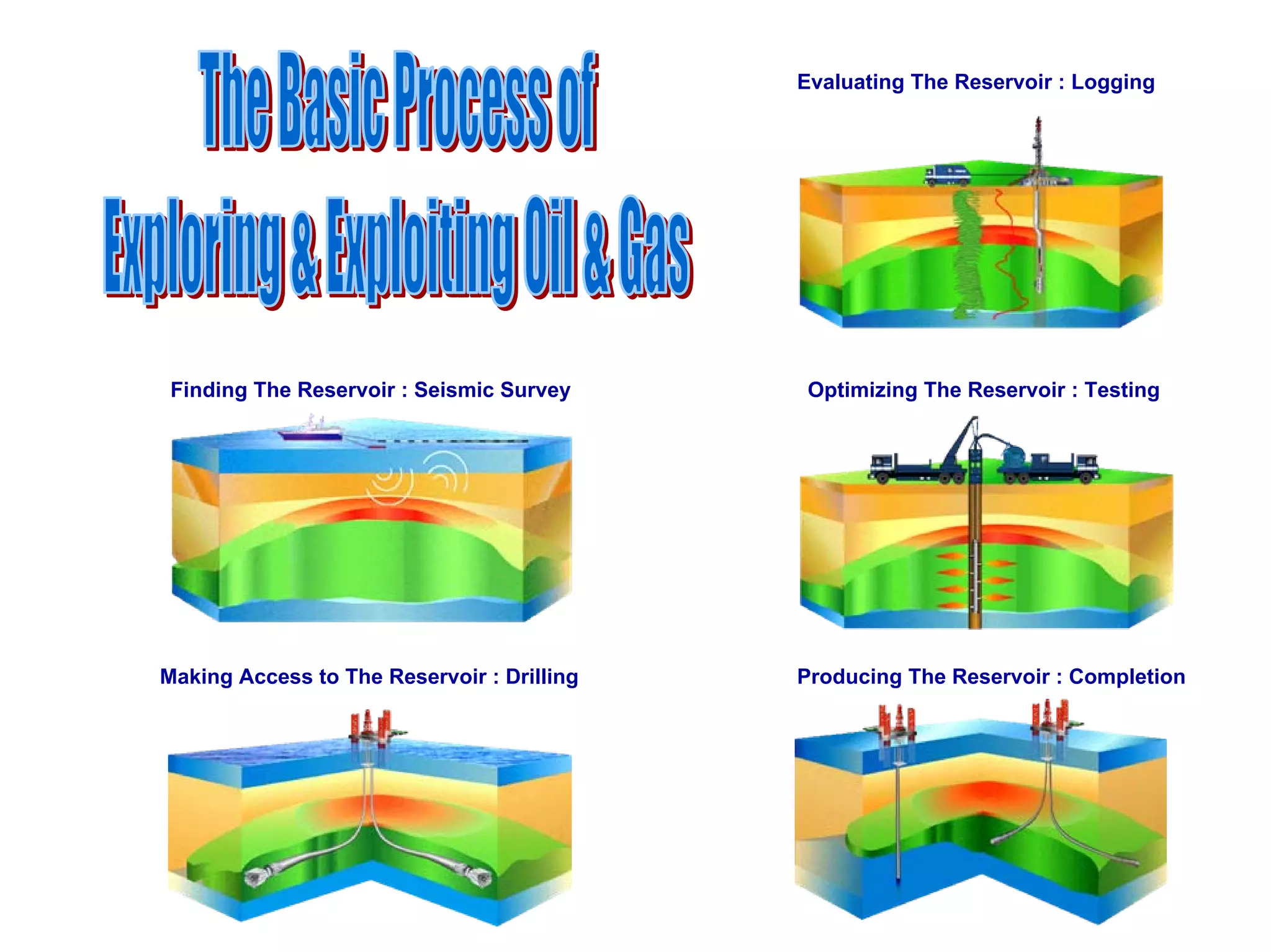
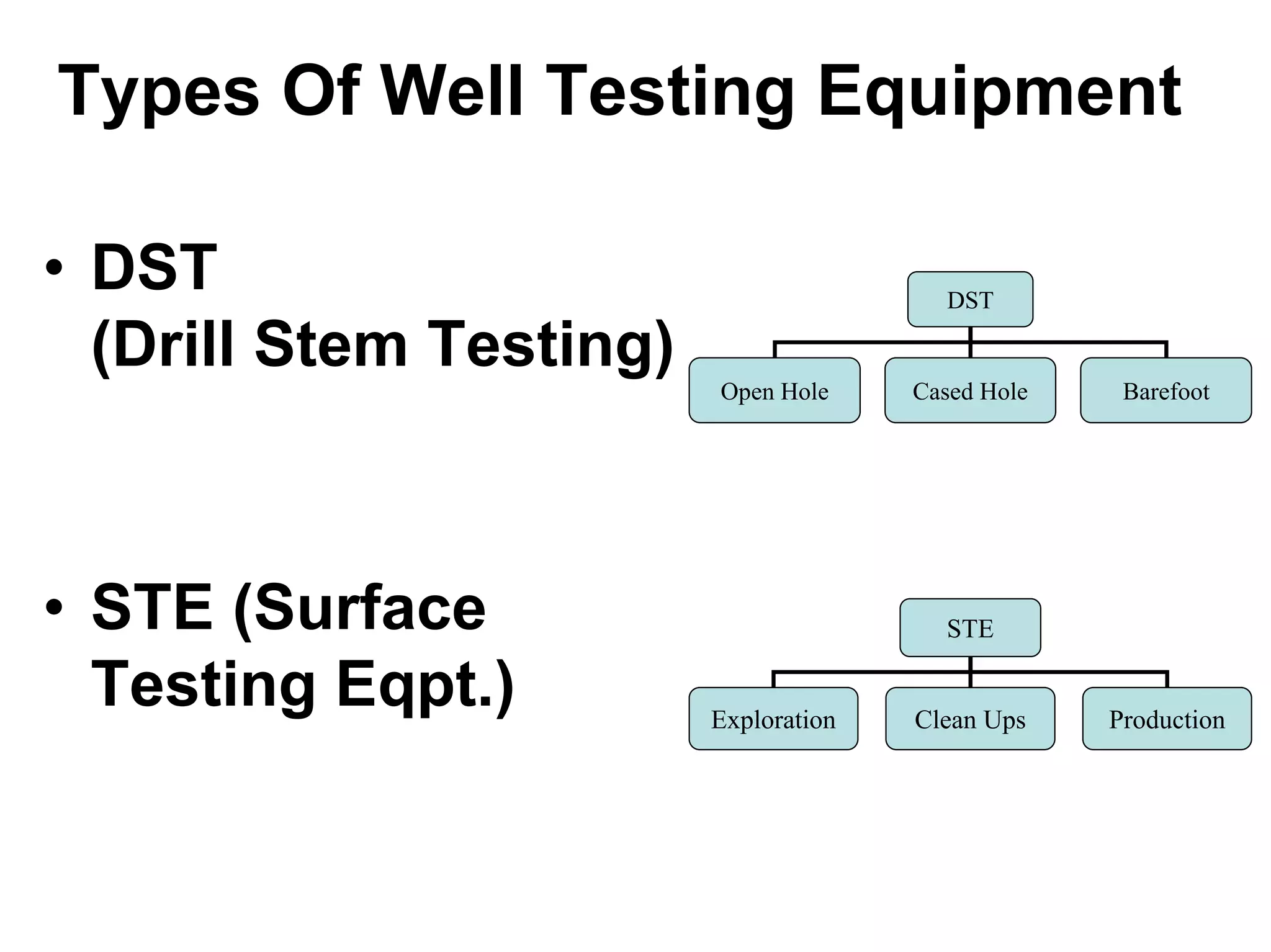
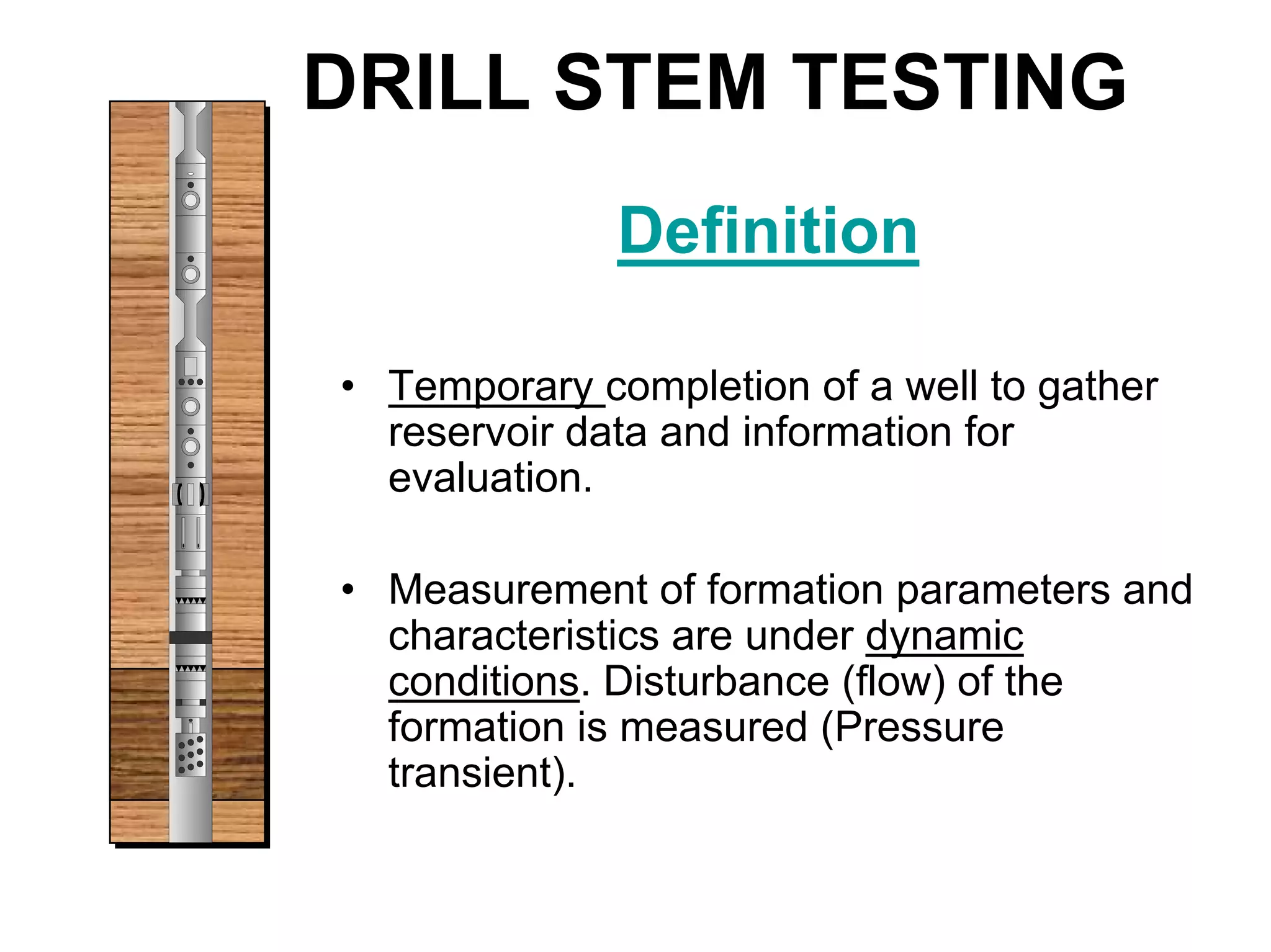
