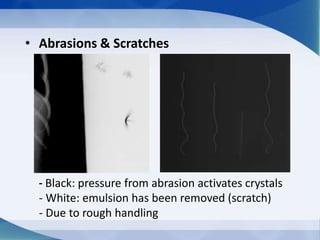
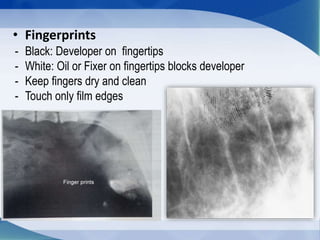
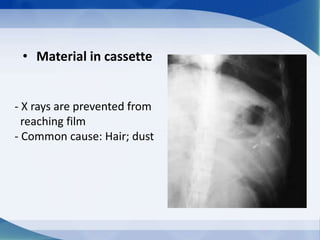
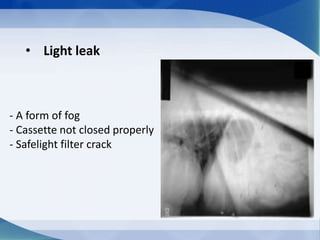
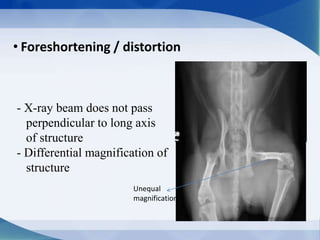
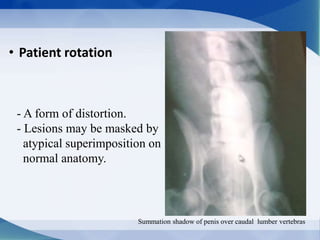
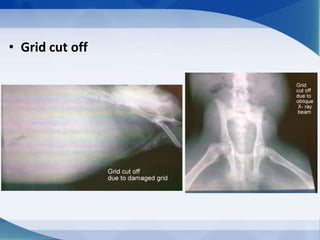
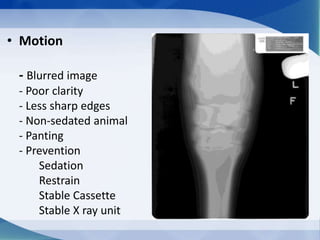
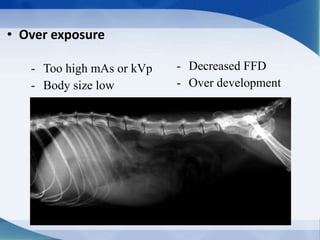
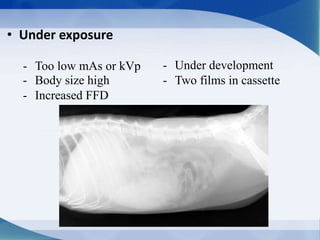
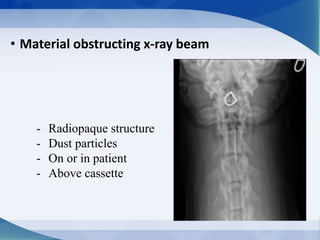
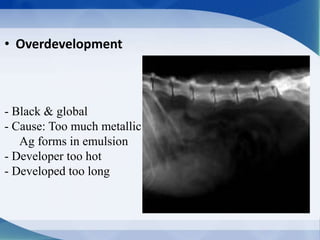
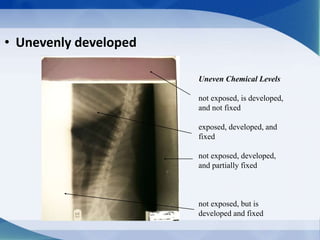
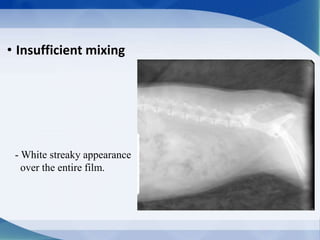
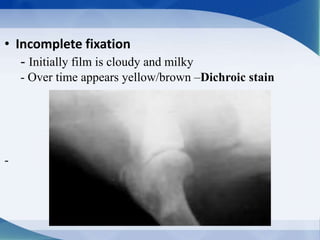
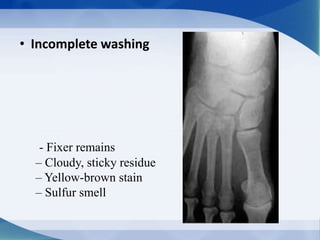
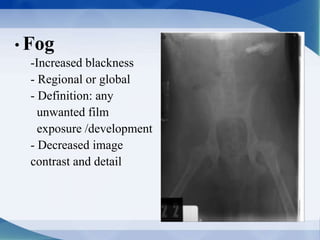
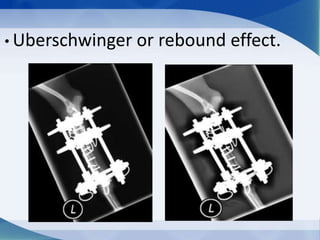
This document discusses various types of artifacts that can appear on radiographic images, degrading image quality and affecting interpretation. It describes pre-exposure artifacts from film handling and storage issues, positioning artifacts from improper patient placement or equipment use, exposure artifacts involving radiation factors, and post-exposure artifacts in film processing. Specific examples are given for each type like pressure marks, scratches, static electricity streaks, magnification errors, motion blur, over/under development, incomplete fixing, and digital transfer or processing issues. The artifacts can mimic pathology, reduce diagnostic value, or lead to misinterpretation if not recognized.