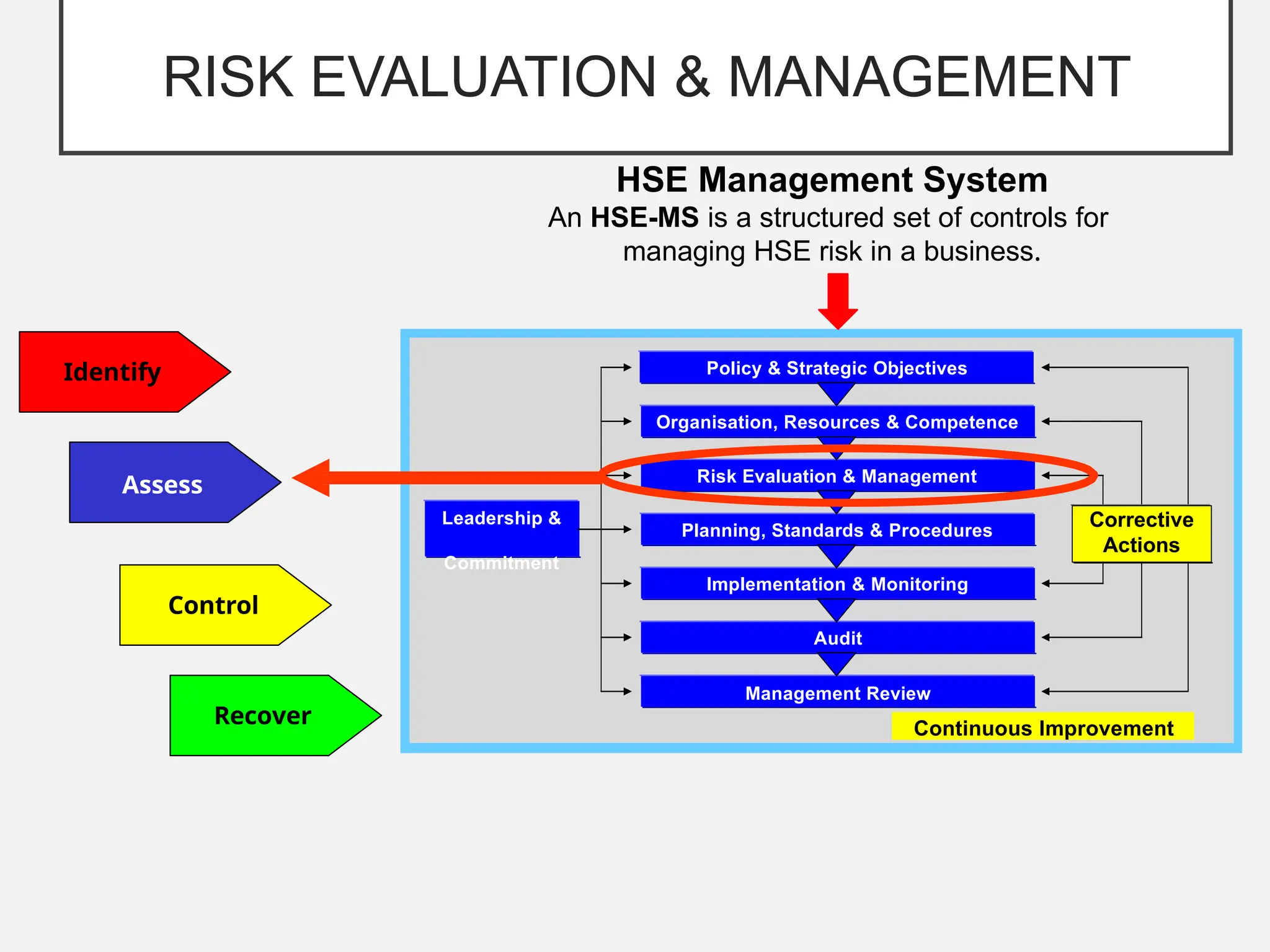
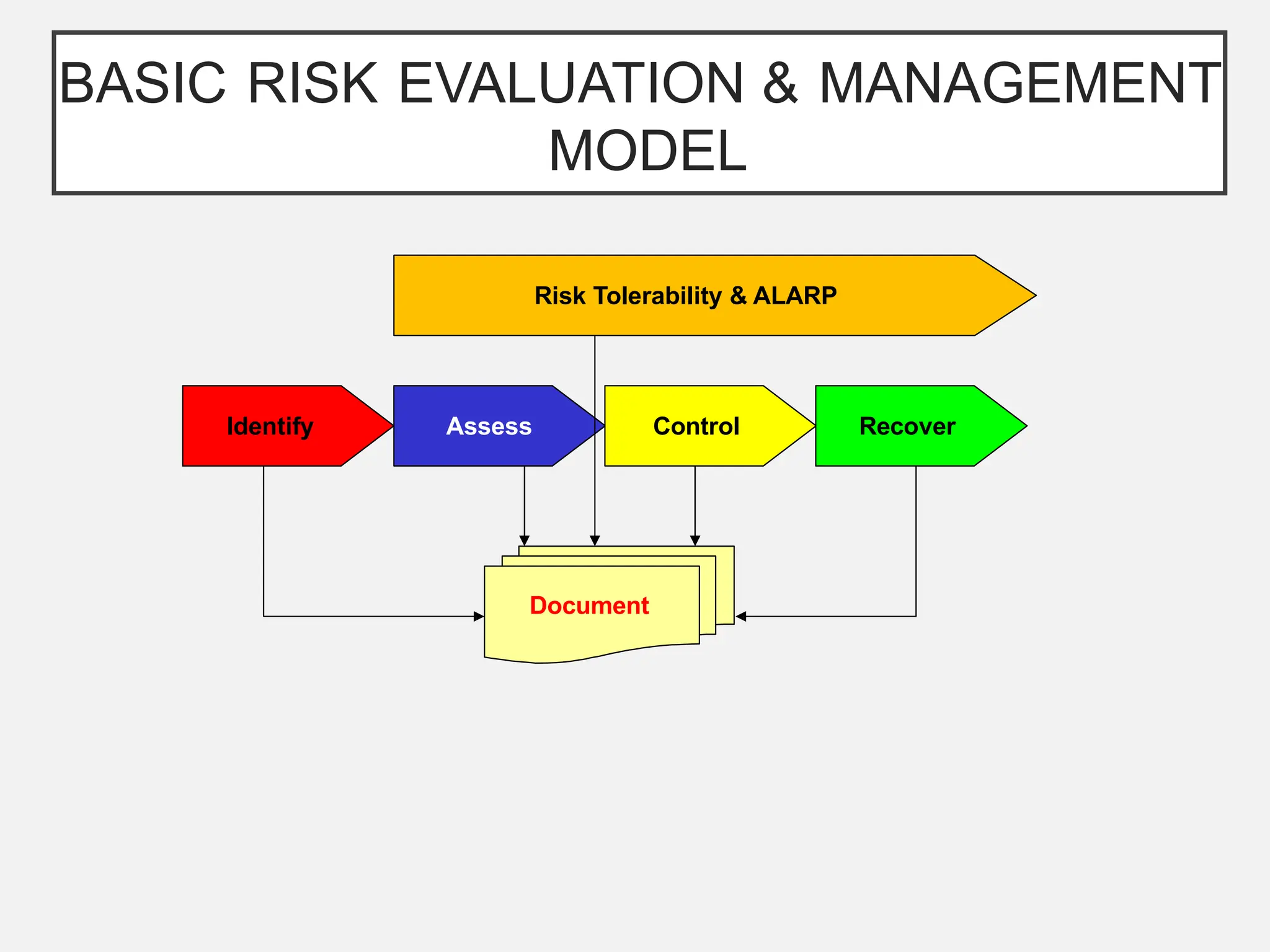
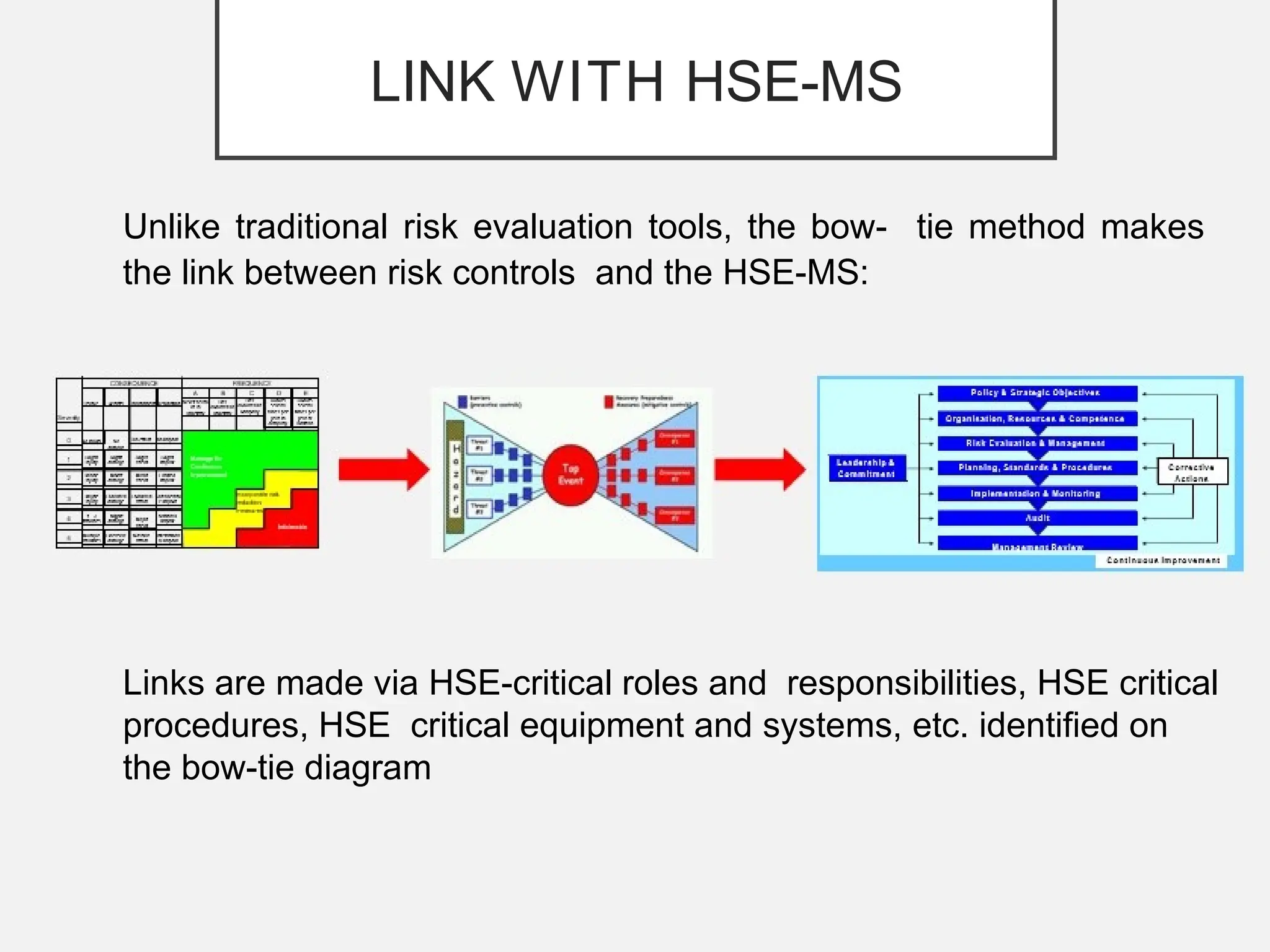