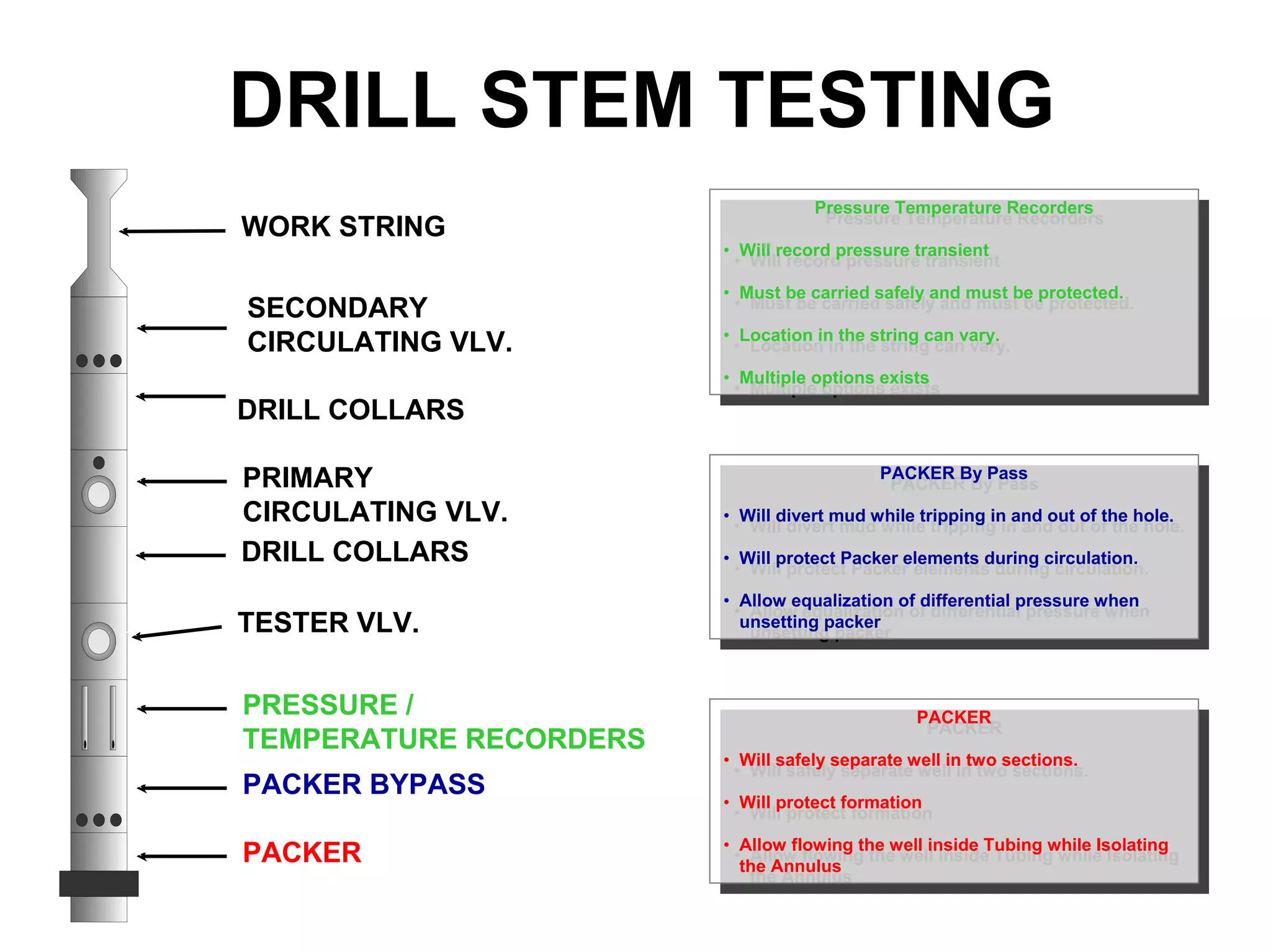
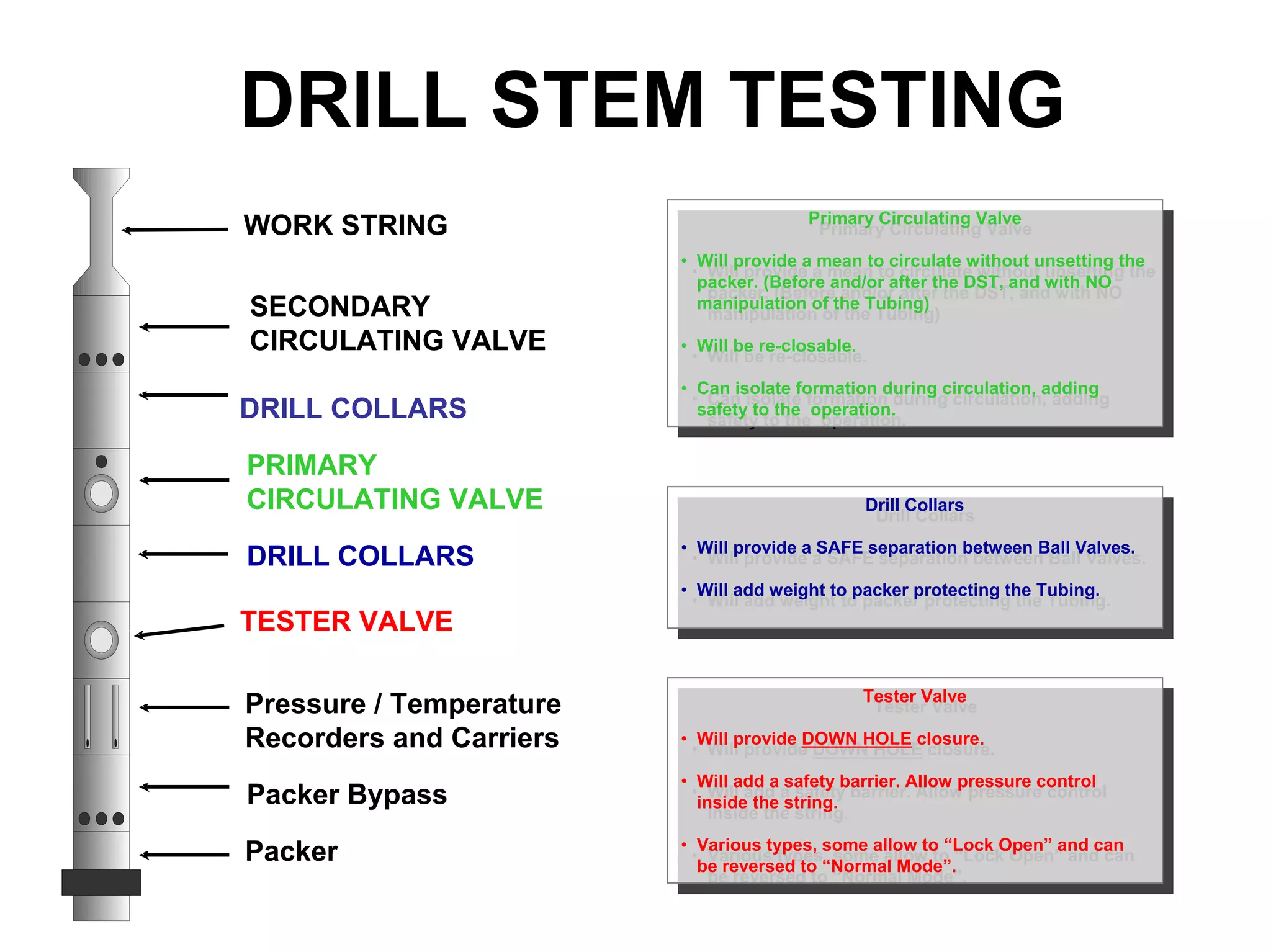
