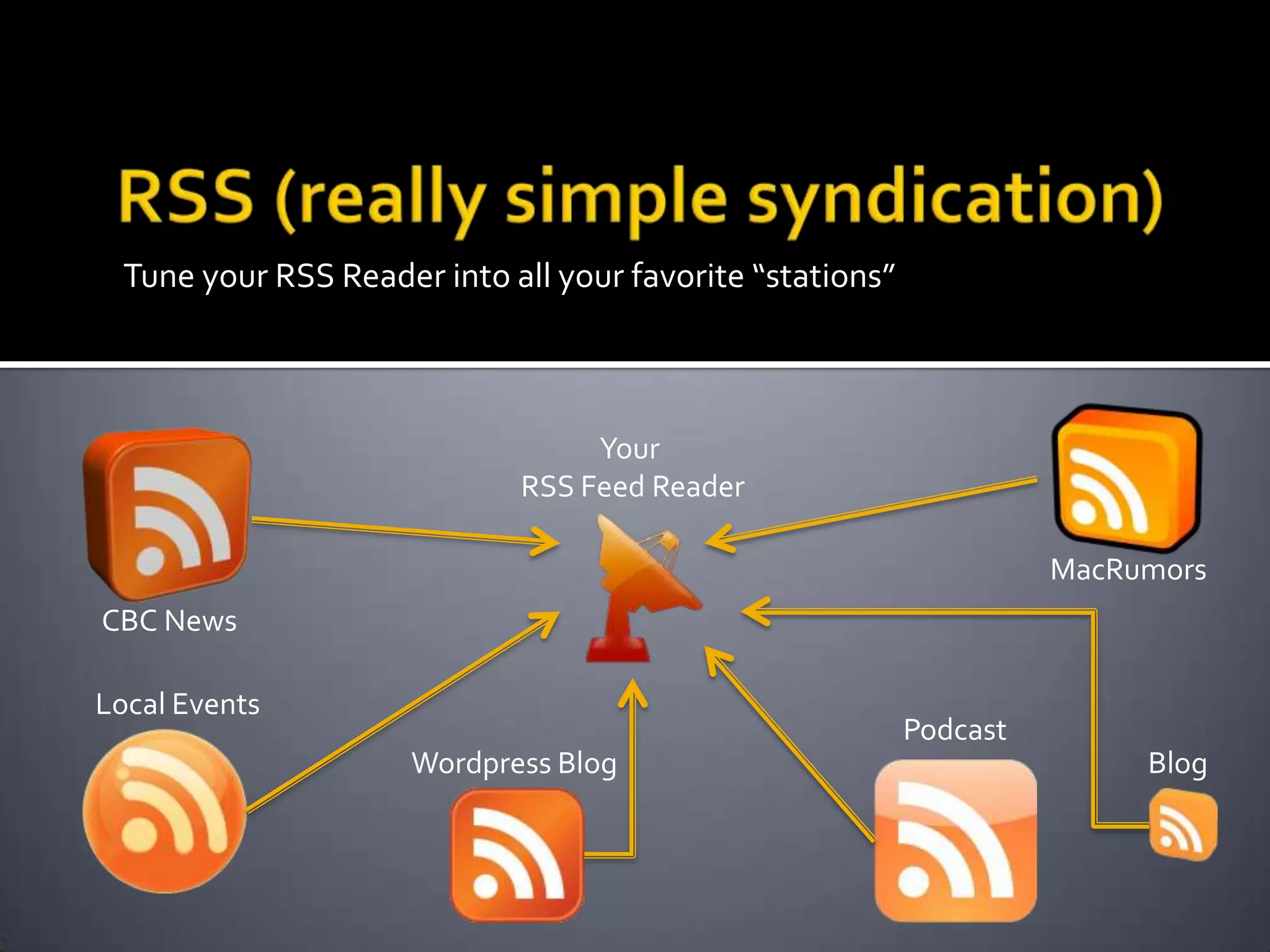
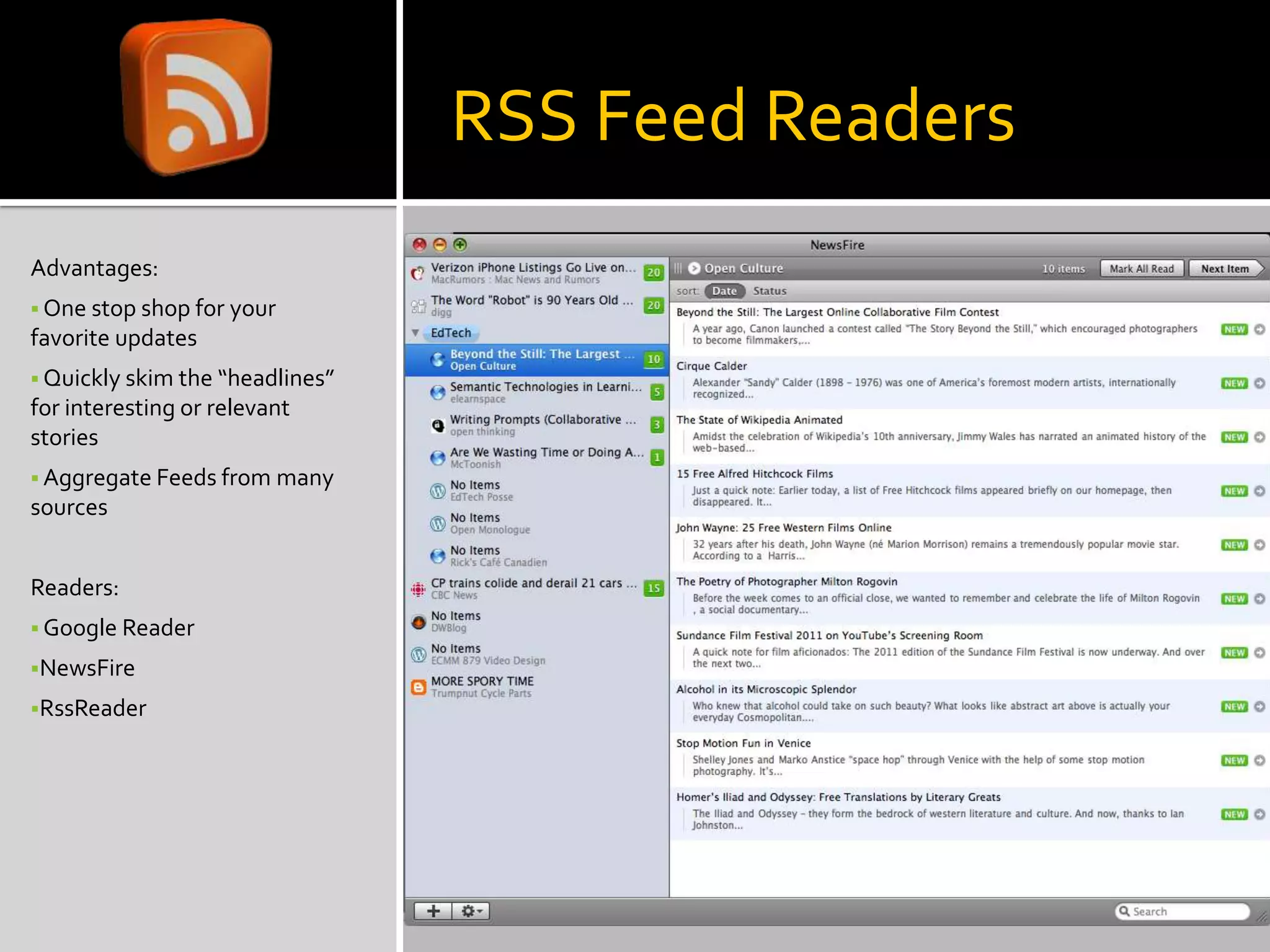
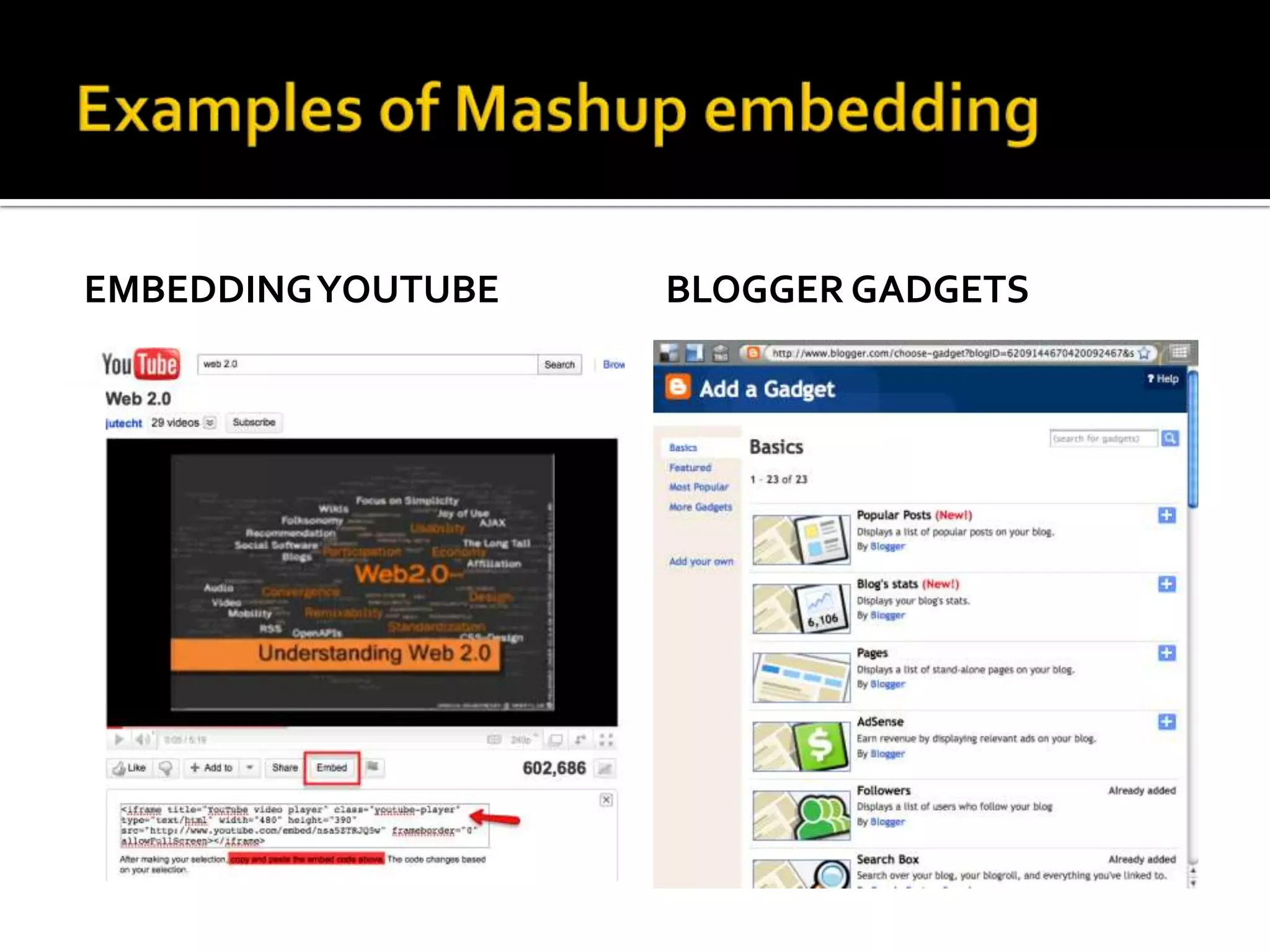
