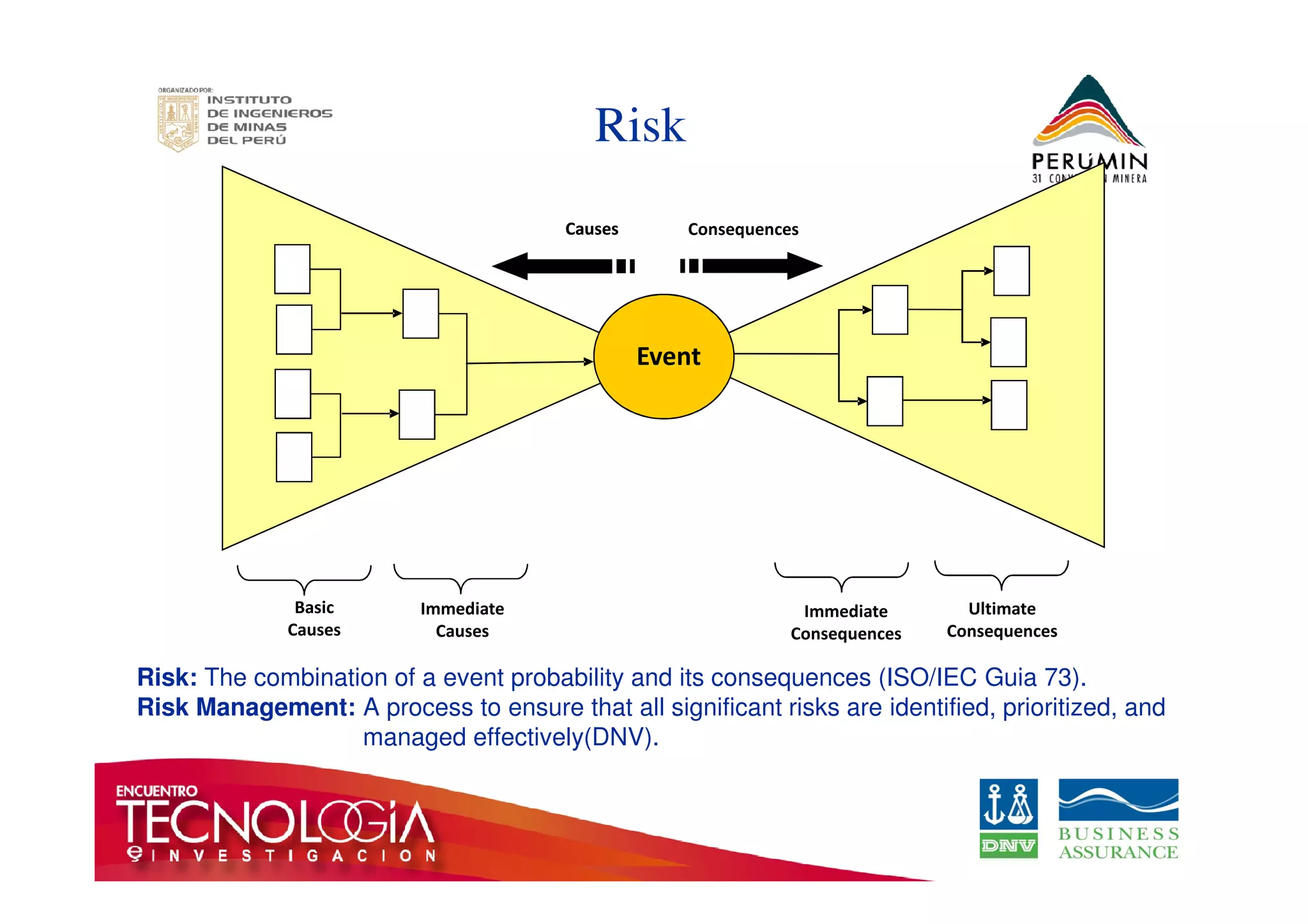
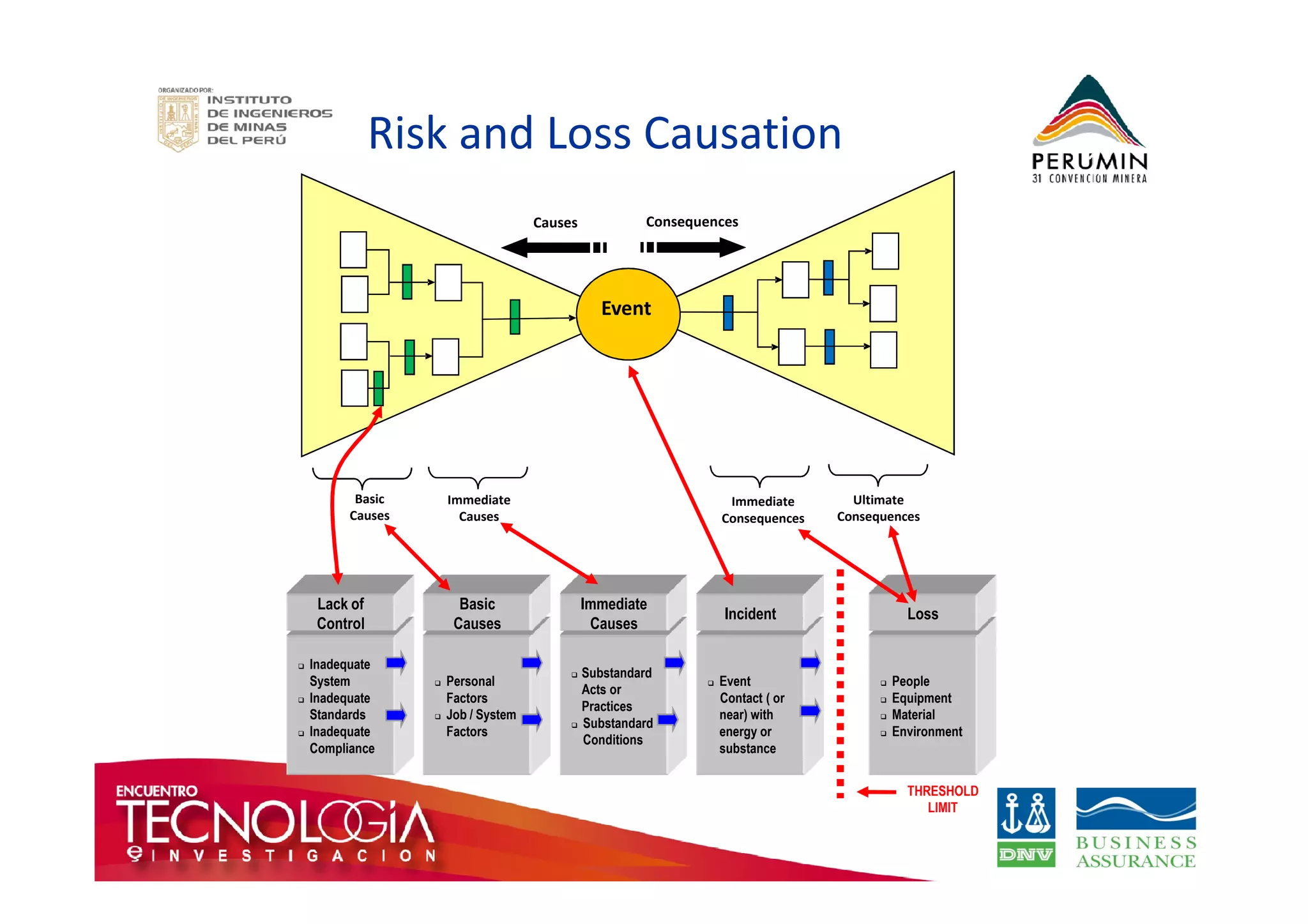
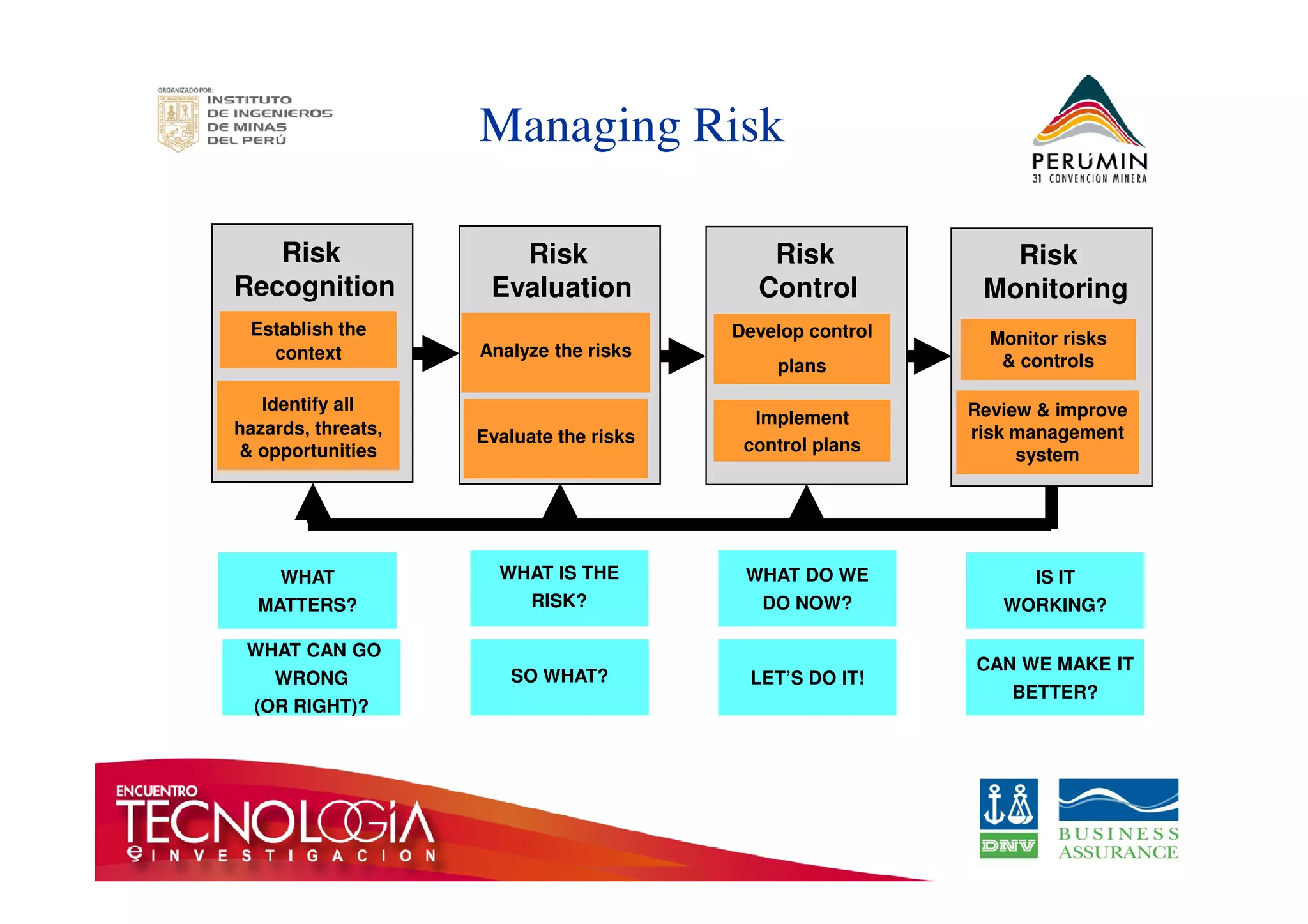