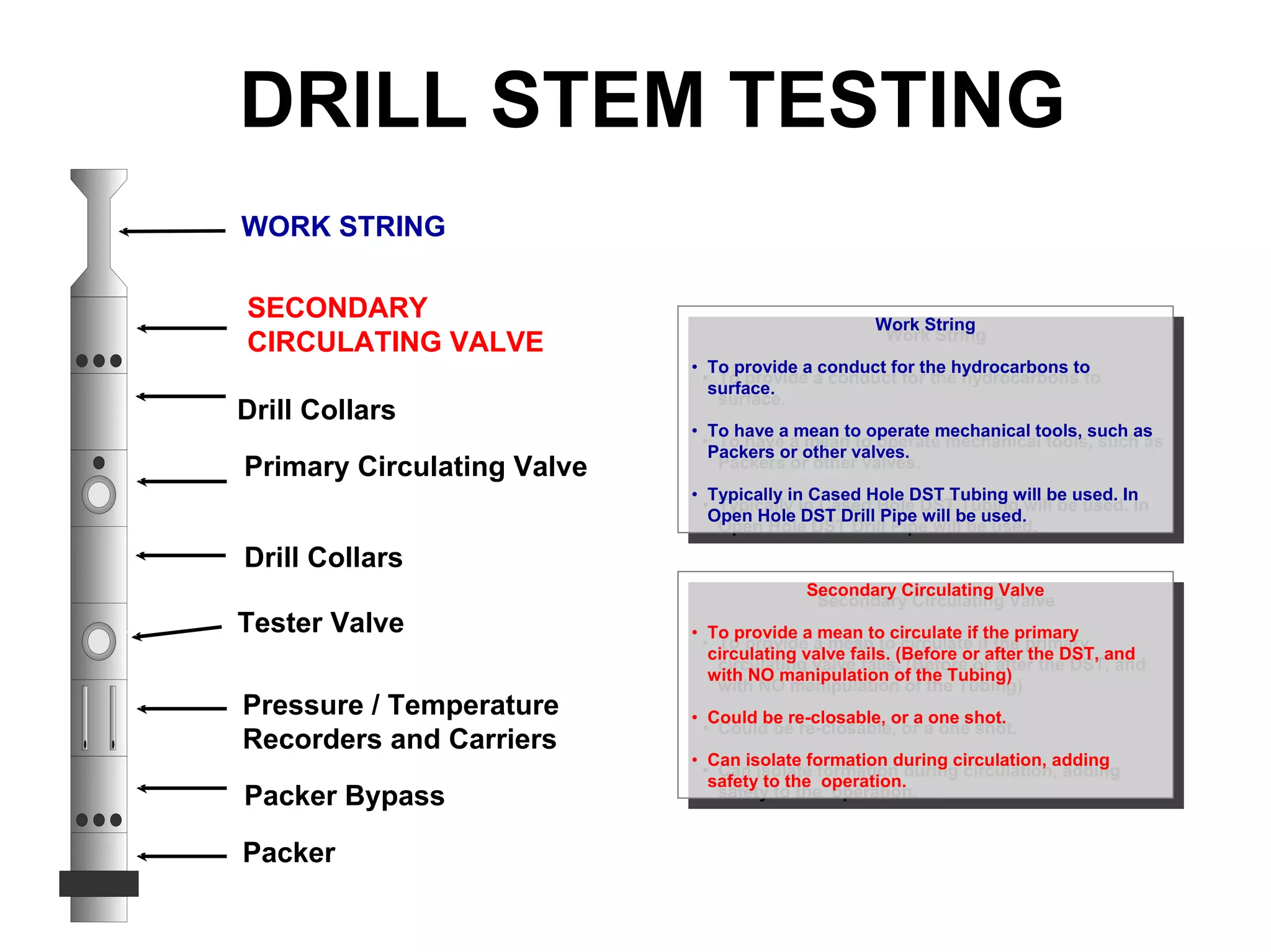
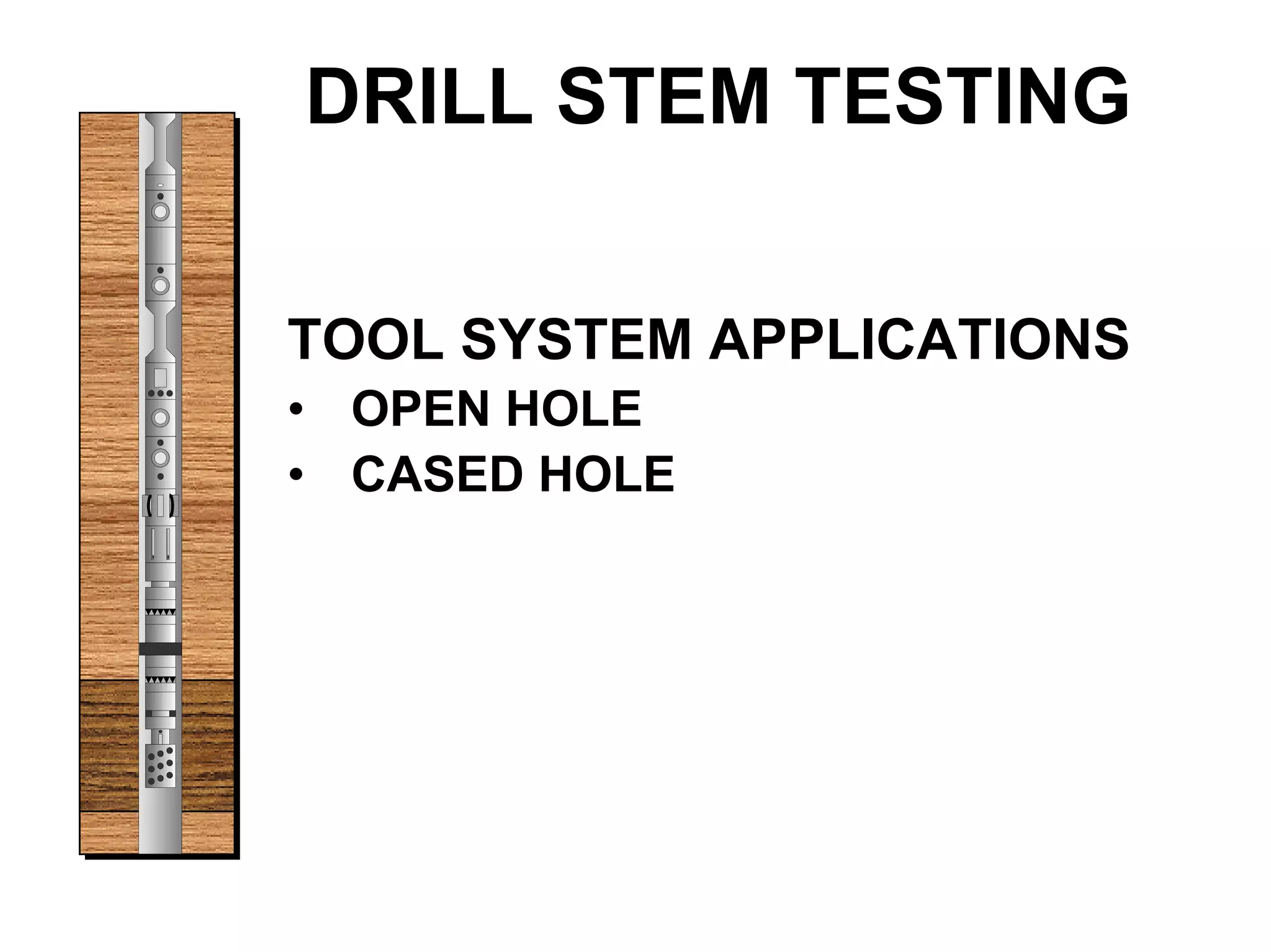
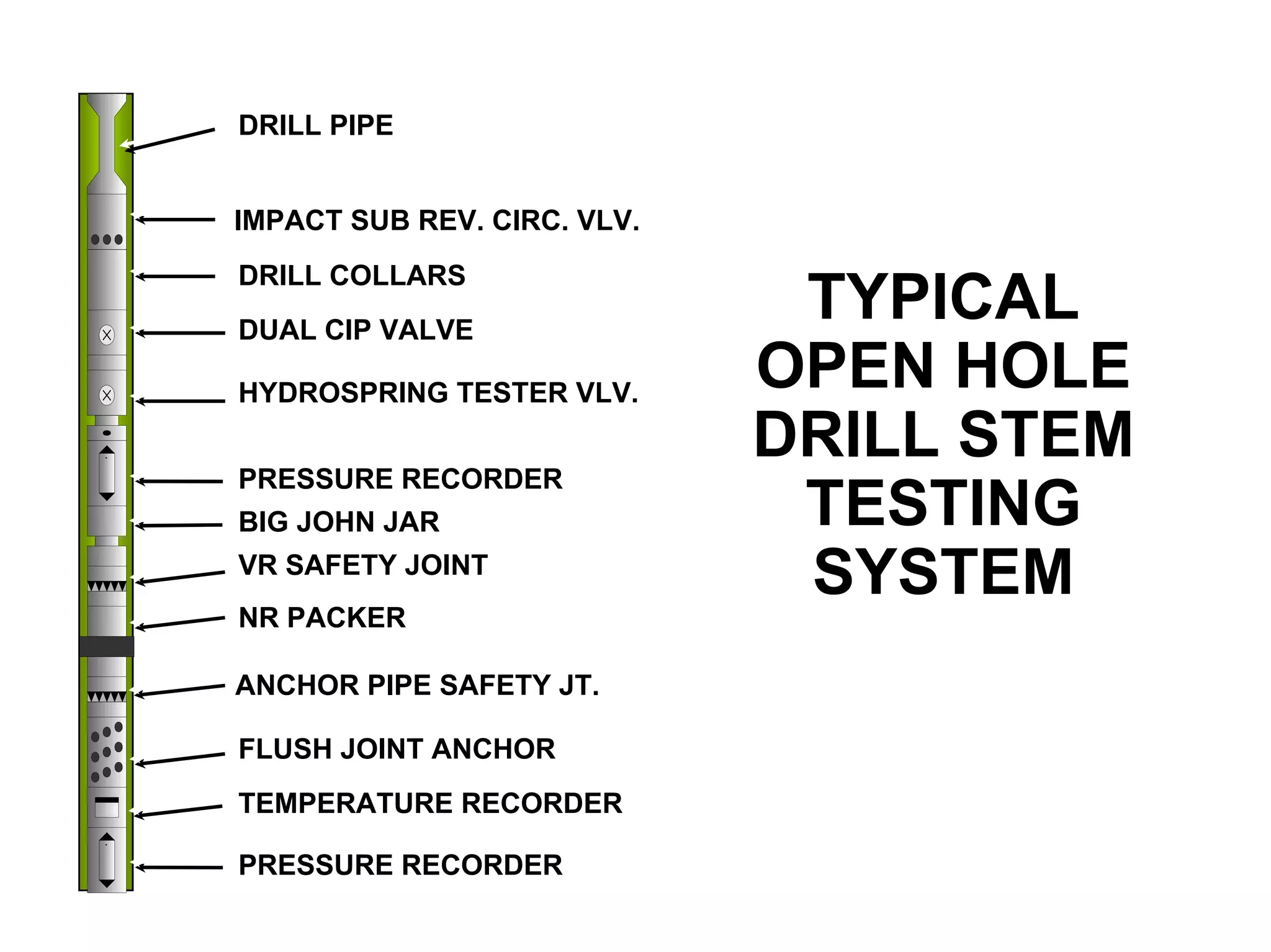