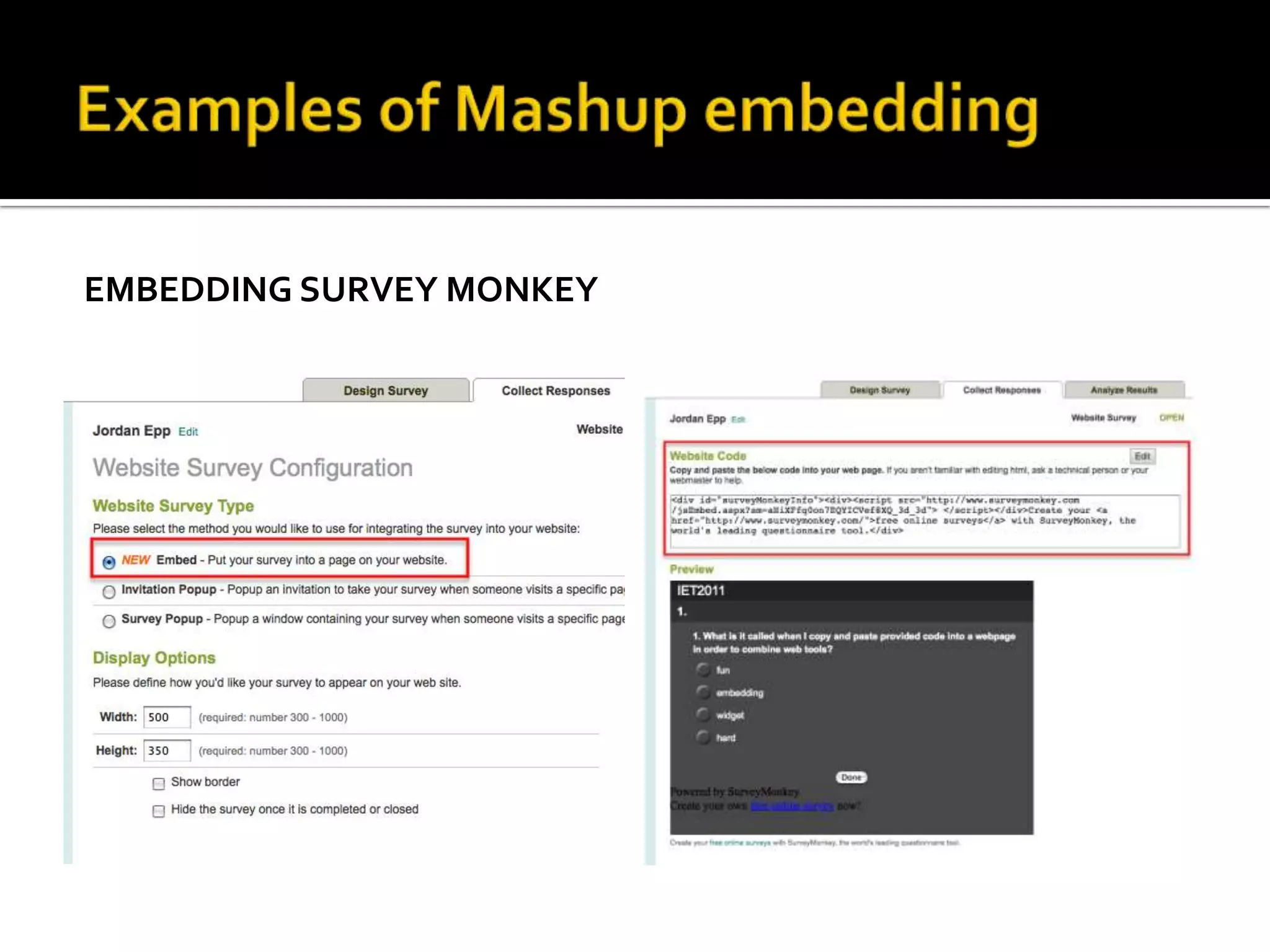
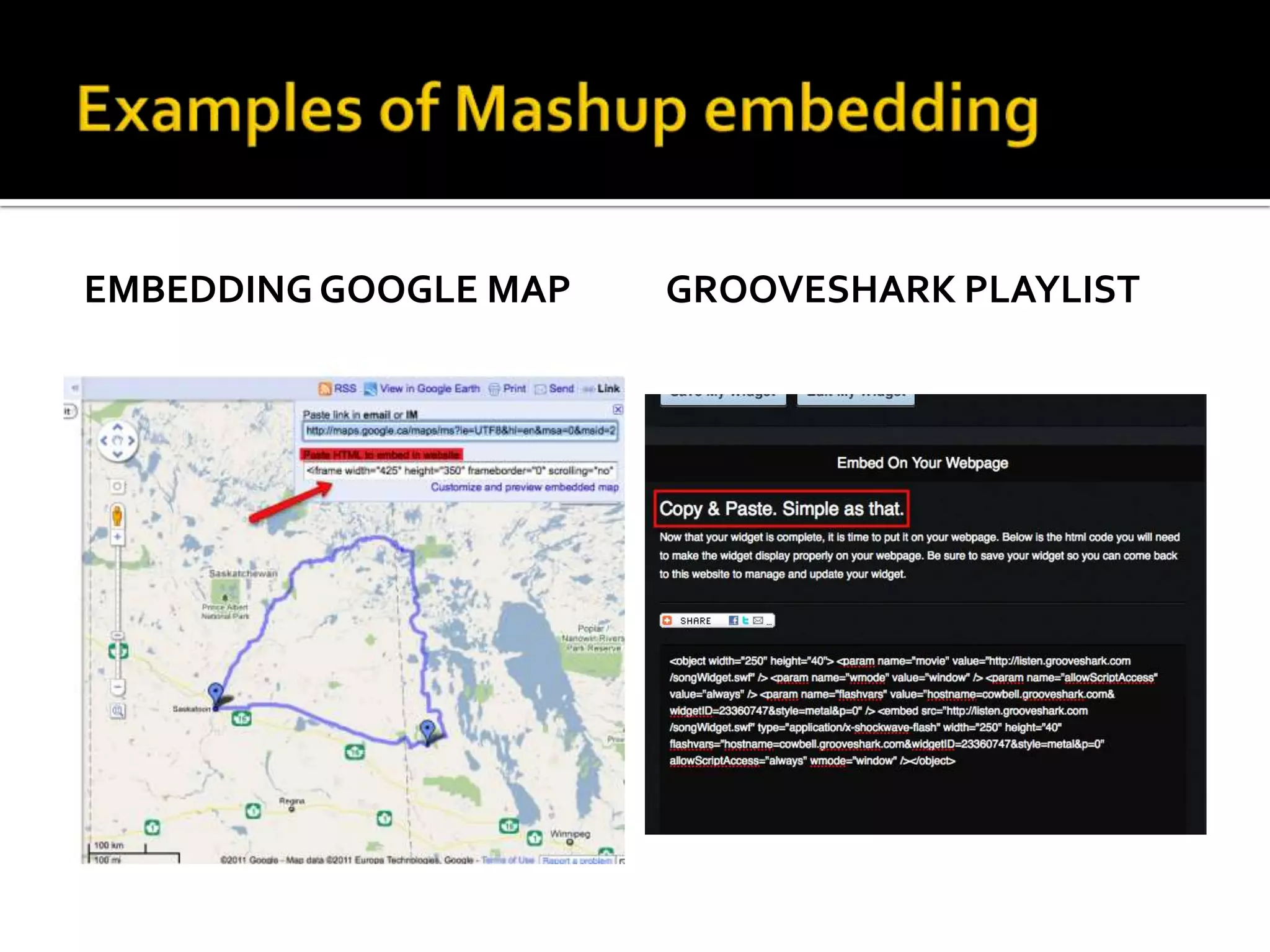
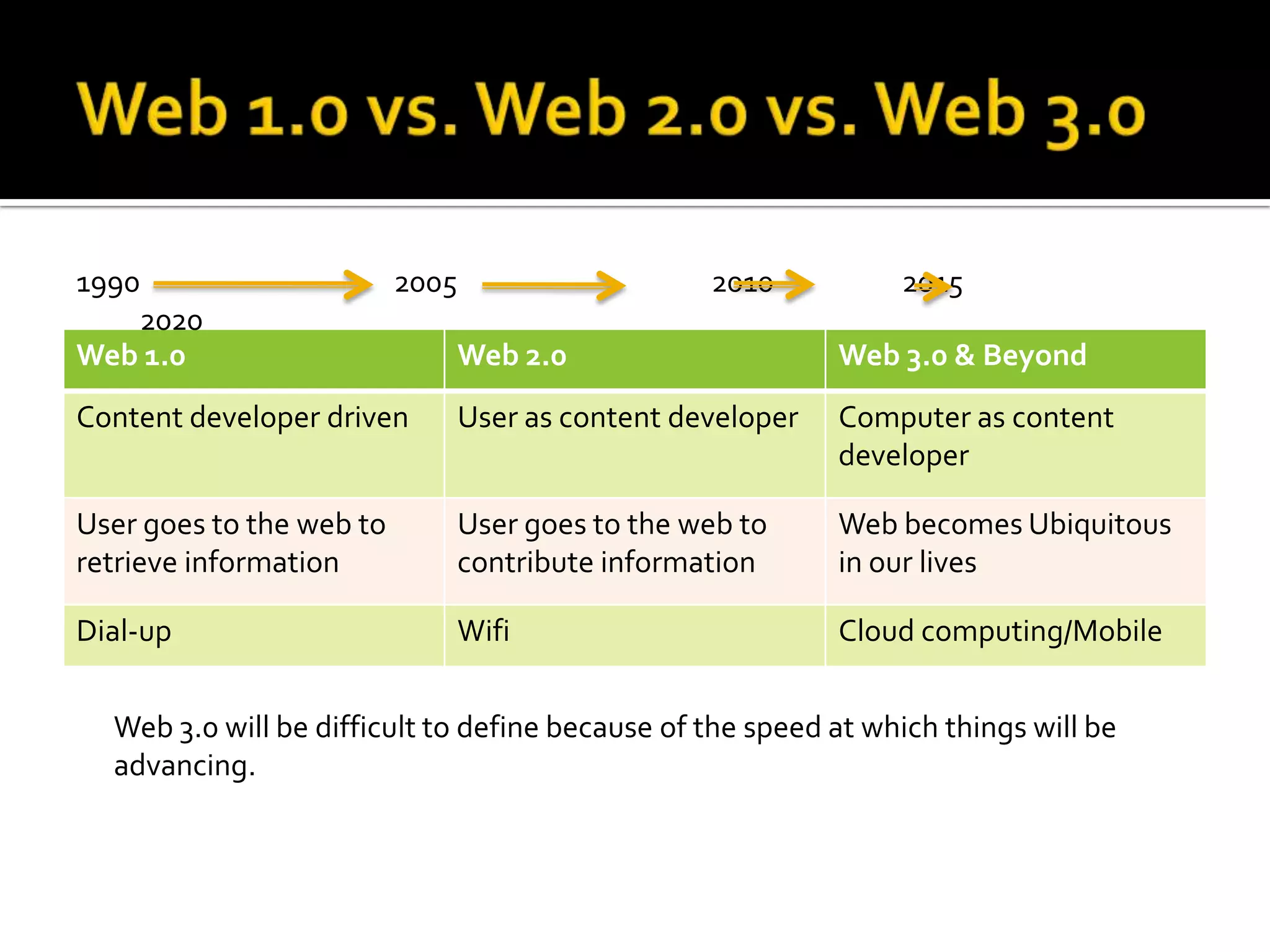
