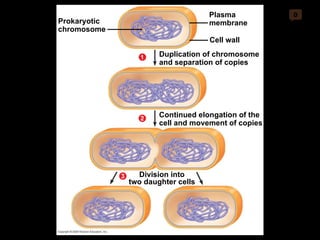
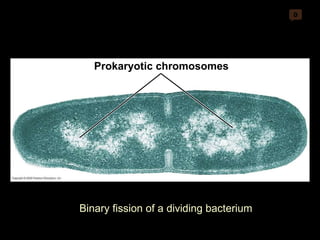
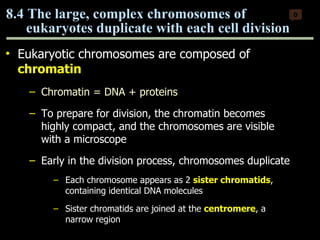
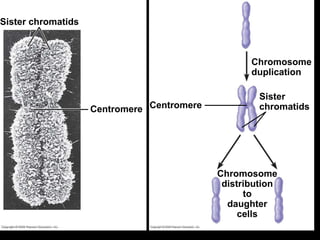
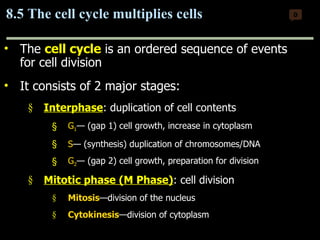
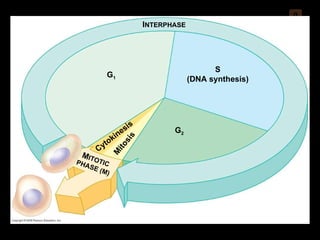
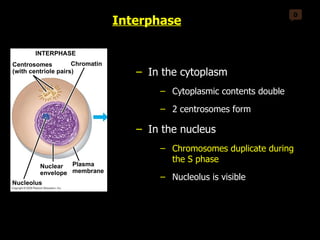
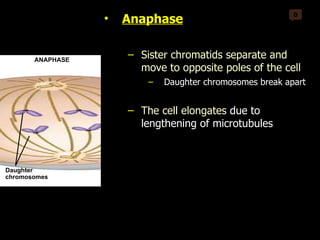
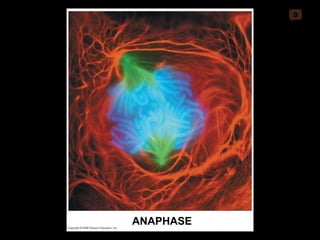
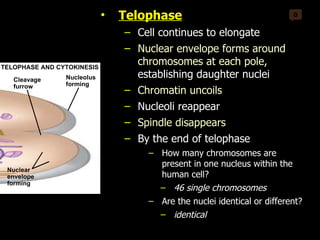
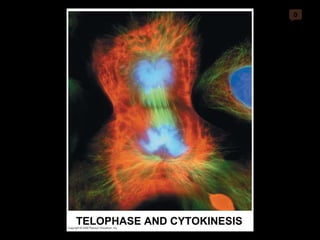
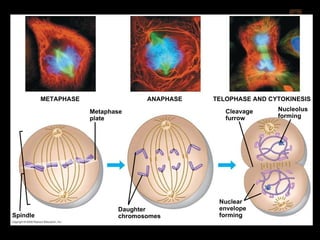
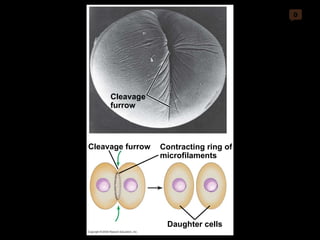
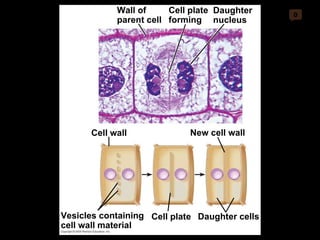
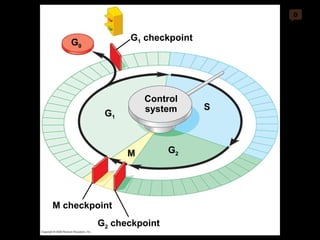
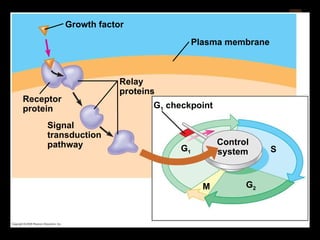
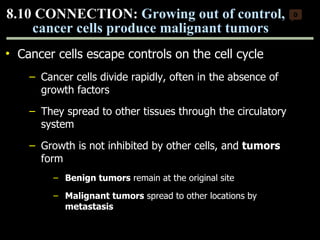
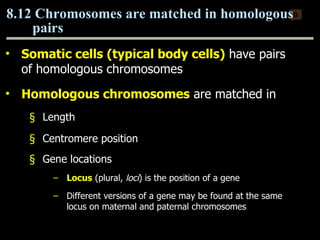
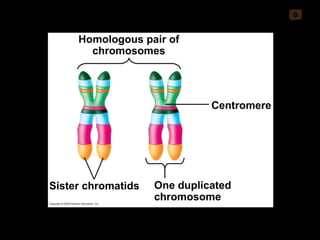
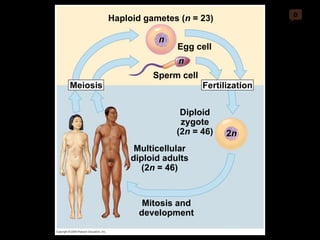
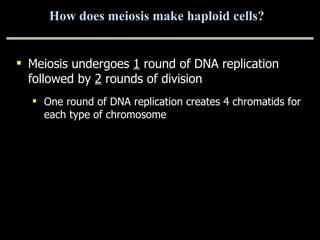
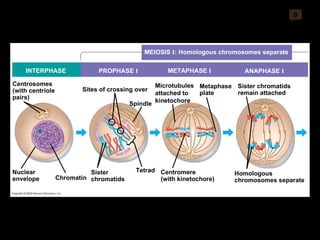
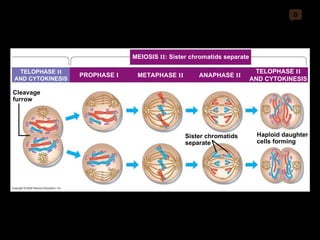
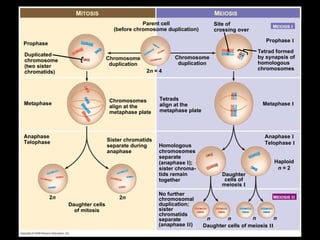
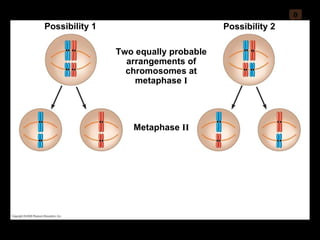
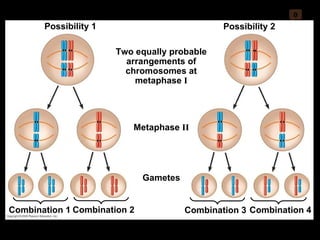
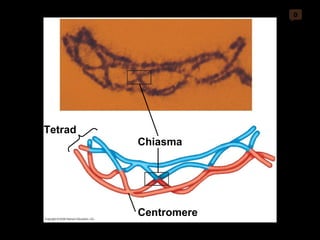
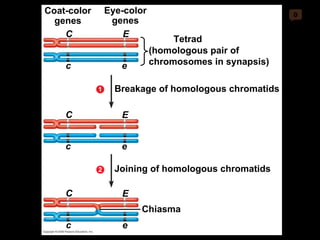