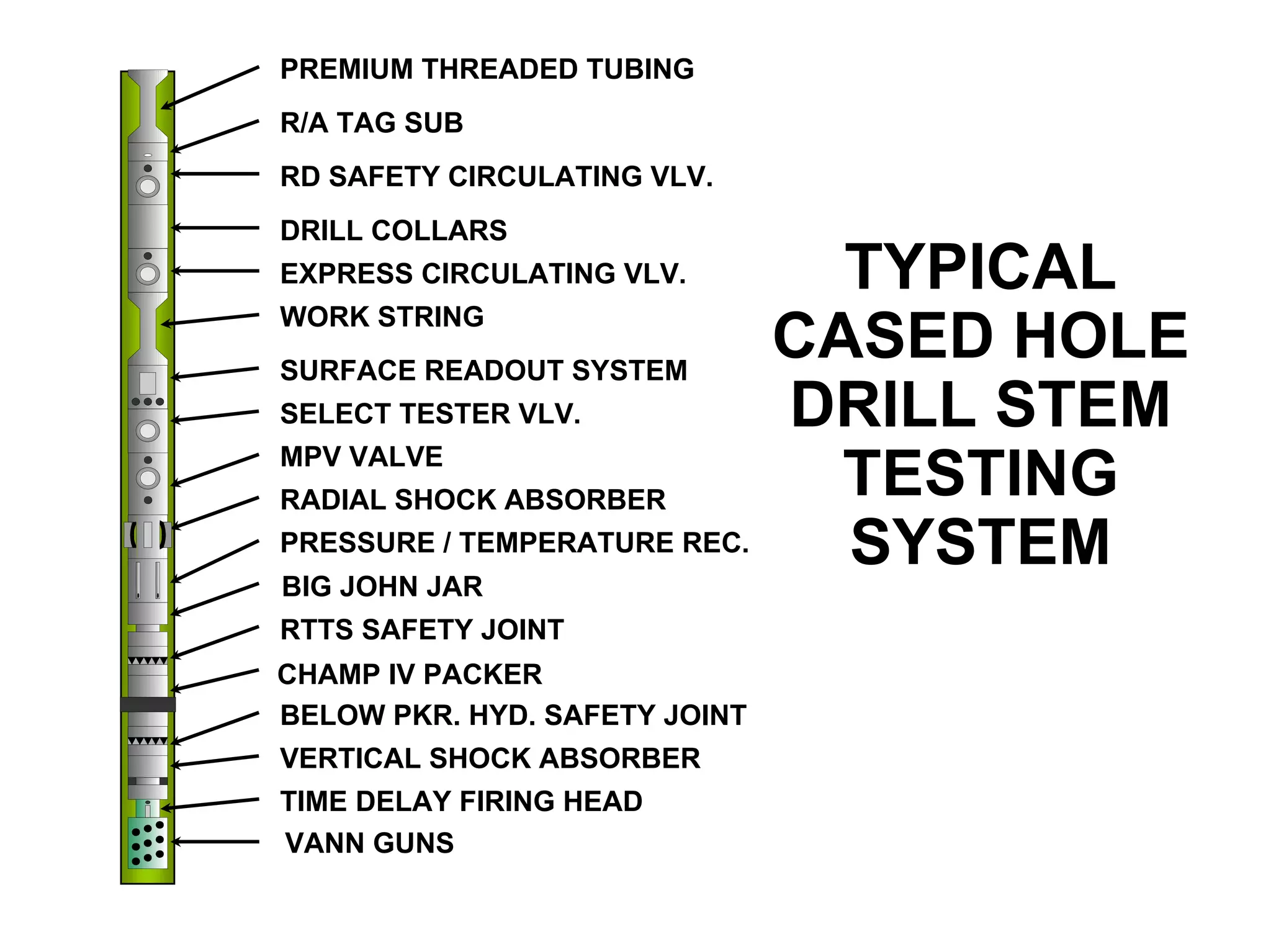
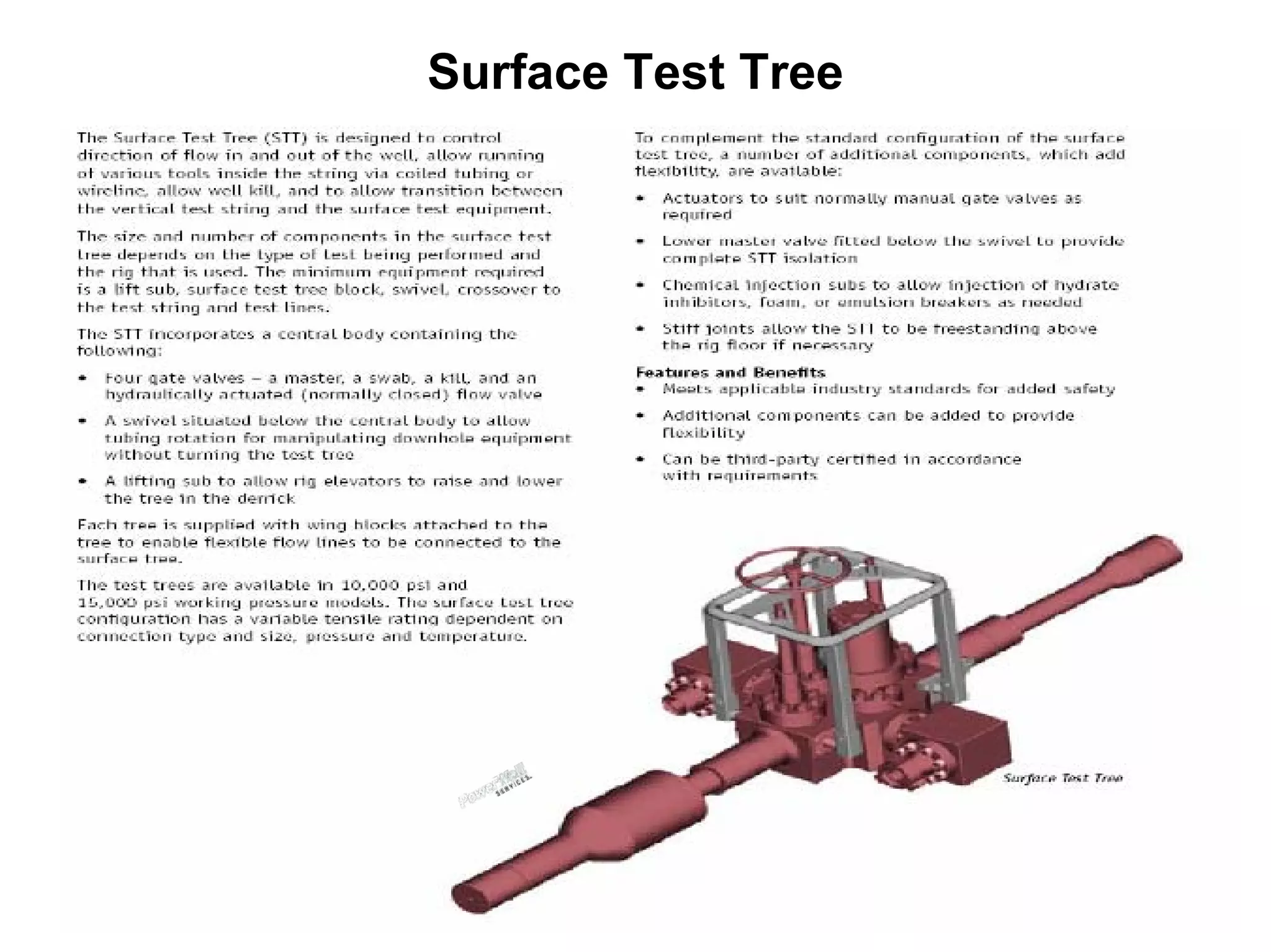
