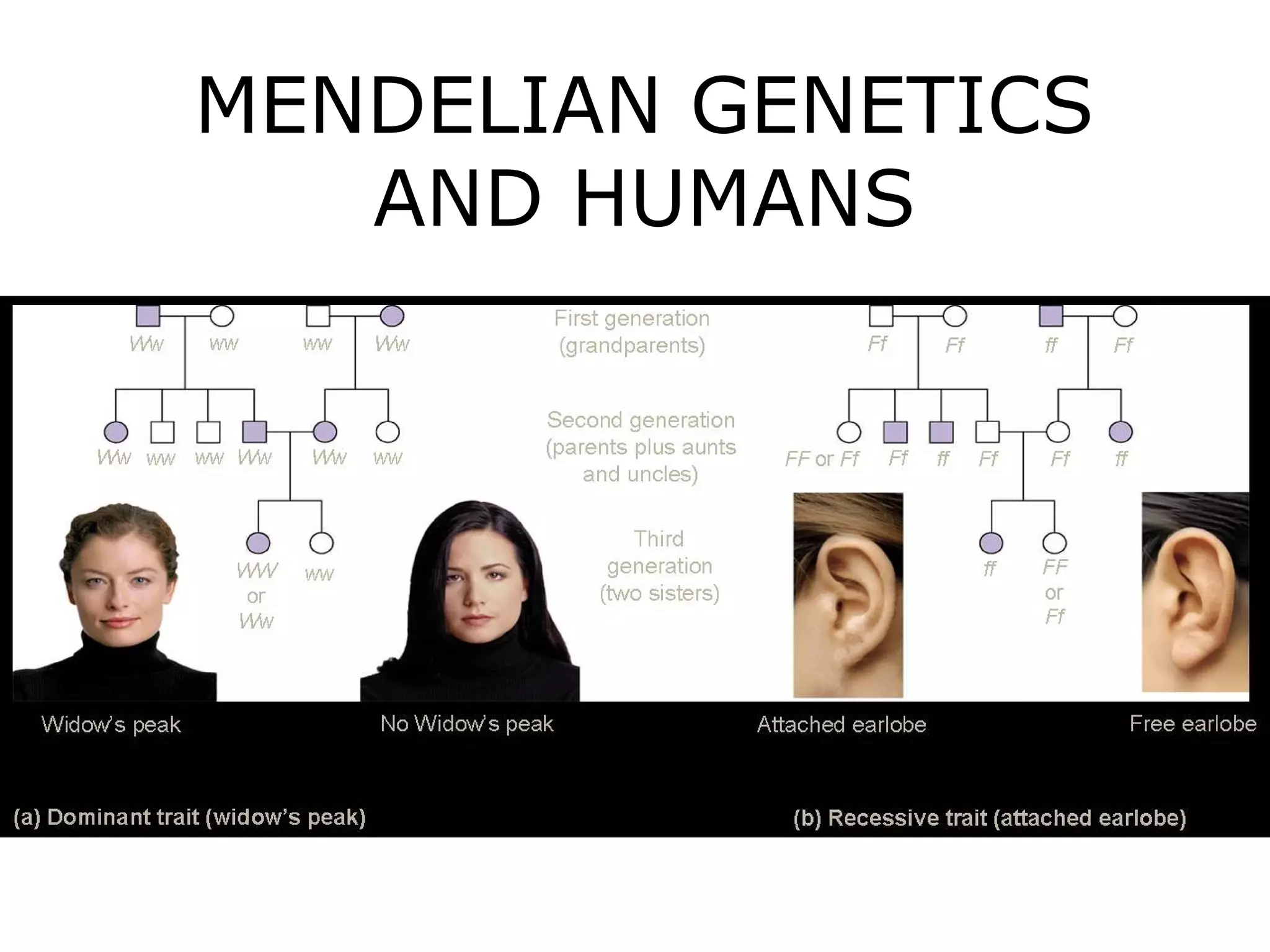
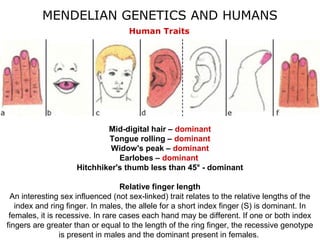
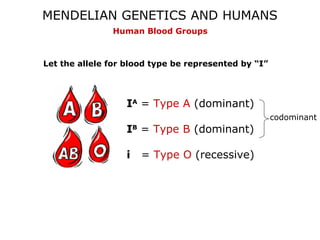
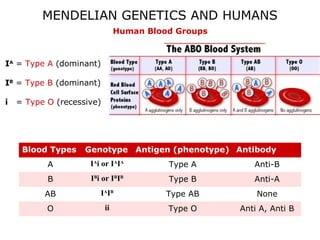
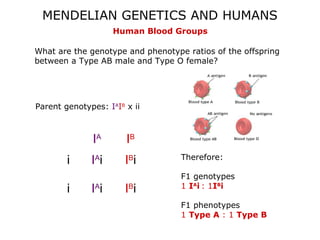
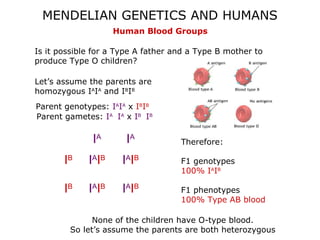
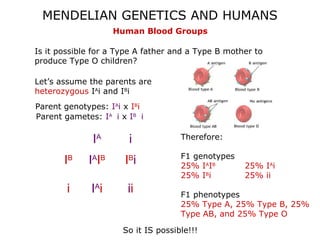
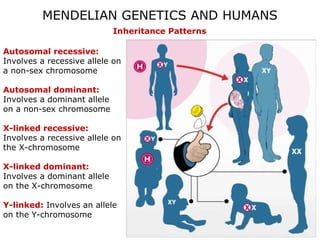
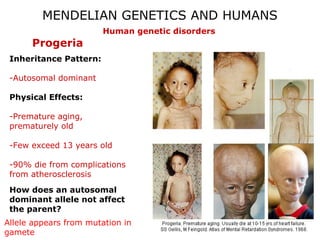
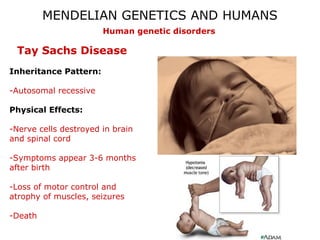
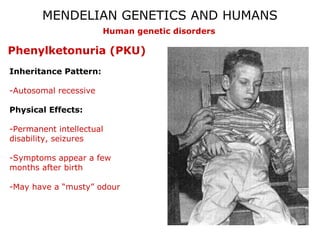
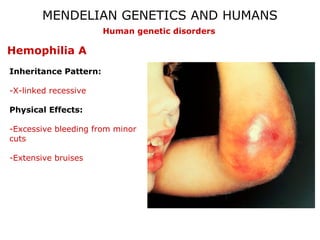
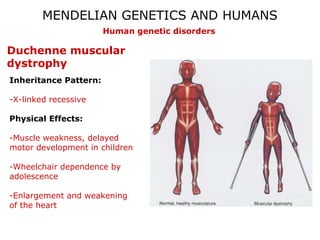
This document discusses Mendelian genetics patterns in humans. It provides examples of dominant and recessive traits for things like earlobes, finger length, and blood types. The document also examines several human genetic disorders and their inheritance patterns, including autosomal dominant disorders like Huntington's disease and progeria, autosomal recessive disorders like Tay-Sachs and PKU, X-linked disorders like hemophilia A and Duchenne muscular dystrophy, and multi-factorial disorders. Examples of physical effects are described for each genetic disorder.