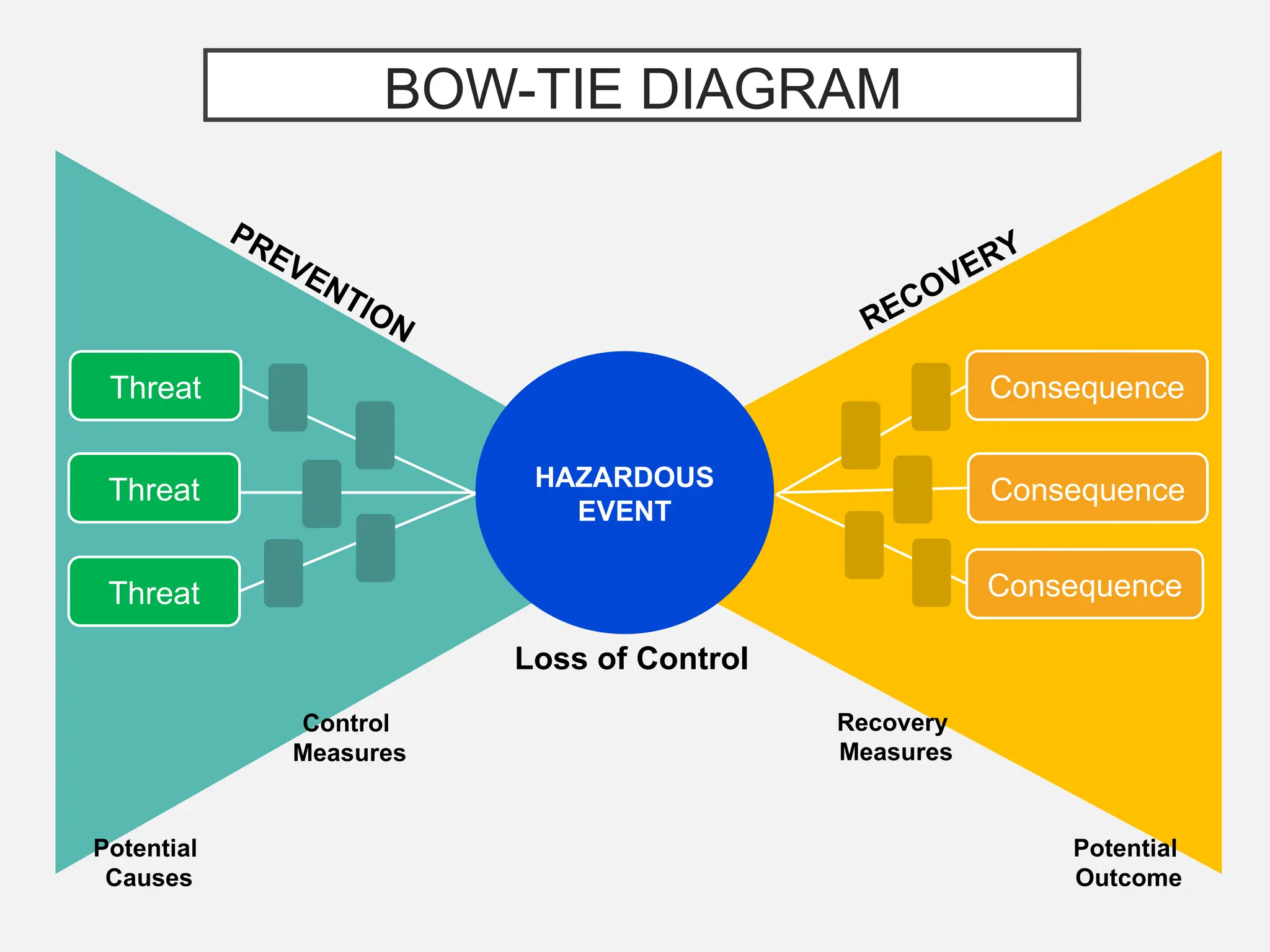
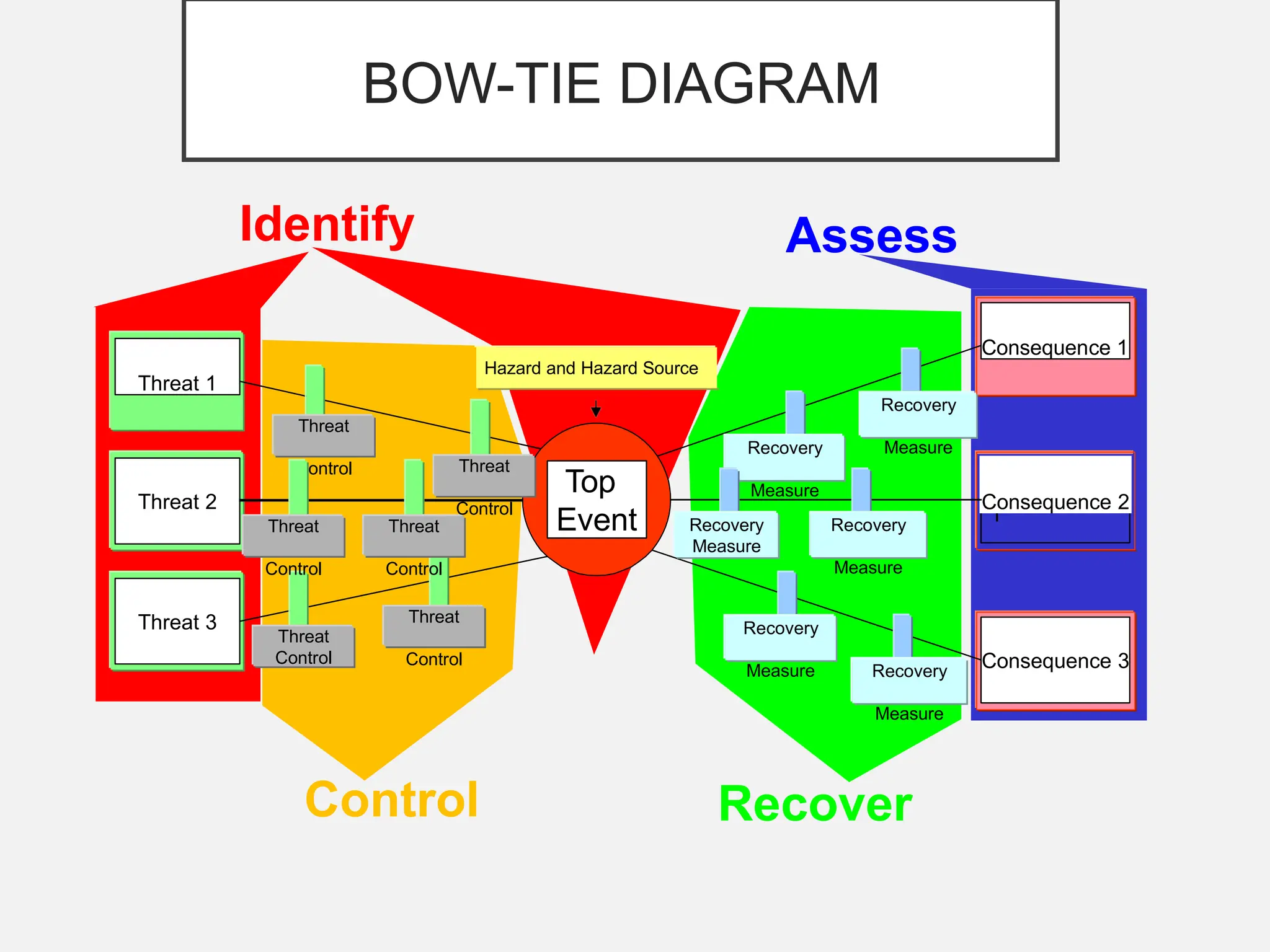
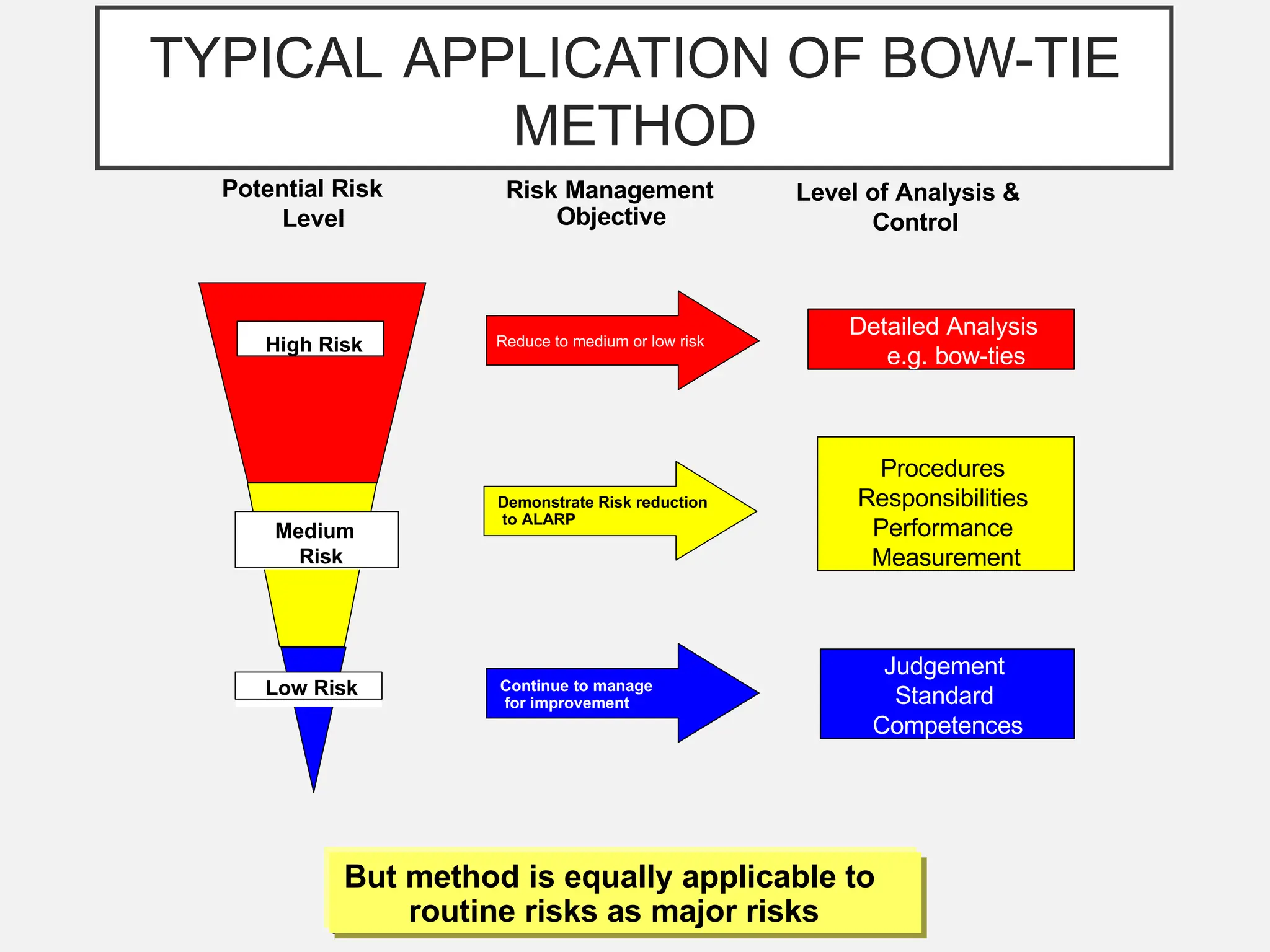