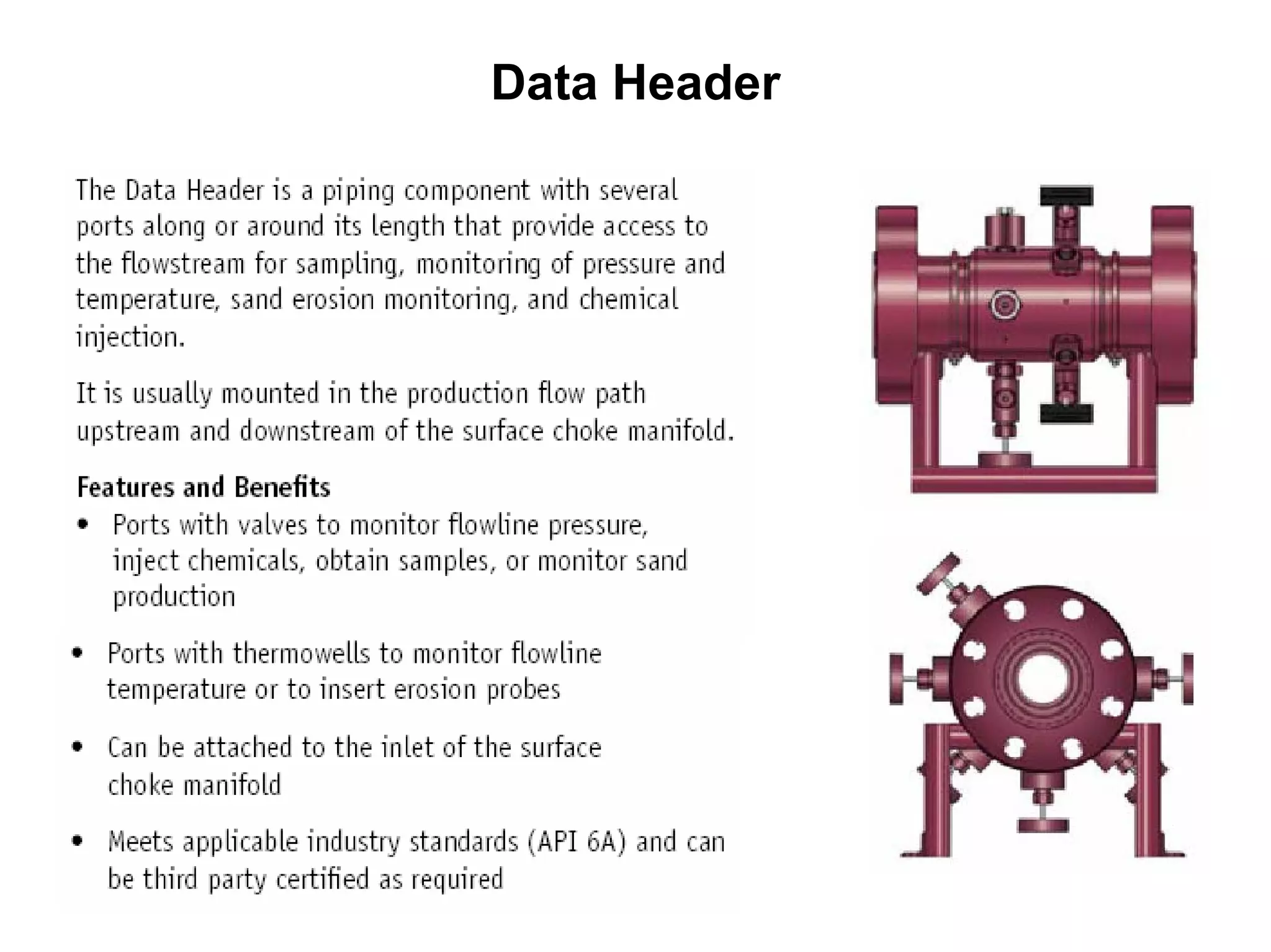
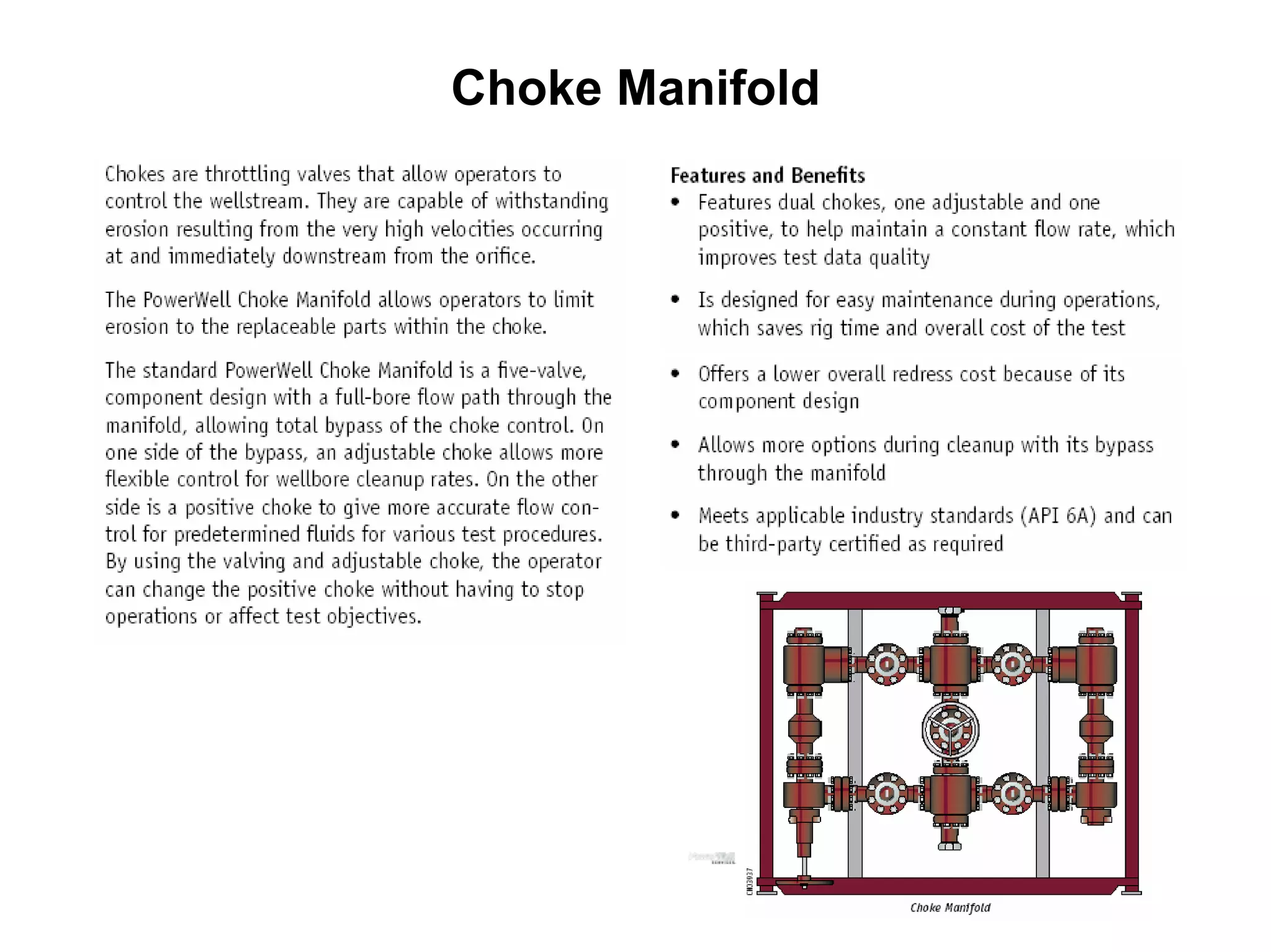
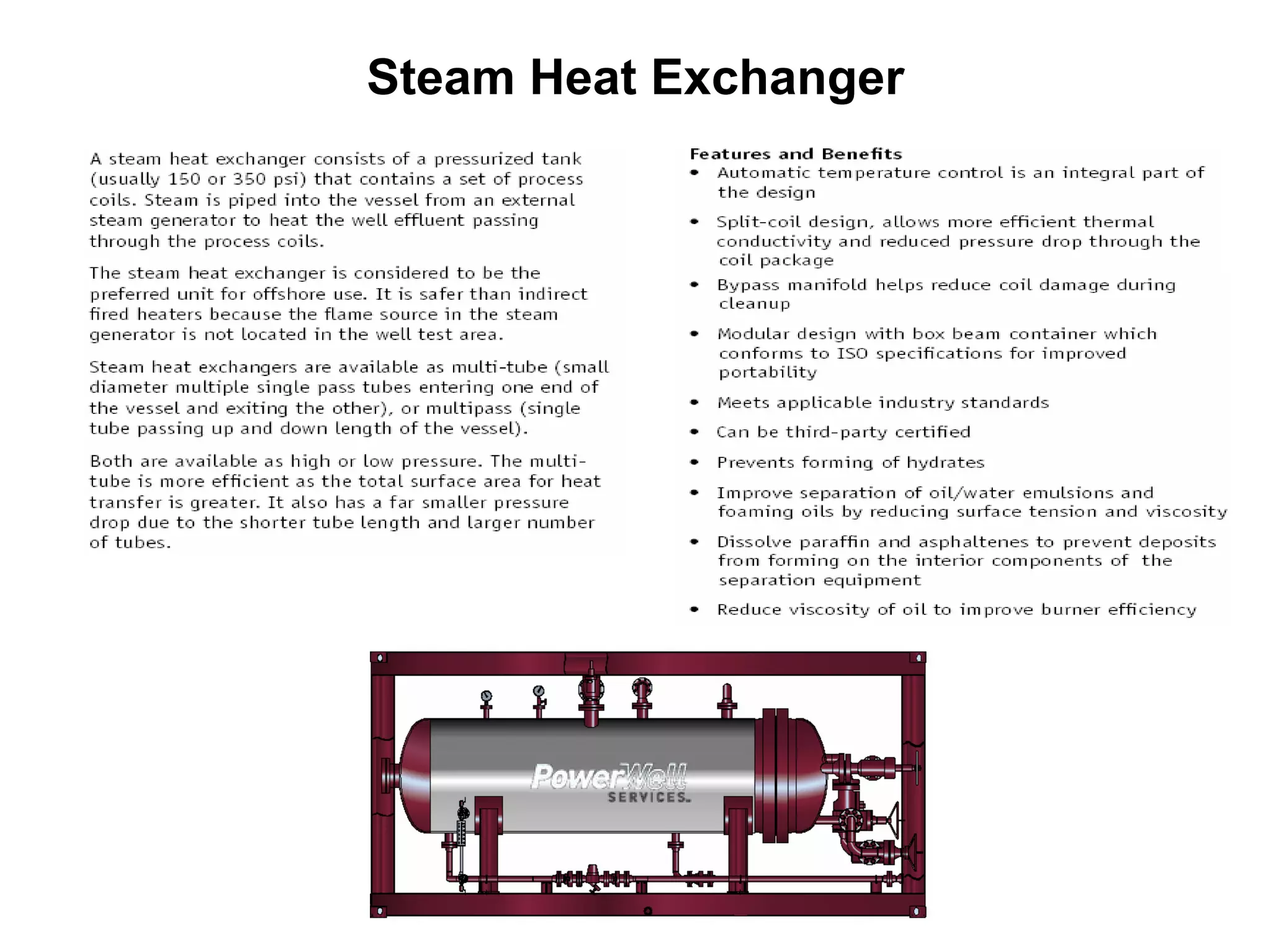
