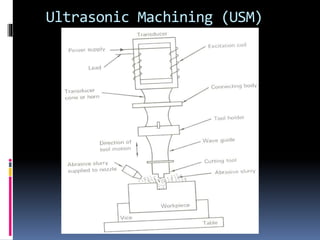
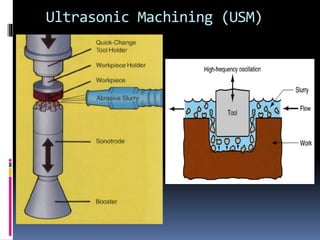
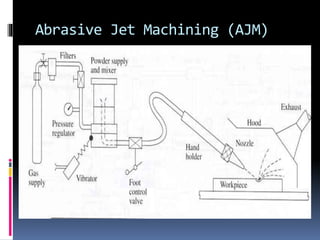
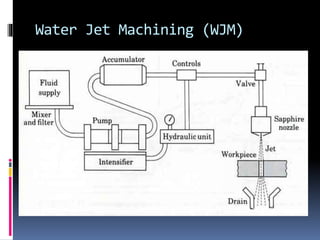
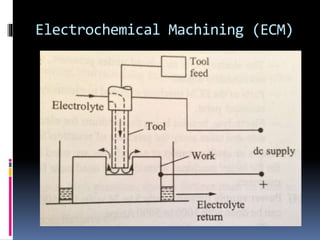
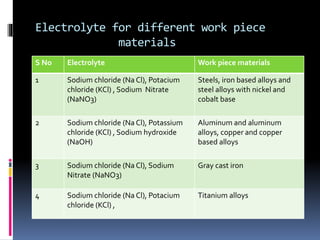
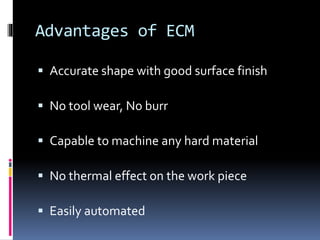
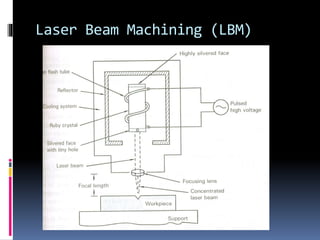
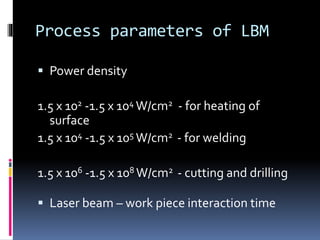
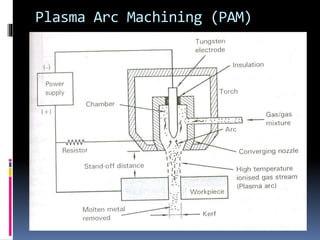
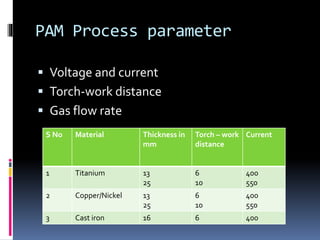
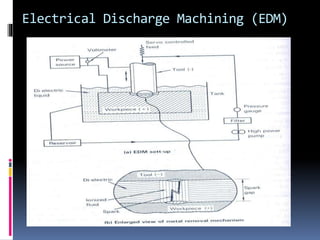
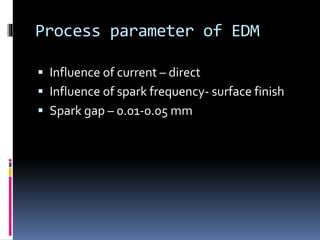
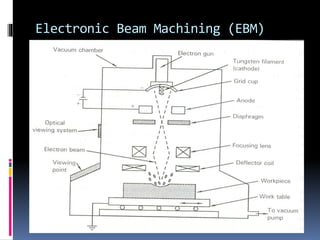
This document discusses various non-traditional machining (NTM) processes, including their need, classification, parameters, advantages, limitations, and applications. It covers mechanical processes like ultrasonic machining, abrasive jet machining, and water jet machining. It also discusses chemical/electrochemical processes like electrochemical machining, thermal/electrothermal processes like laser beam machining and plasma arc machining, and electrical discharge machining. Each process is explained along with diagrams and tables of parameters for different materials.