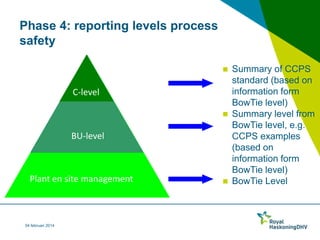
This document outlines a 4-phase approach to determining process safety key performance indicators (KPIs) using the BowTie methodology. Phase 1 involves setting up BowTie diagrams using risk assessment reports. Phase 2 selects leading and lagging KPIs linked to barriers in the BowTie diagrams. Phase 3 establishes criteria and reporting standards for the KPIs. Phase 4 integrates incident data into the BowTie diagrams and starts an improvement cycle. The approach aims to comply with legislation and standards while identifying relevant process safety KPIs in a bottom-up manner tied to an organization's safety management system.