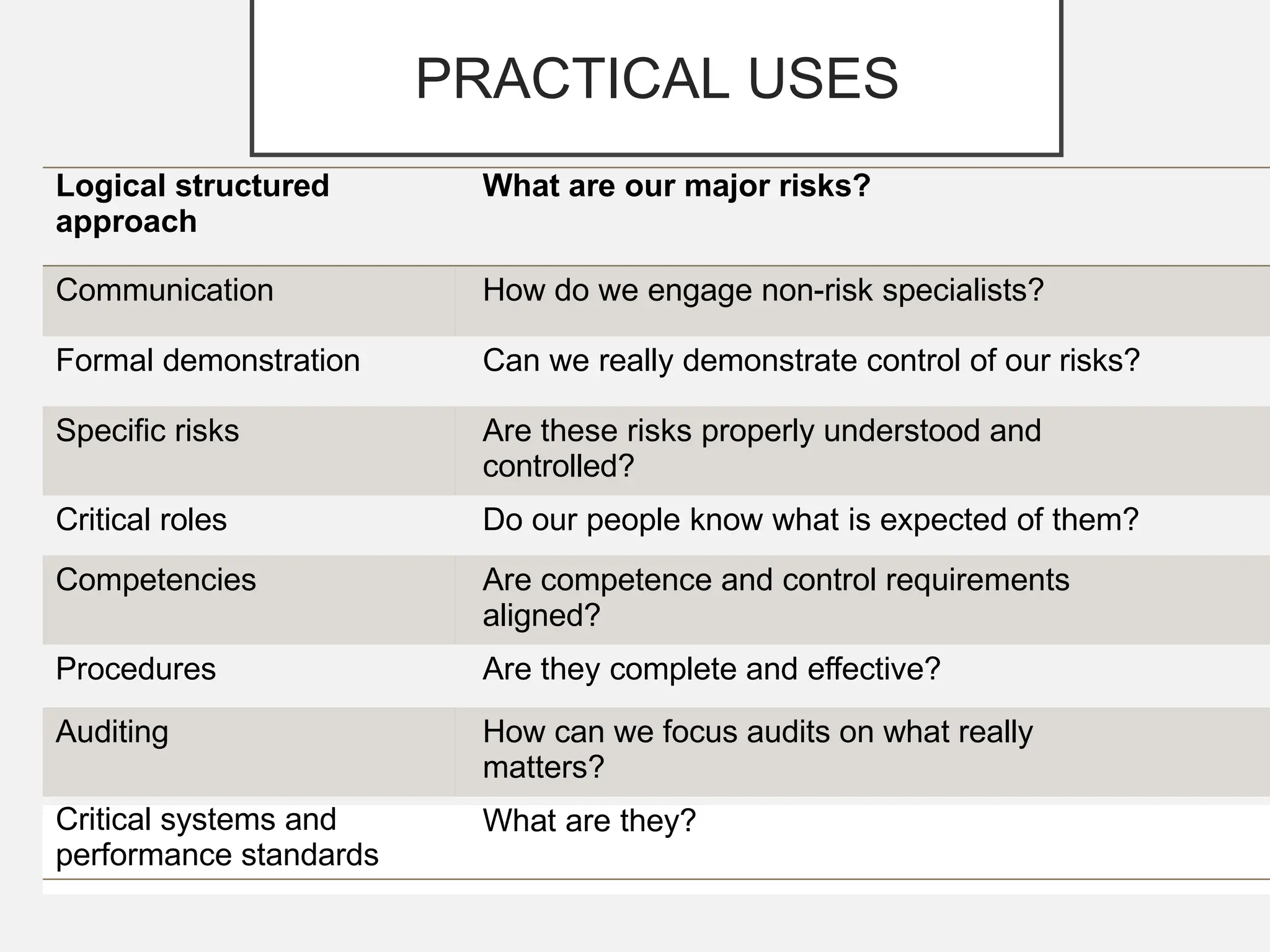
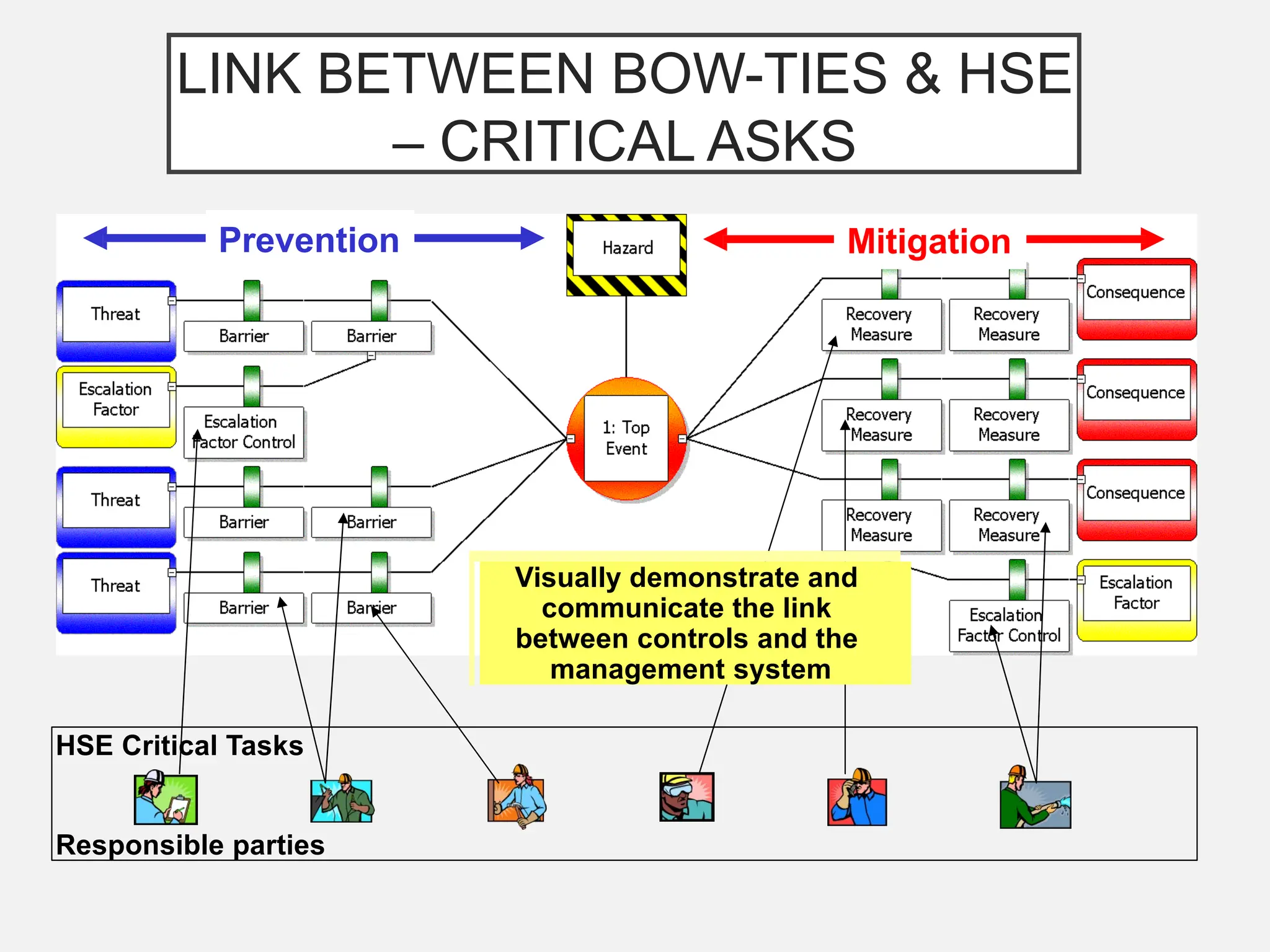
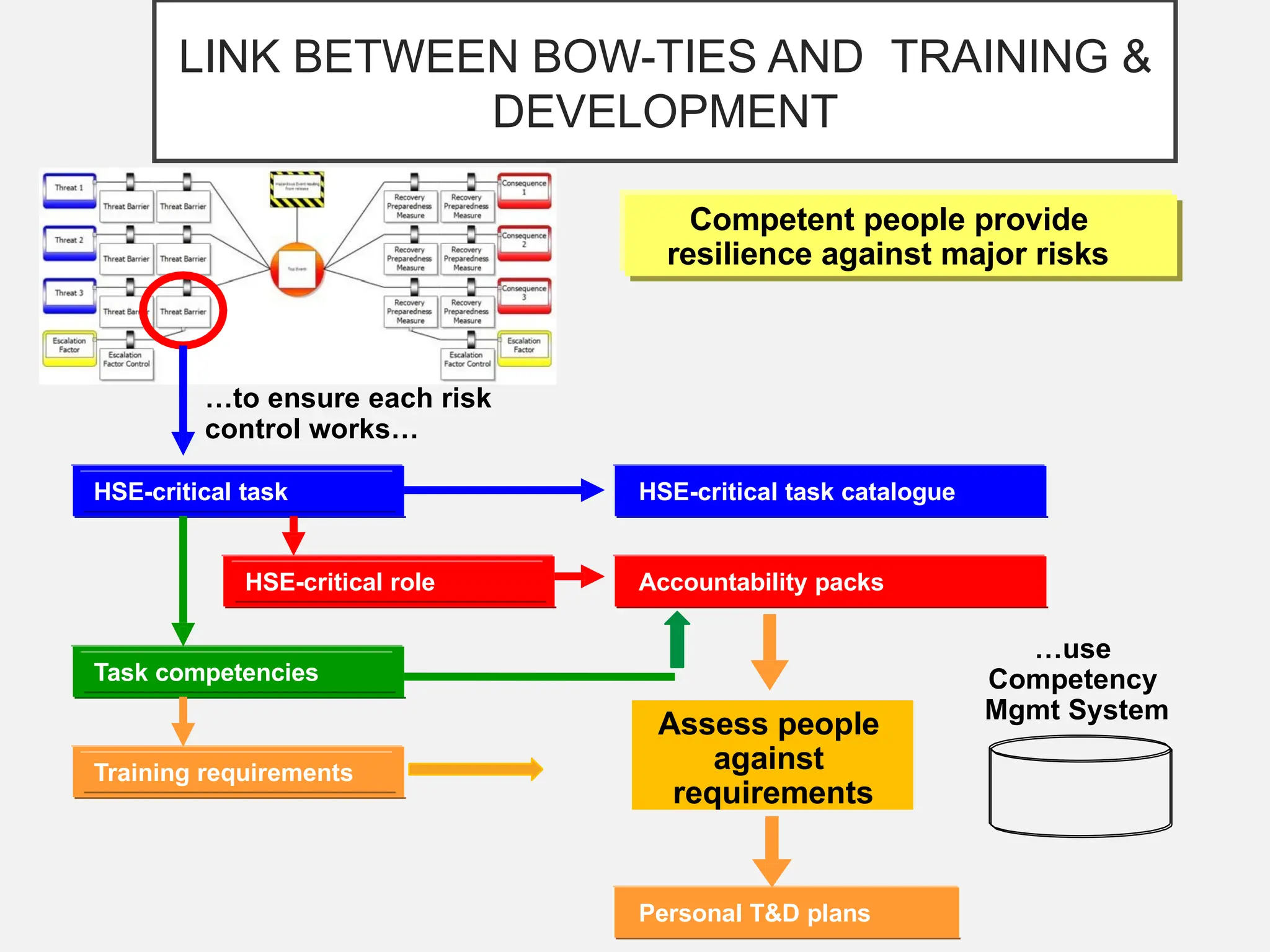
