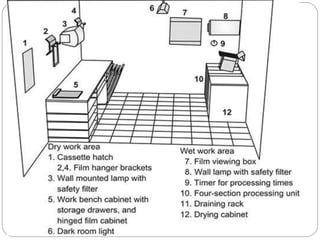
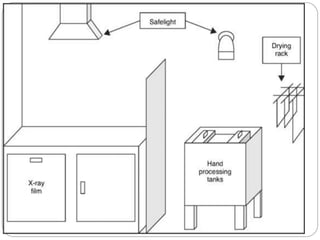
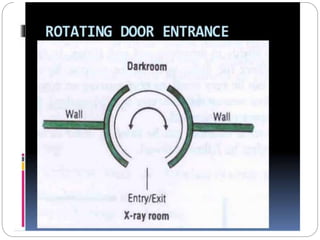
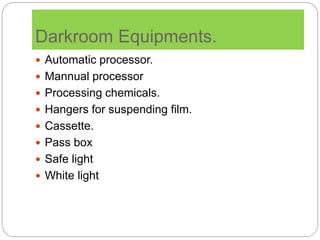
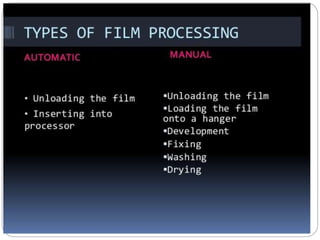
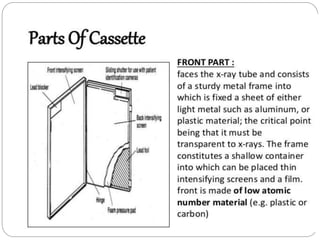
The document discusses the key components and requirements of a darkroom used for processing photographic film. An ideal darkroom is about 100 square feet, located away from damp areas and accessed via hatches from an adjacent imaging room. It must be completely dark to allow film processing and include safelights for loading/unloading and white lights for maintenance. Proper floors, walls, ventilation and radiation shielding are also needed. A darkroom contains manual or automatic film processors, chemicals and hangers for developing, fixing and washing photographic film.