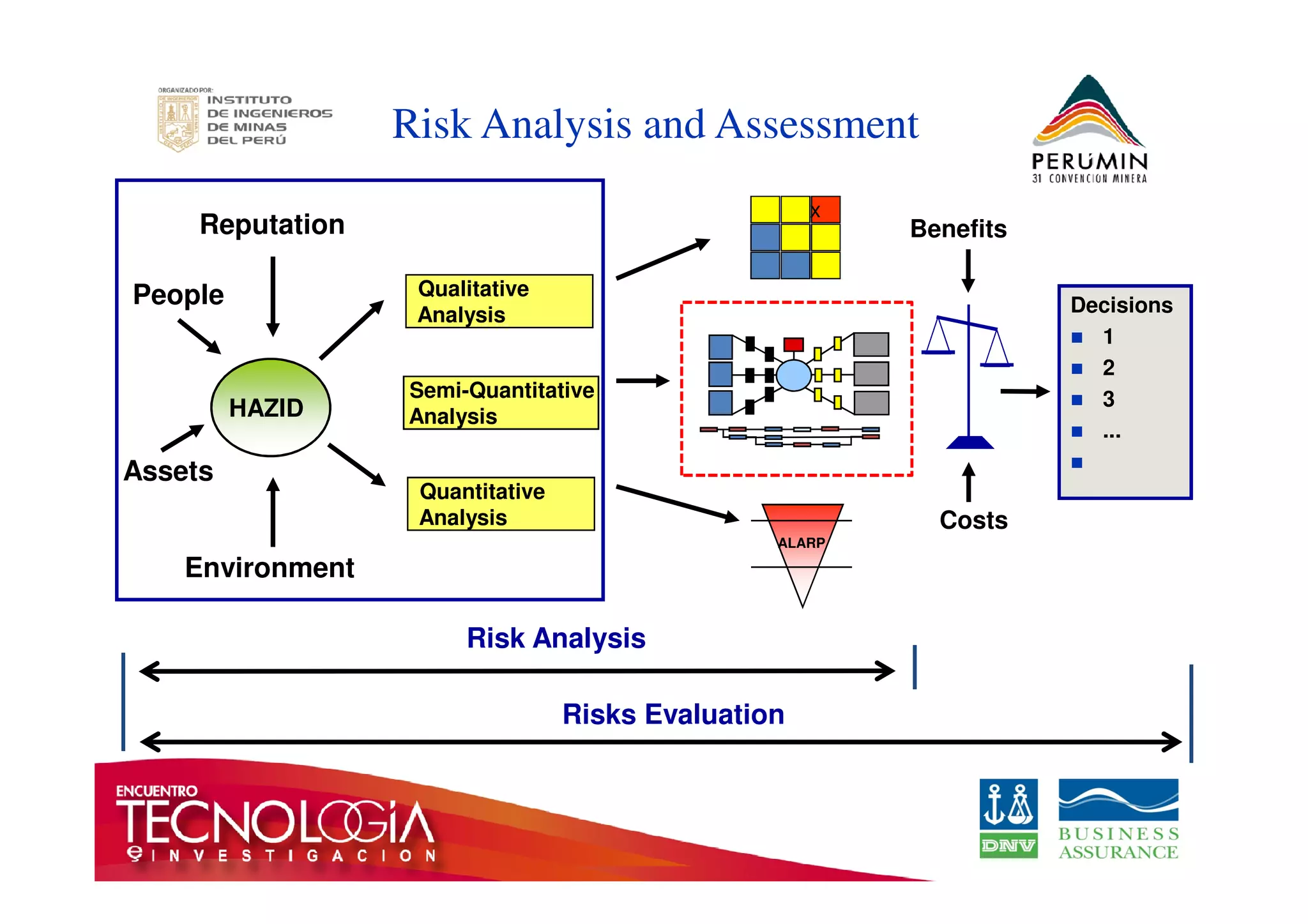
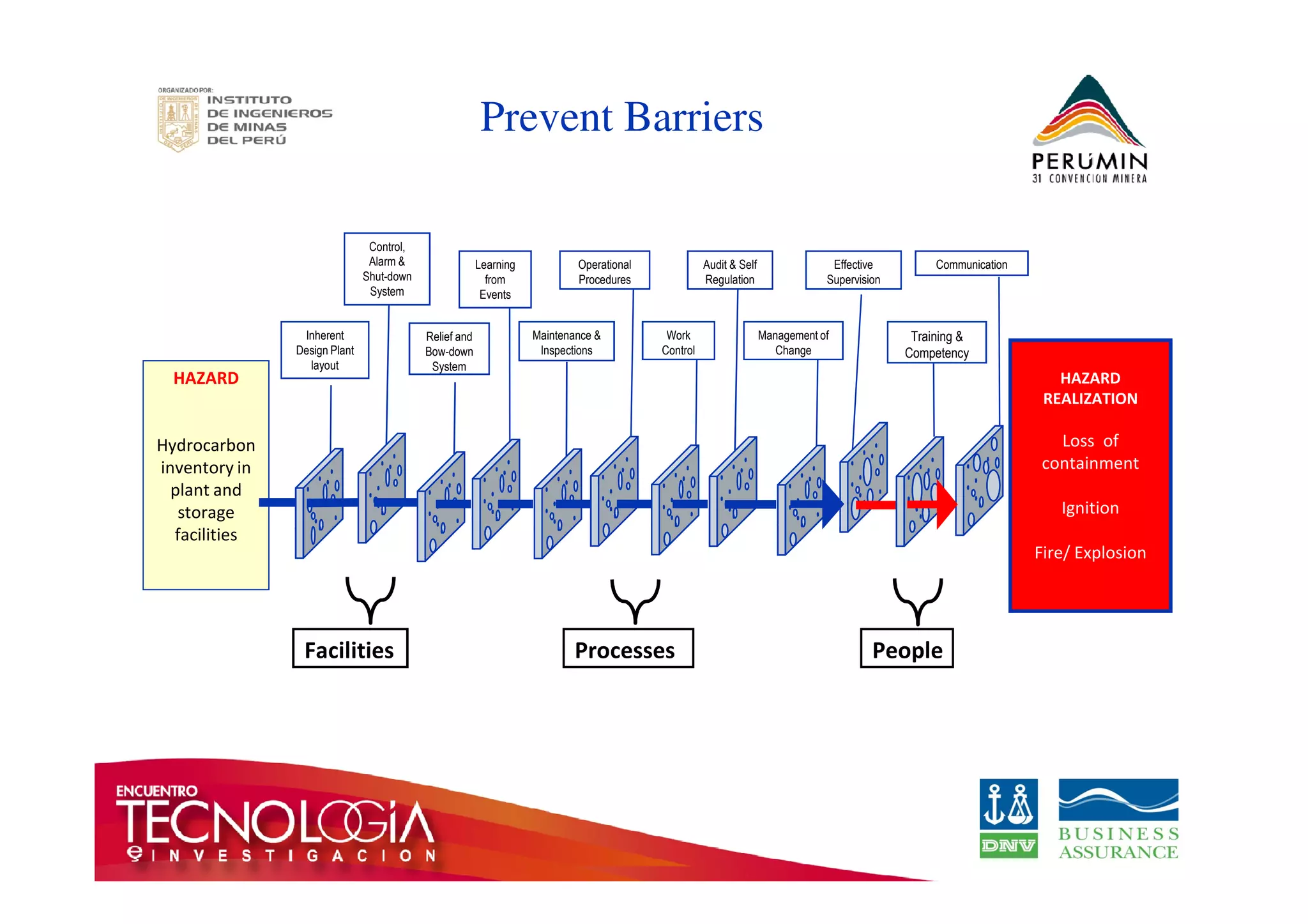
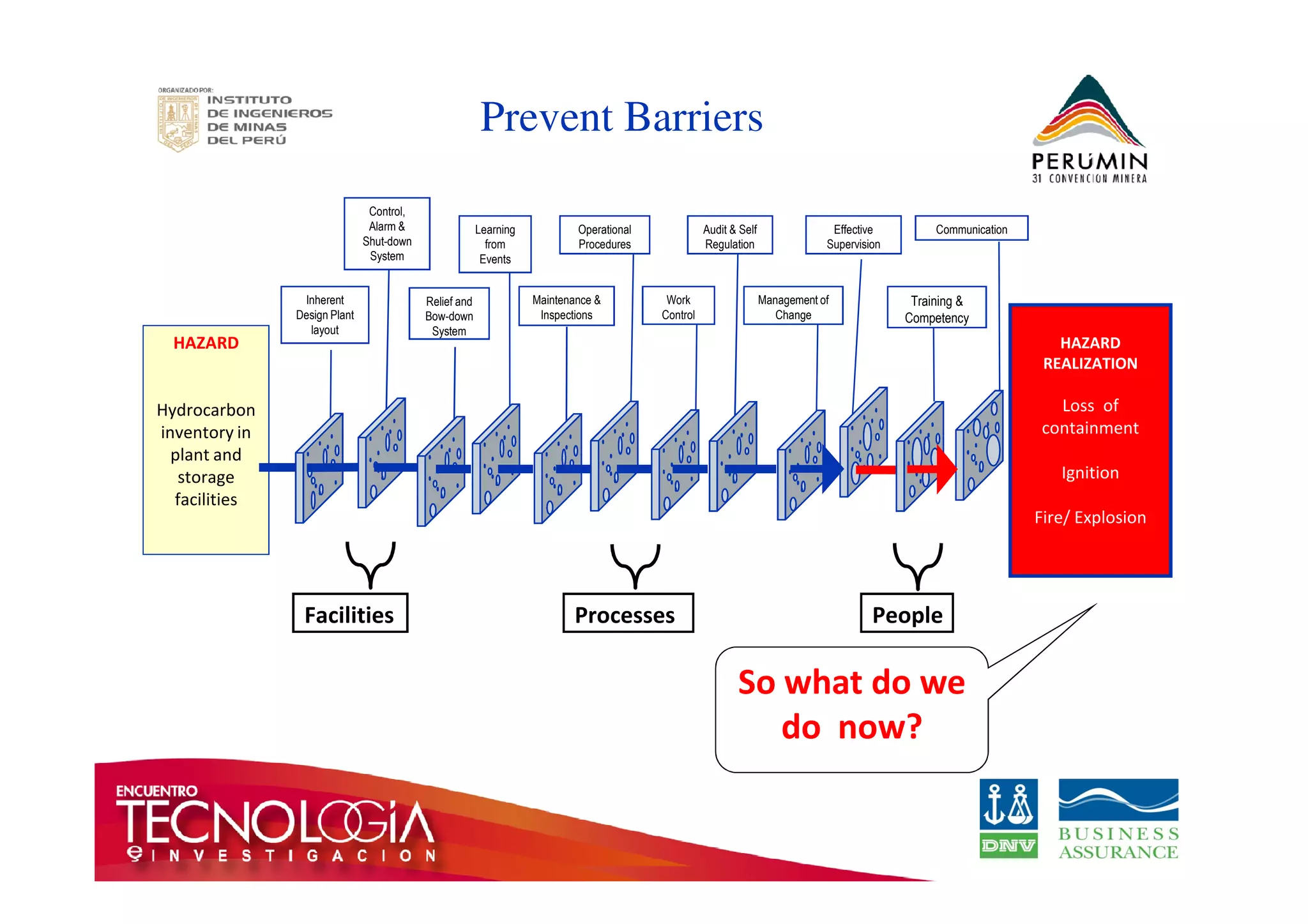
