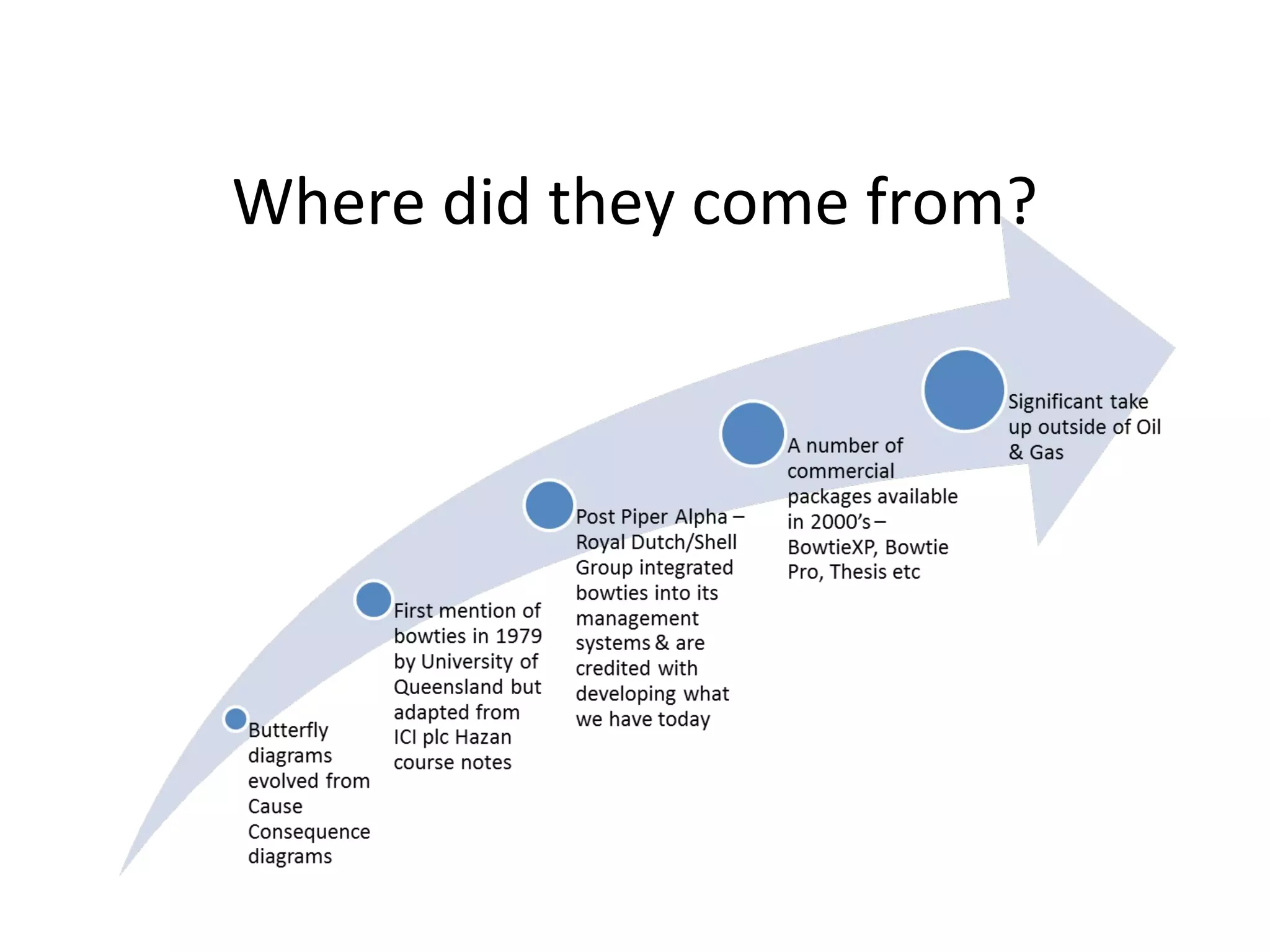
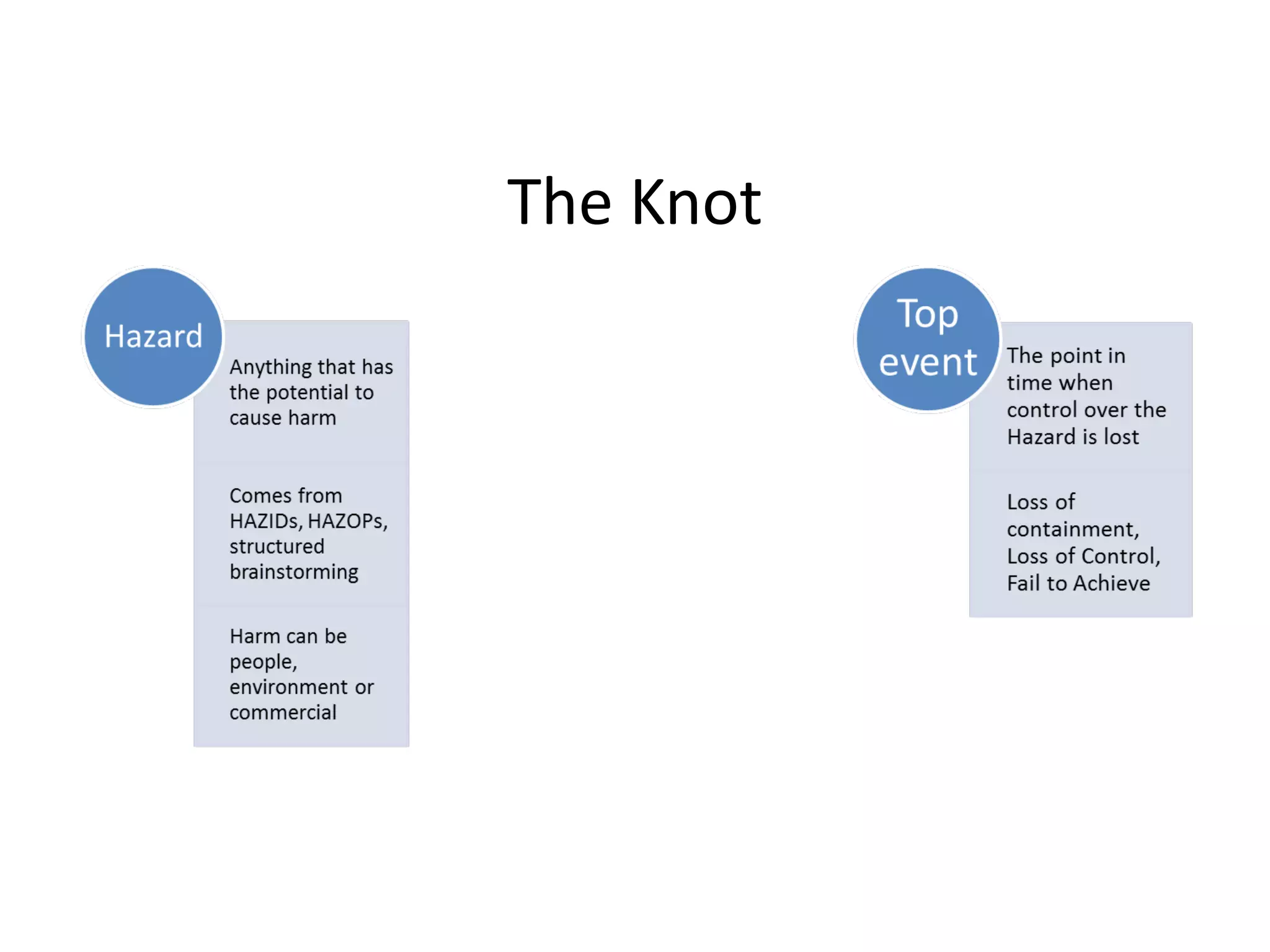
This document provides an overview of bowtie diagrams and how they are used for risk management. It discusses the origins of bowtie diagrams, which evolved from cause-consequence diagrams. Bowtie diagrams visually represent hazards, threats, consequences, and prevention/recovery barriers on a diagram shaped like a bowtie. They provide a clear visual representation of risk that can be more engaging for teams to discuss than traditional text-based risk analysis outputs. The document notes that bowtie diagrams have significant usage outside of oil and gas and that commercial software is available to create them.