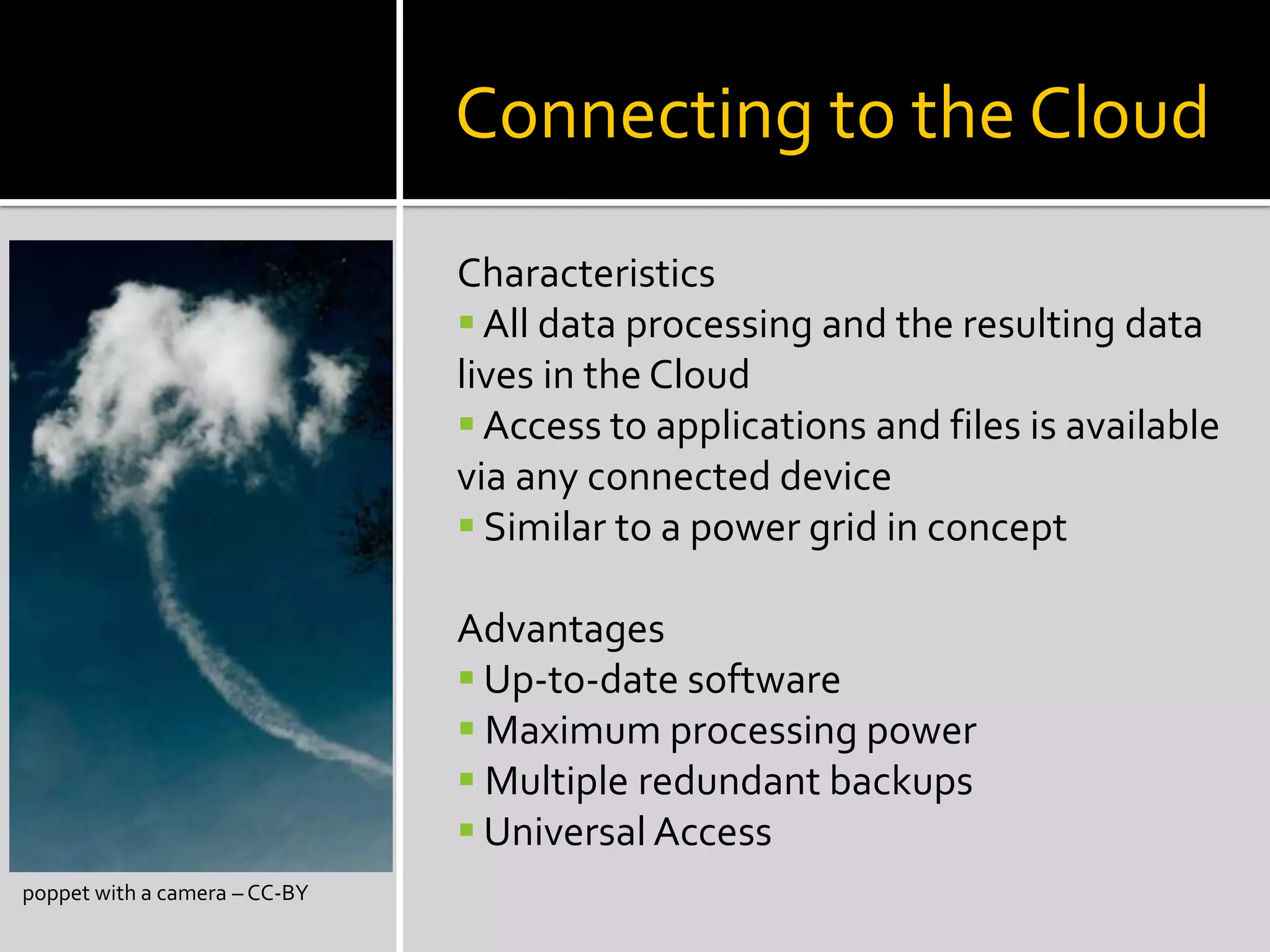
This document discusses trends in social media and web technologies. It describes how wikis, social networks, and RSS feeds can help filter large amounts of online information. Mashups allow combining different web tools in one place for efficiency. Emerging trends include the semantic web, which will enable computers to better understand meaning; mobile technologies and ubiquitous wireless access; and cloud computing, which stores all data and software online. The future web will be more accessible, efficient, and intelligent.