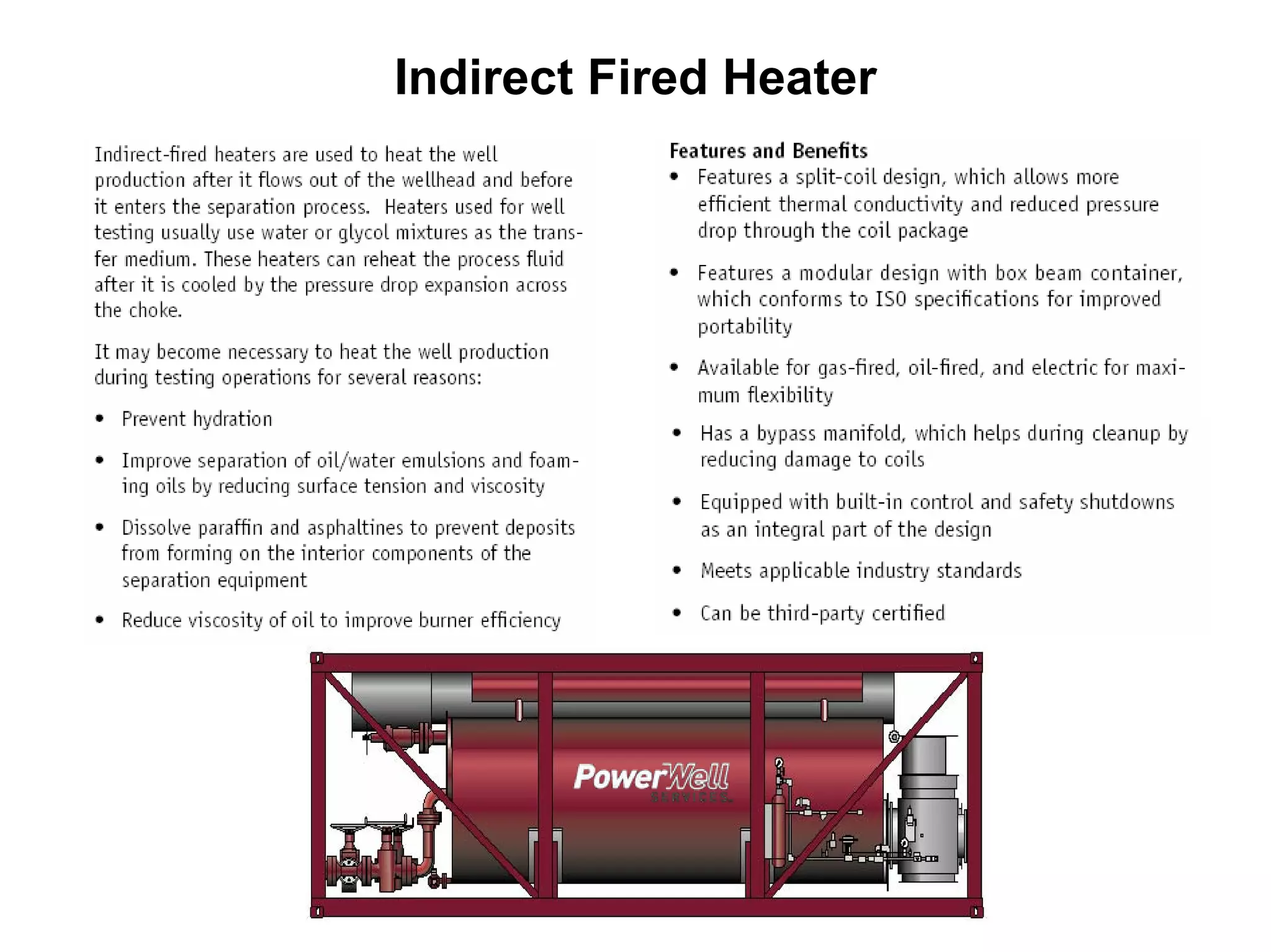
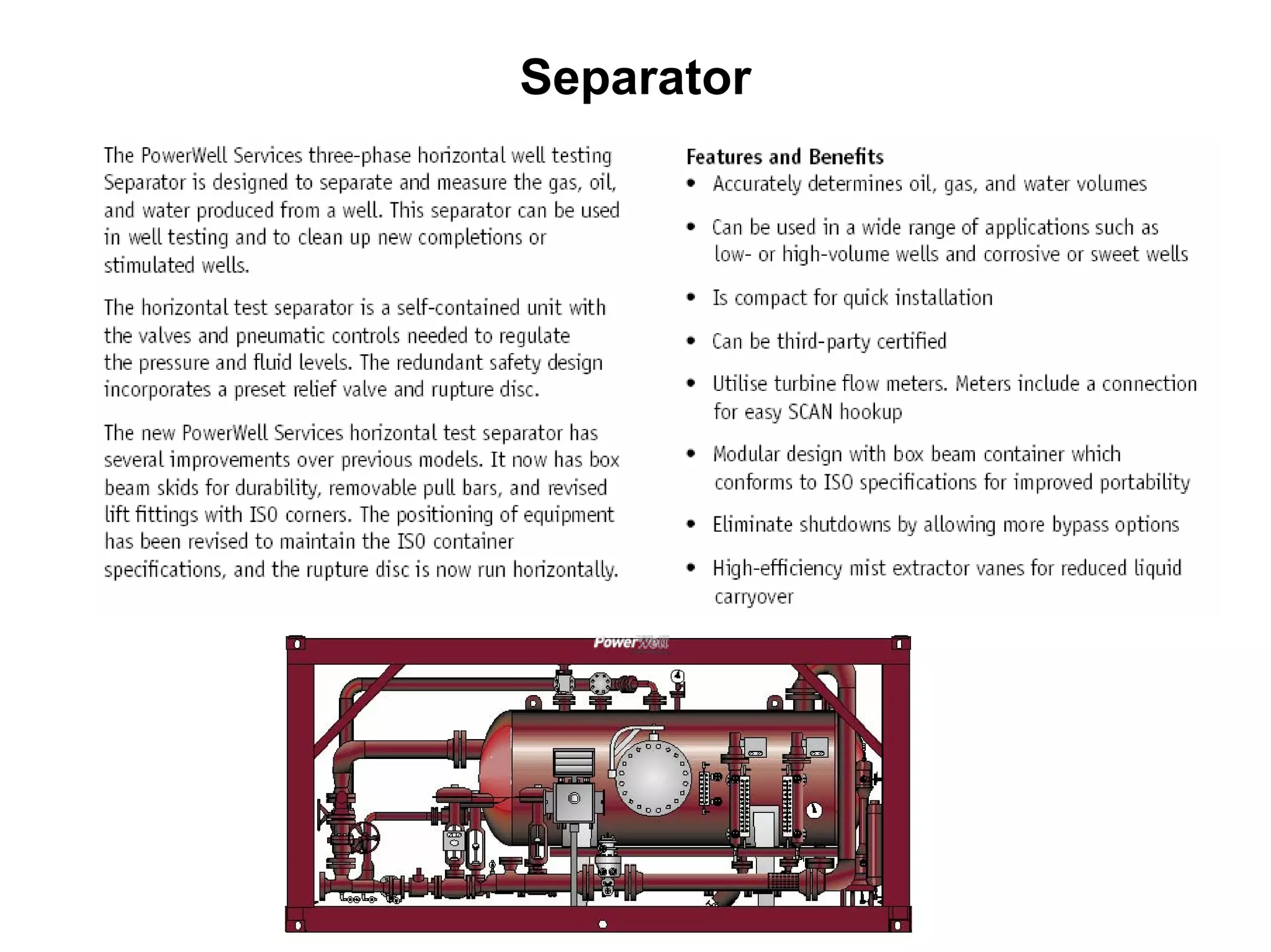
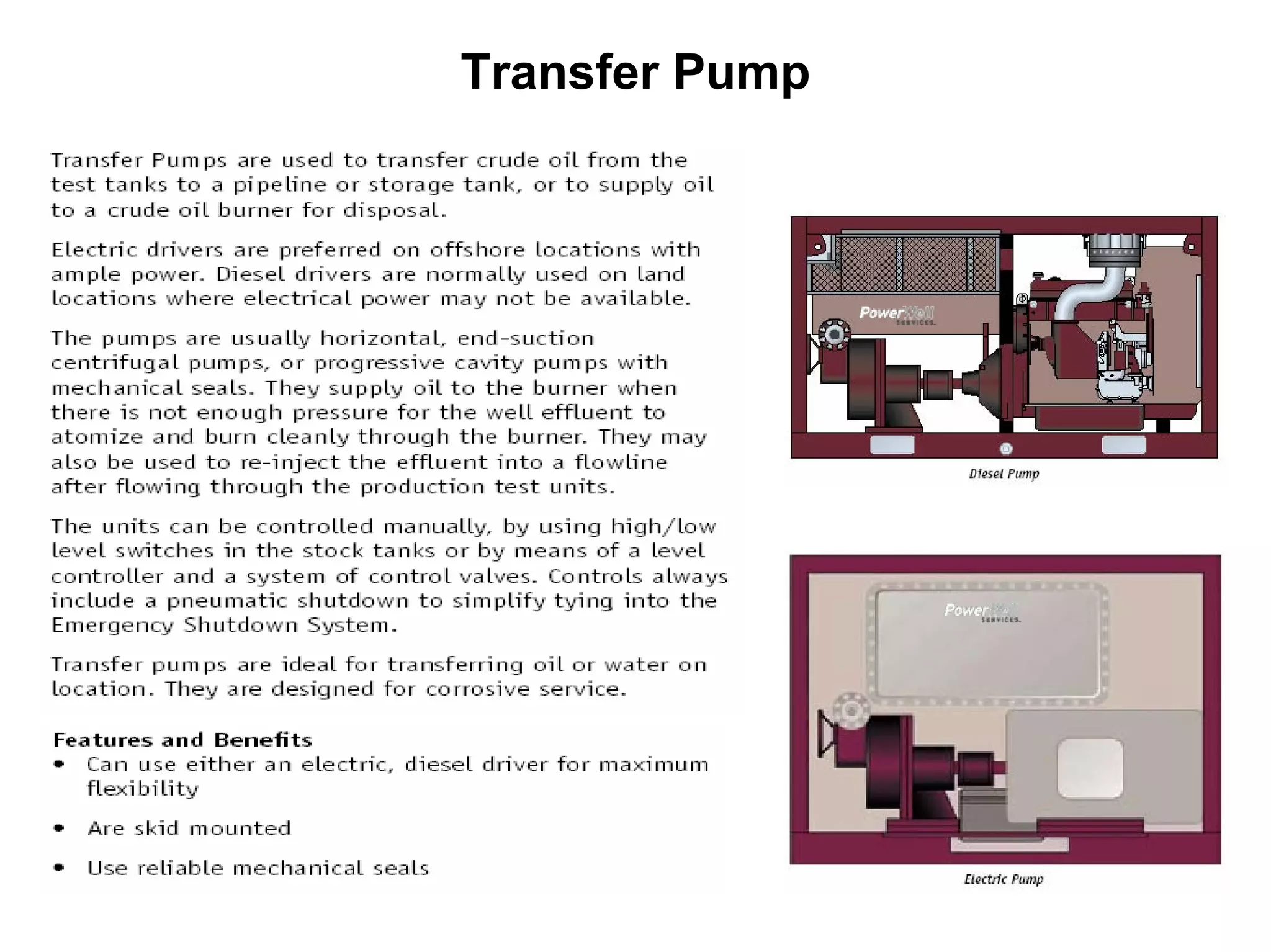