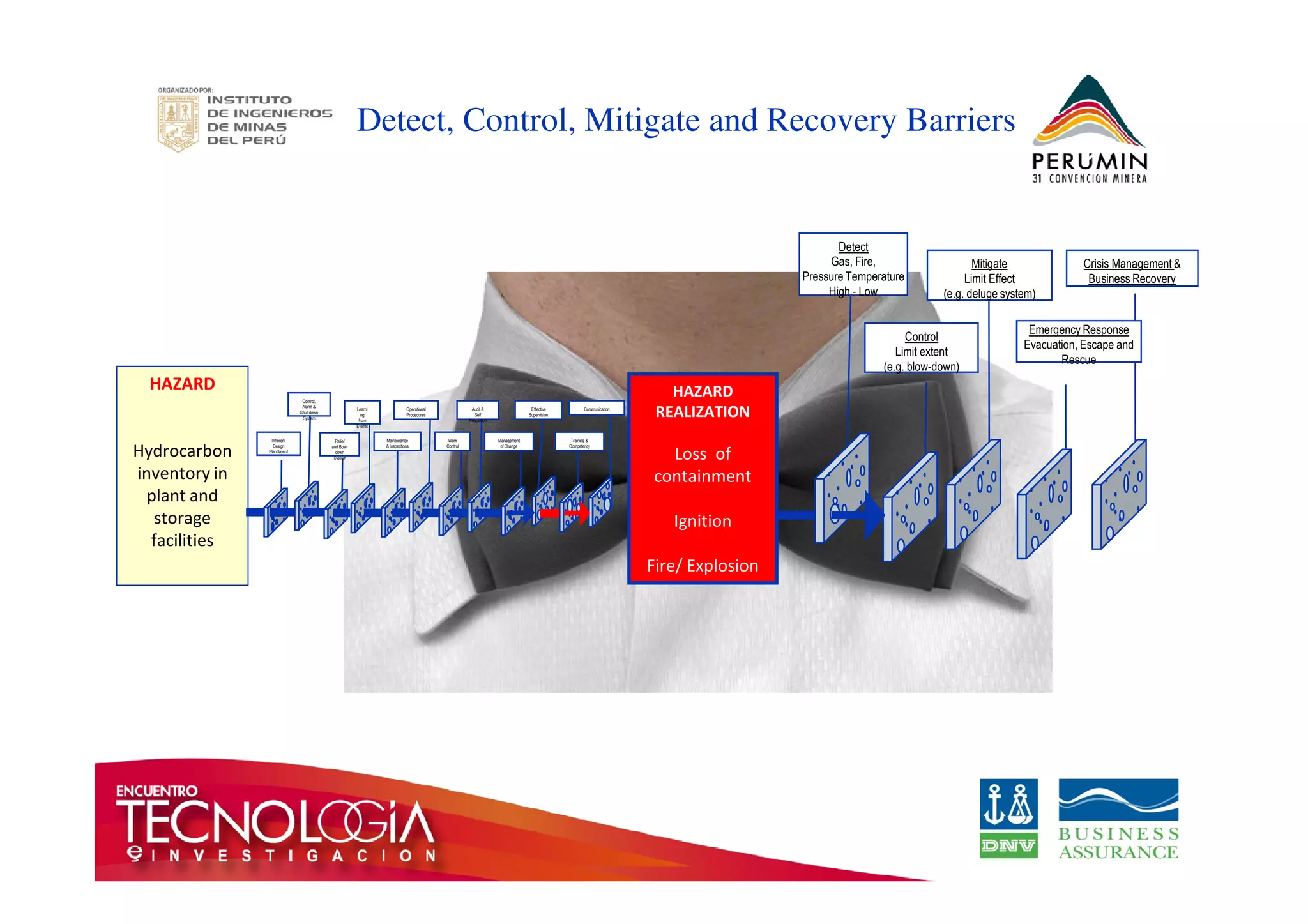
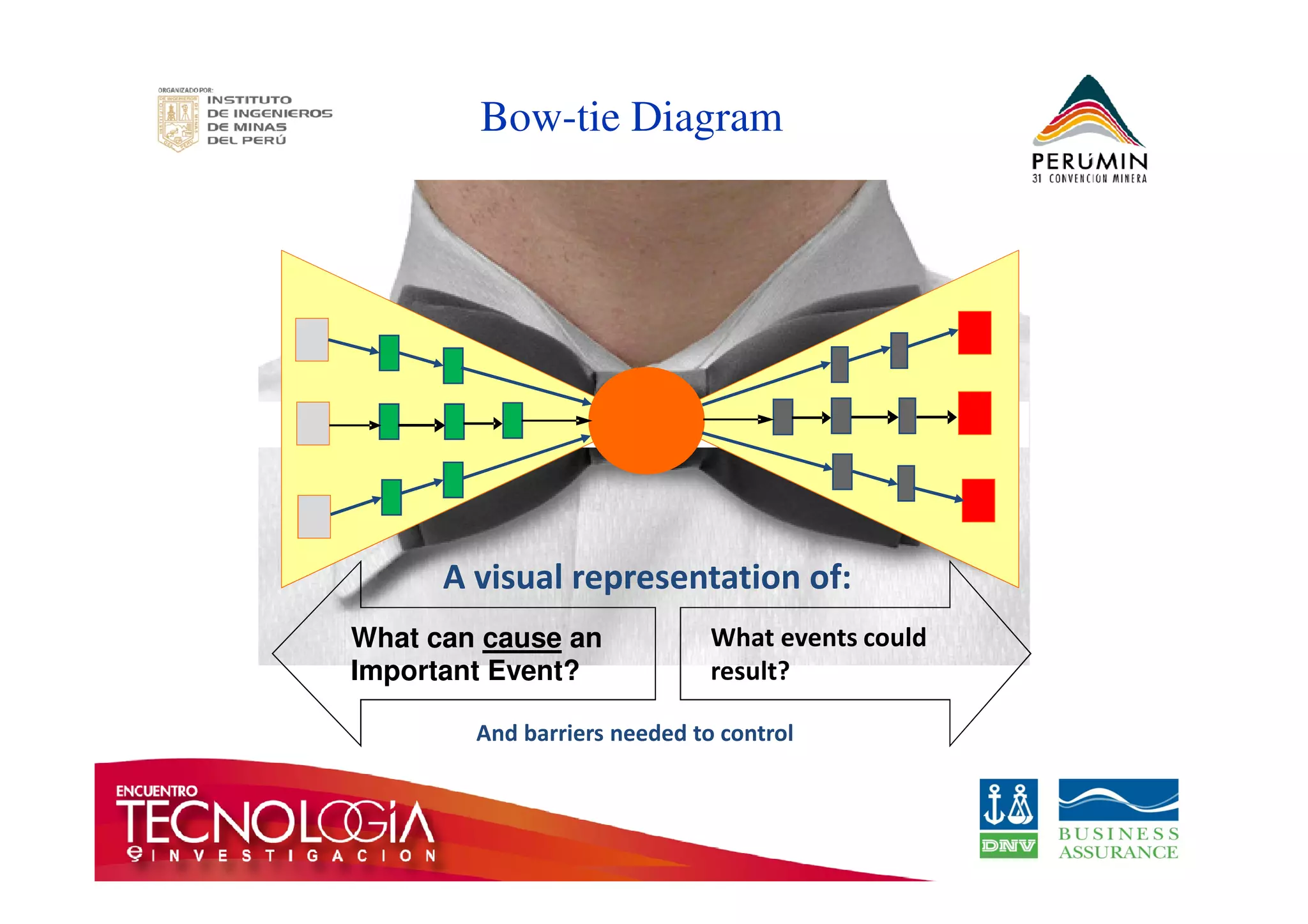
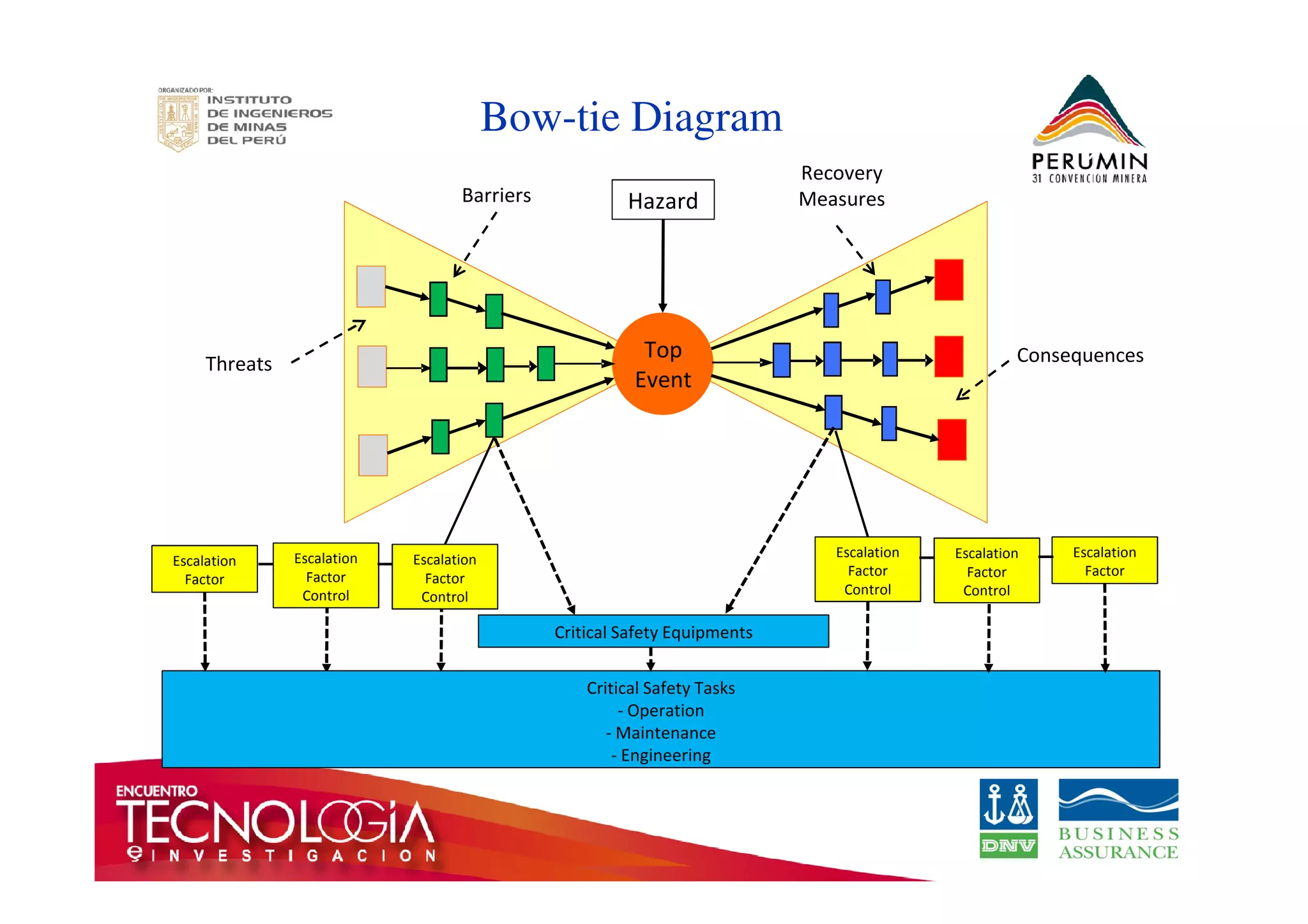
