safelights for illumination and white lights for maintenance. Finally, it provides an overview of the chemistry and stages involved in automatic film processing, including development, fixing, washing and drying.