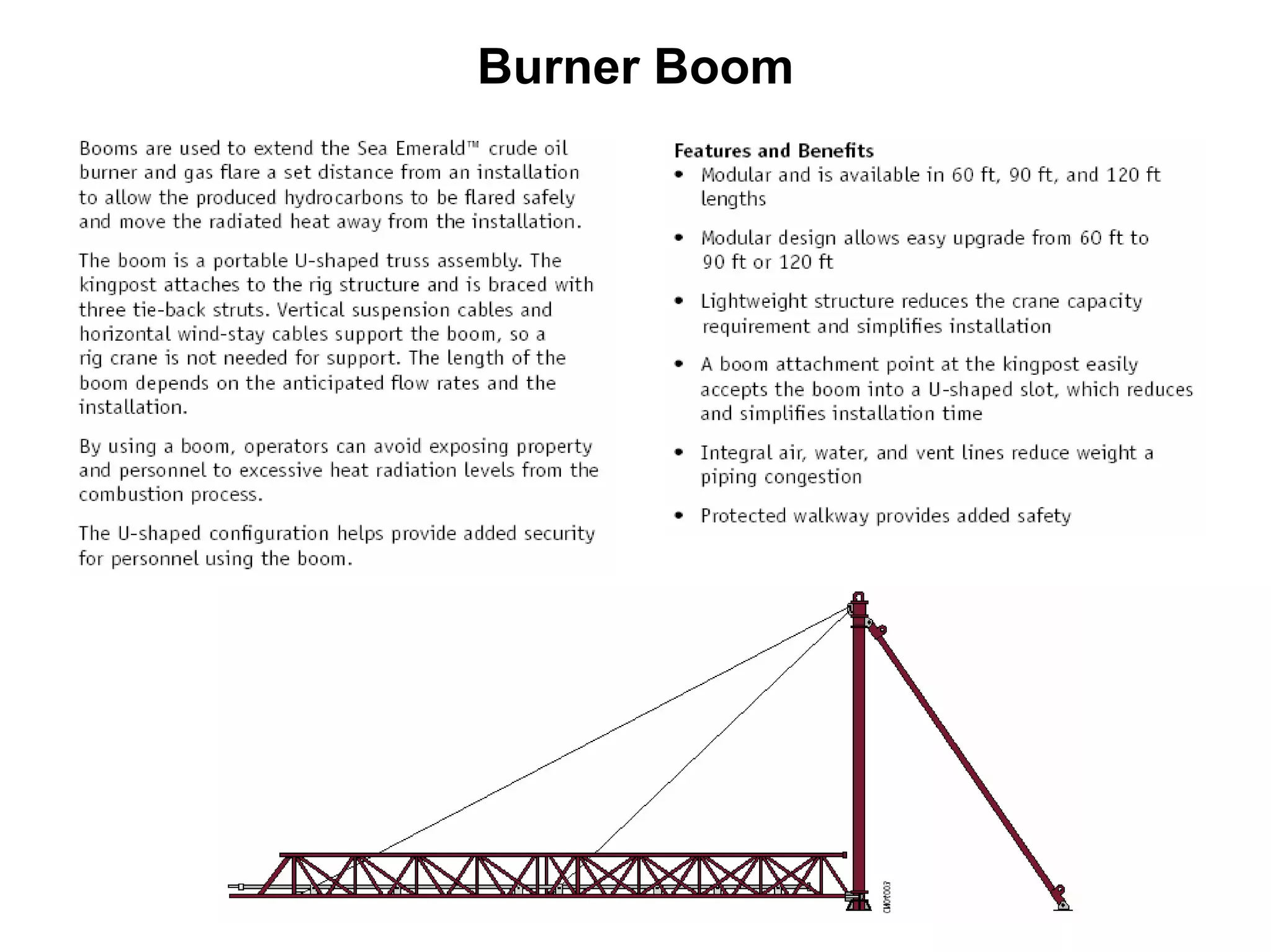
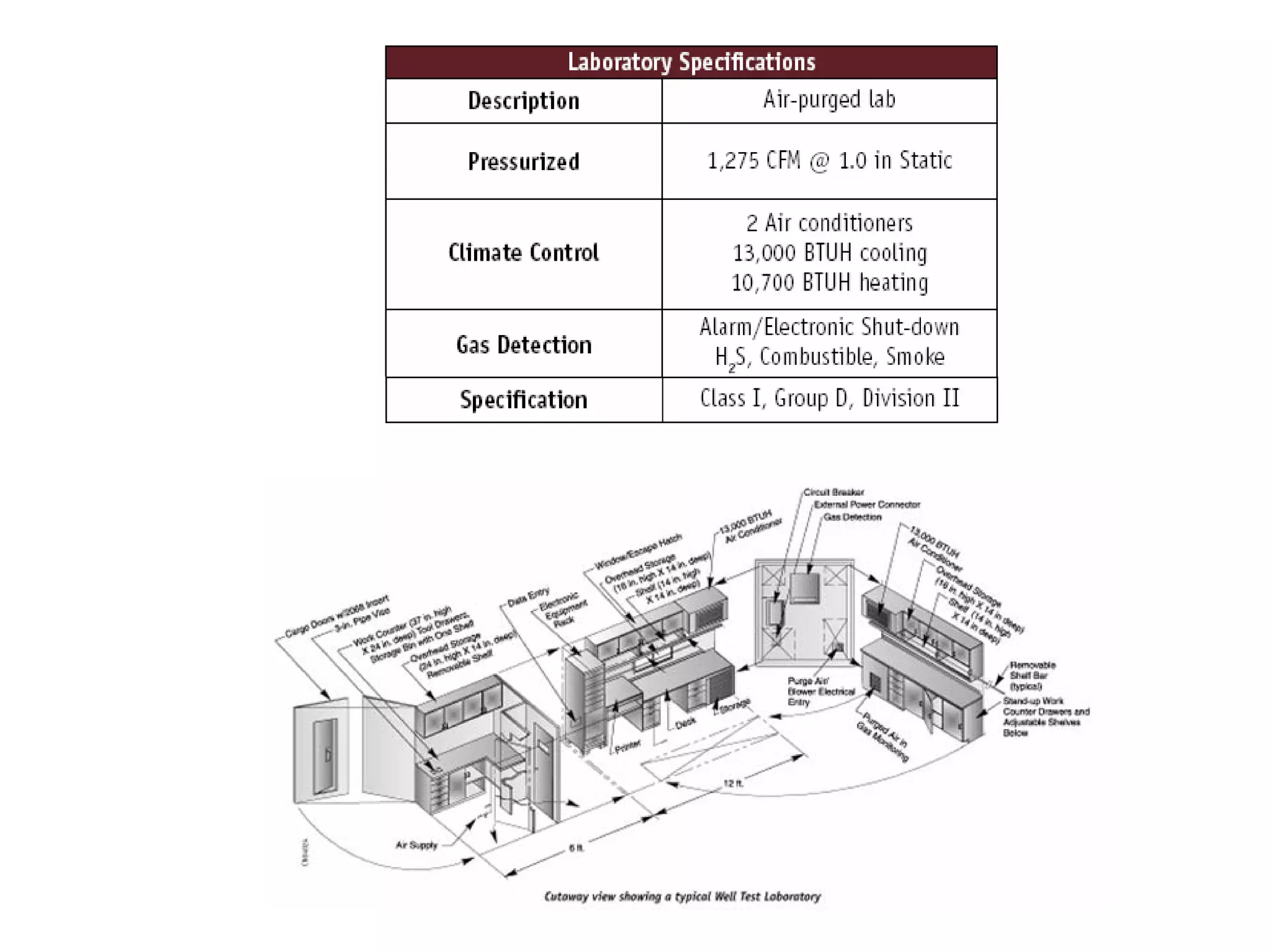