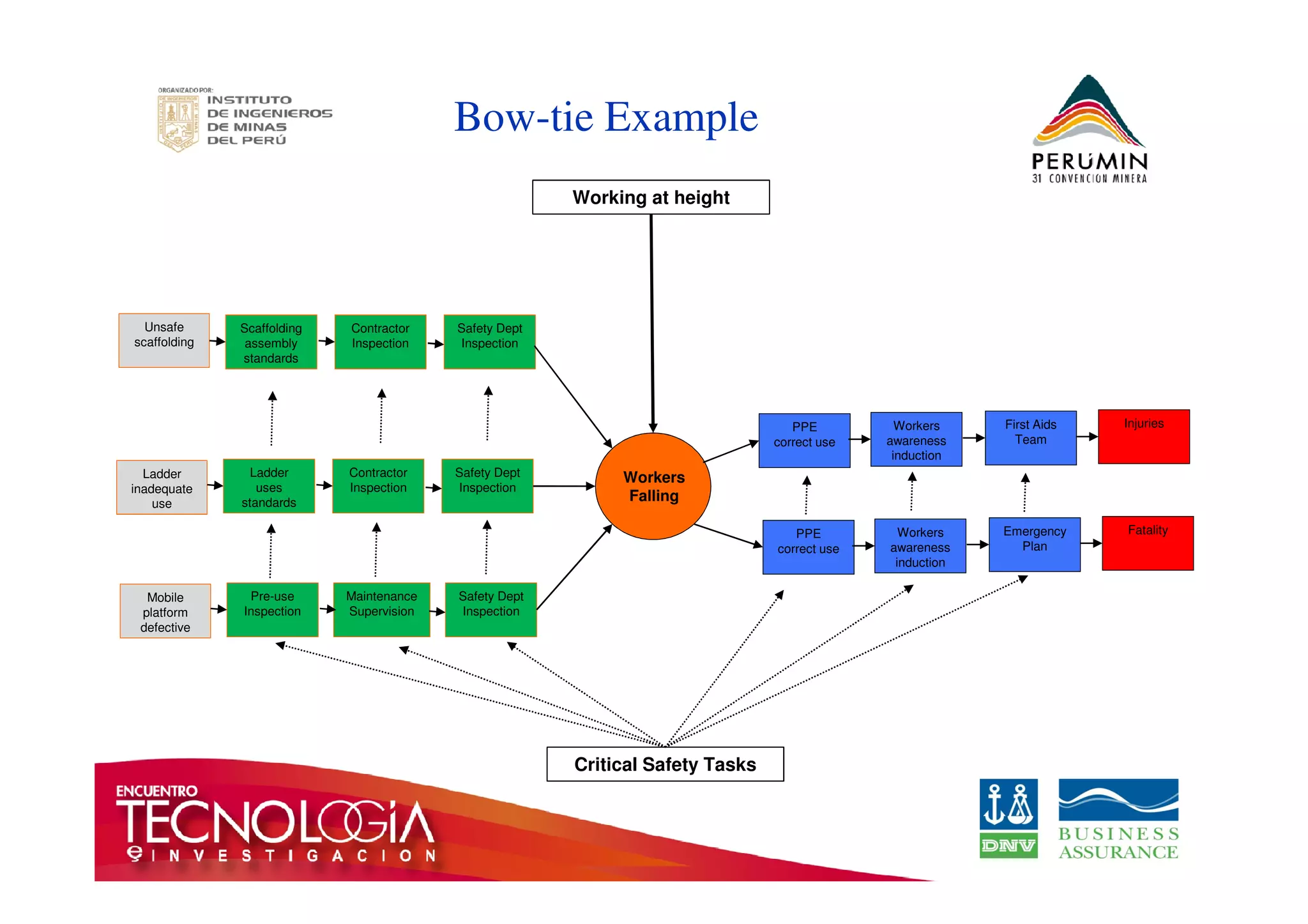
The document outlines the Bow-Tie Risk Analysis methodology, emphasizing the importance of managing both upside and downside risks in complex work environments. It explains how to identify hazards, evaluate risks, and implement controls through a structured approach featuring a visual Bow-Tie diagram that illustrates potential causes, consequences, and necessary barriers. The document also highlights the significance of critical safety tasks and the need for effective communication and training to ensure a successful risk management process.