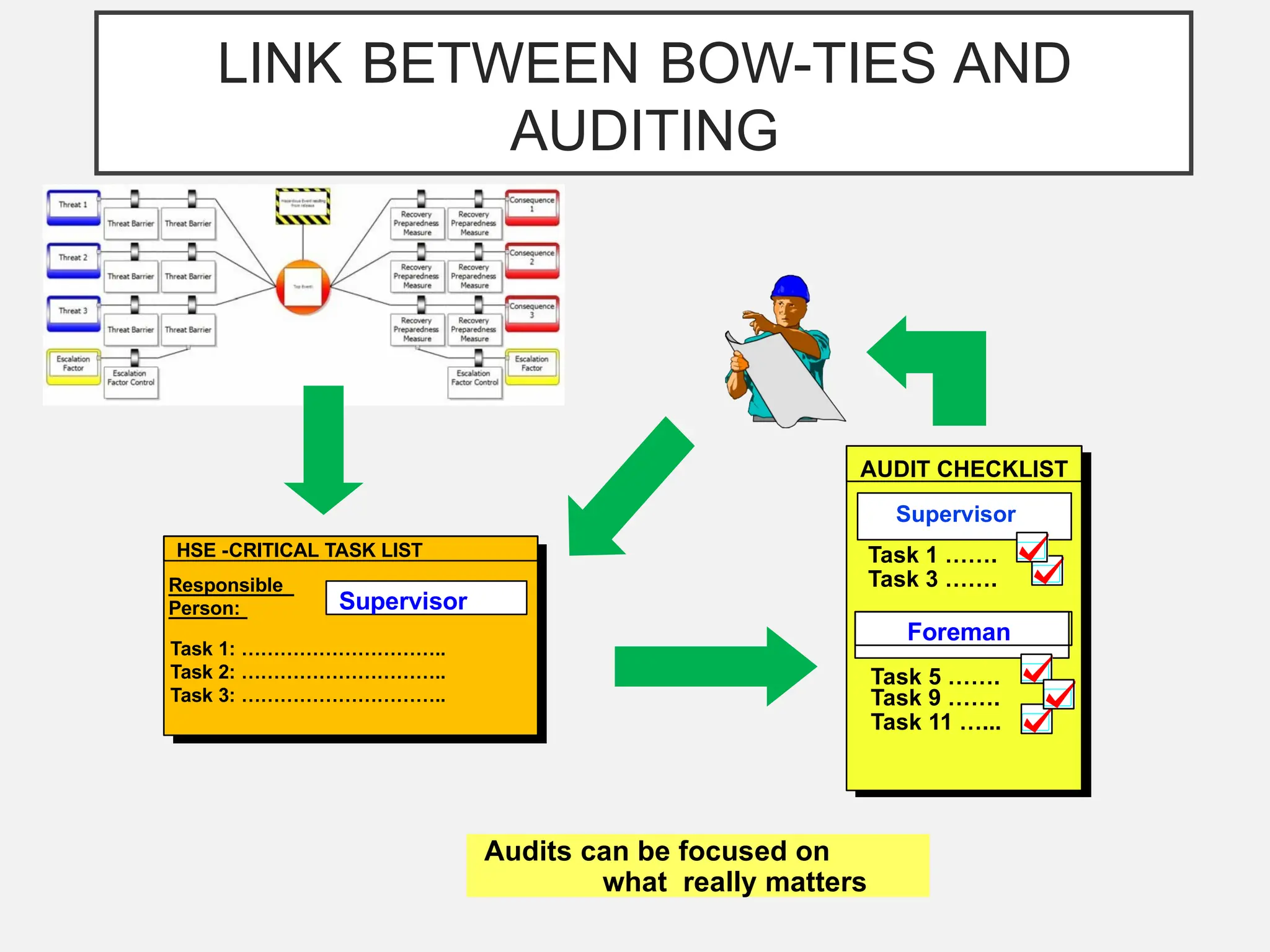
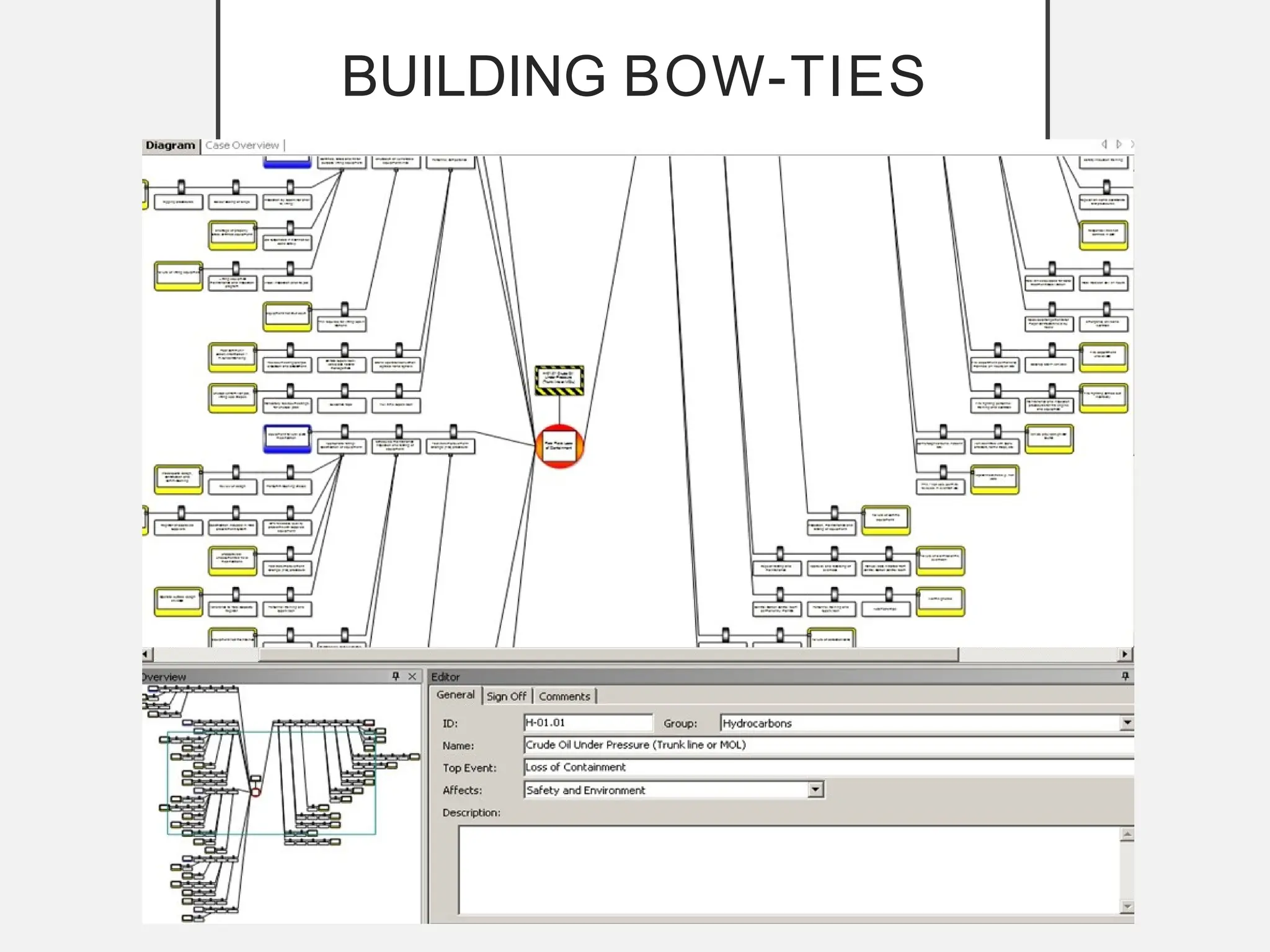
The bow-tie method for risk analysis originated in the aviation and oil and gas sectors to manage complex operational risks and was first developed by Imperial Chemical Industries in 1979. It has since become a standard tool, adopted by Royal Dutch/Shell Group and expanded to various industries, including healthcare and mining. The method establishes a clear link between risk controls and health, safety, and environmental management systems, enhancing understanding and management of risks.