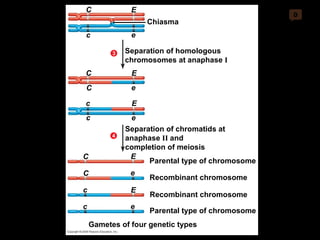
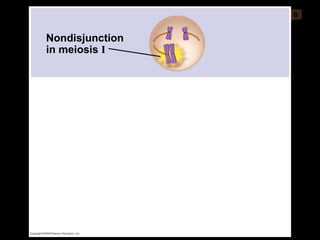
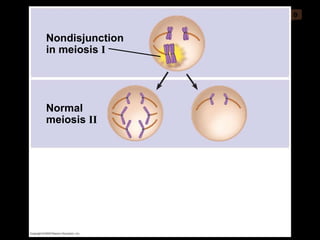
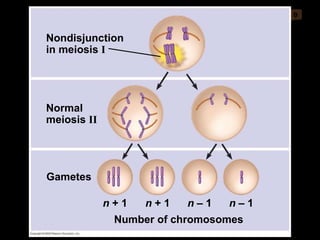
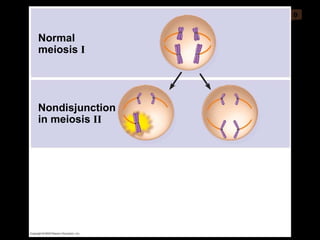
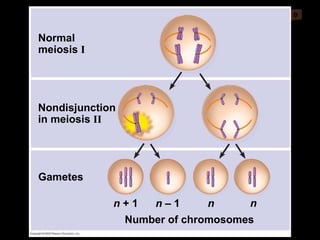
Mitosis and meiosis are both cell division processes in eukaryotes. Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells through chromosome duplication and separation, while meiosis reduces the chromosome number through two cell divisions. Meiosis results in four haploid daughter cells through homologous chromosome separation in meiosis I and sister chromatid separation in meiosis II. Both processes involve the duplication of chromosomes followed by their orderly separation through different stages including prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.











































![Need Chemistry Help? Contact Veronica Walker for FREE tutoring! [email_address] Need Biology Help?? Contact Veronica Walker for FREE tutoring! [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08lecturepresentation-110303120220-phpapp02/85/08-lecture-presentation-106-320.jpg)