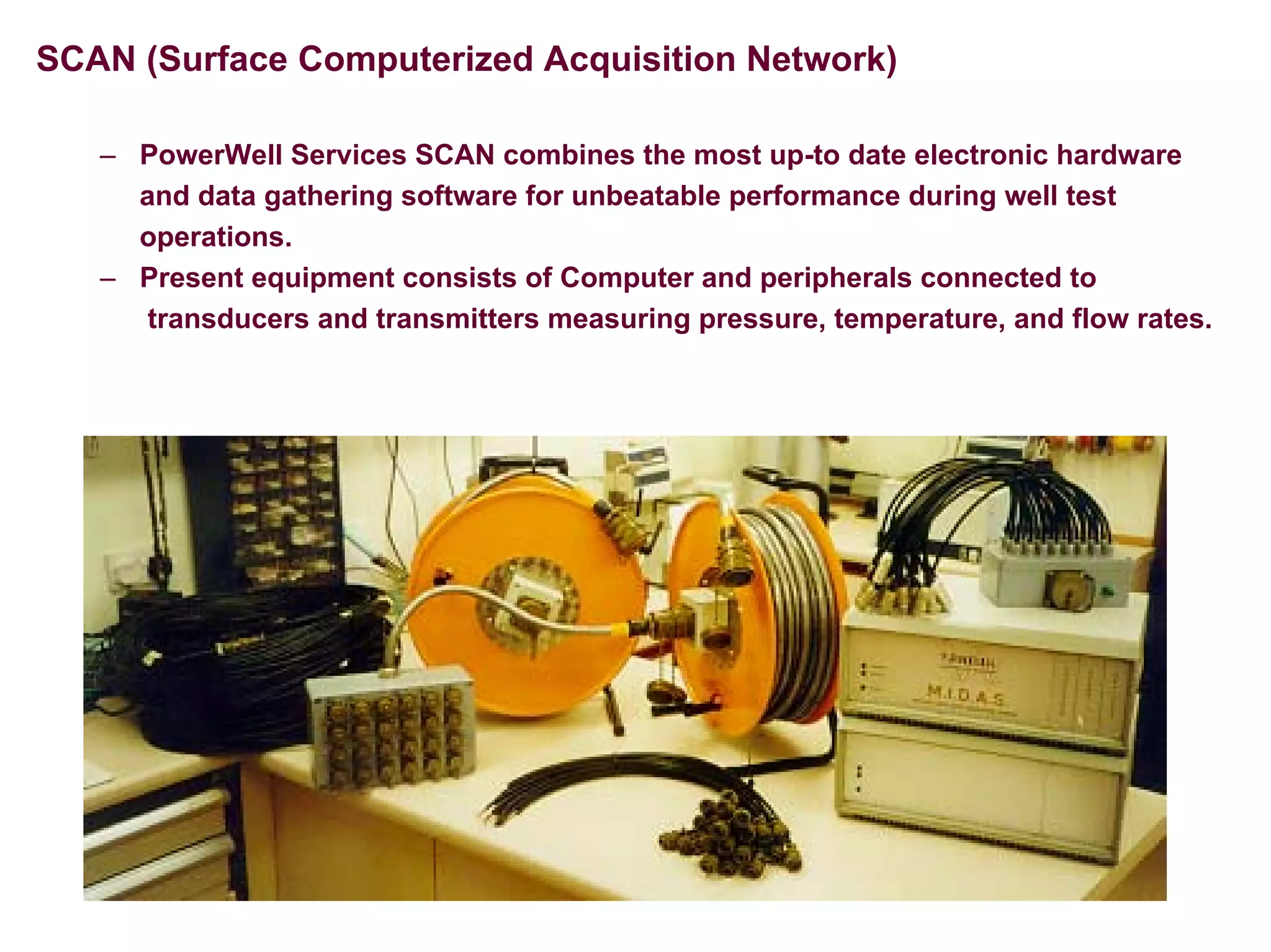
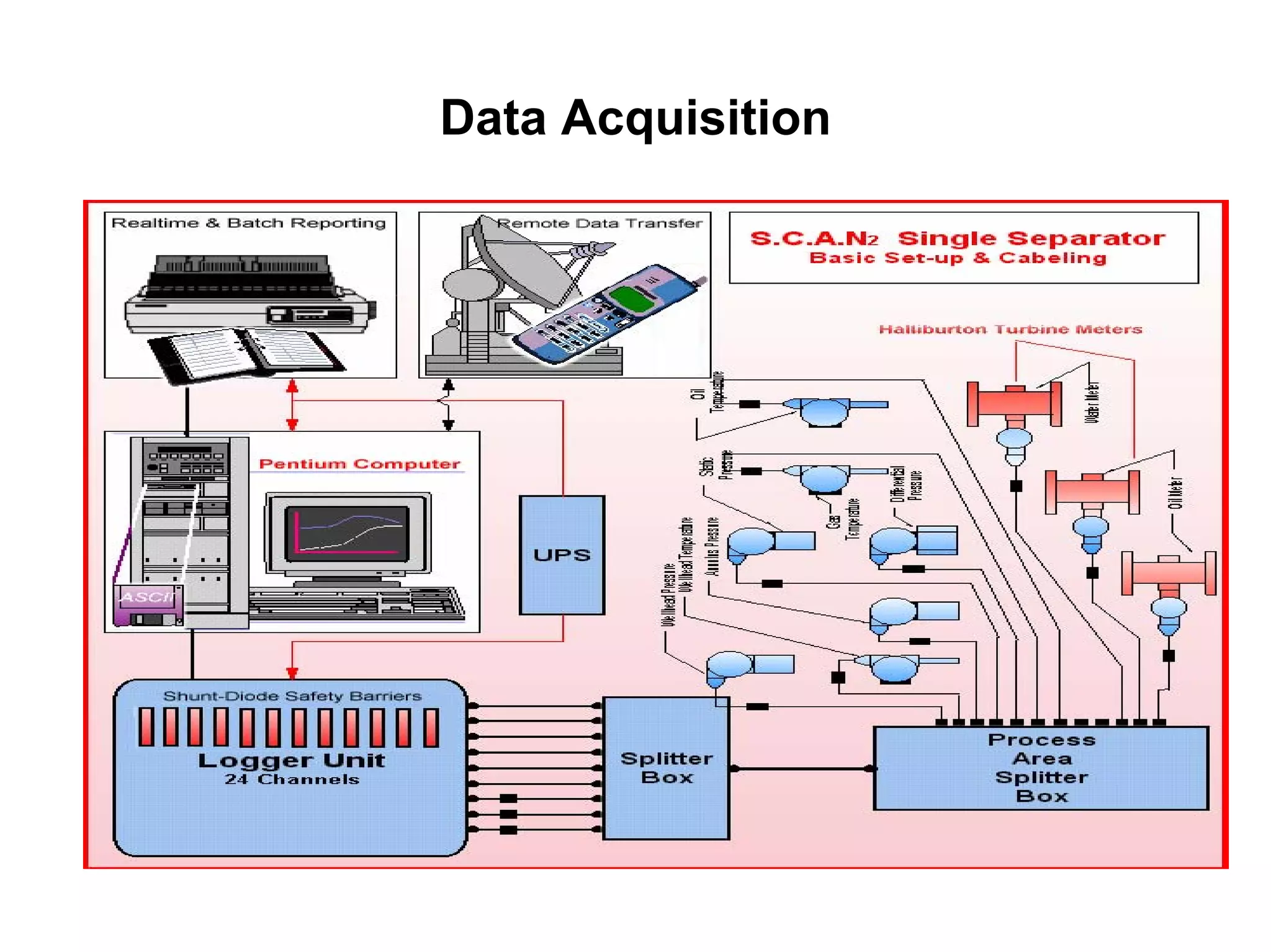
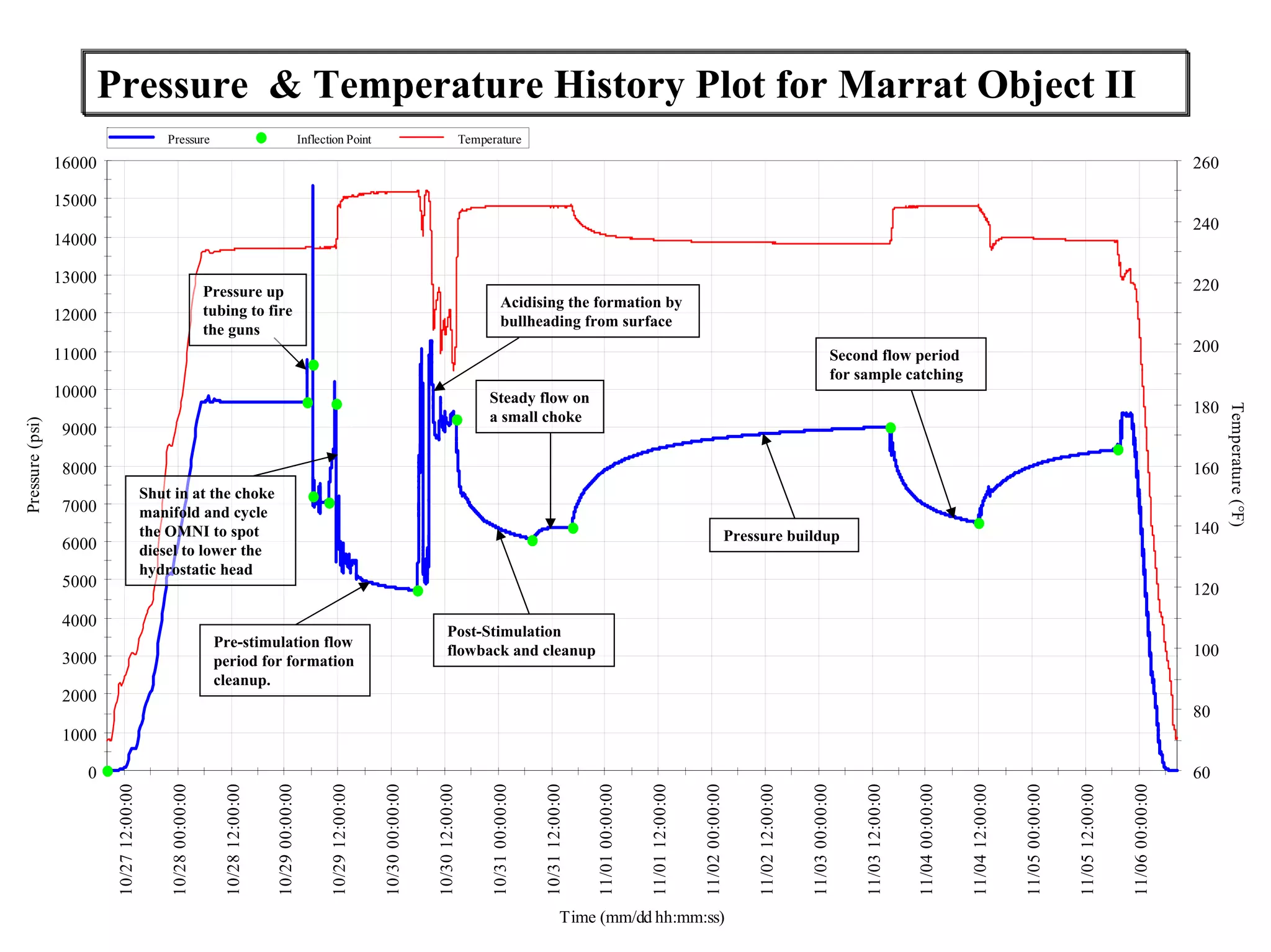
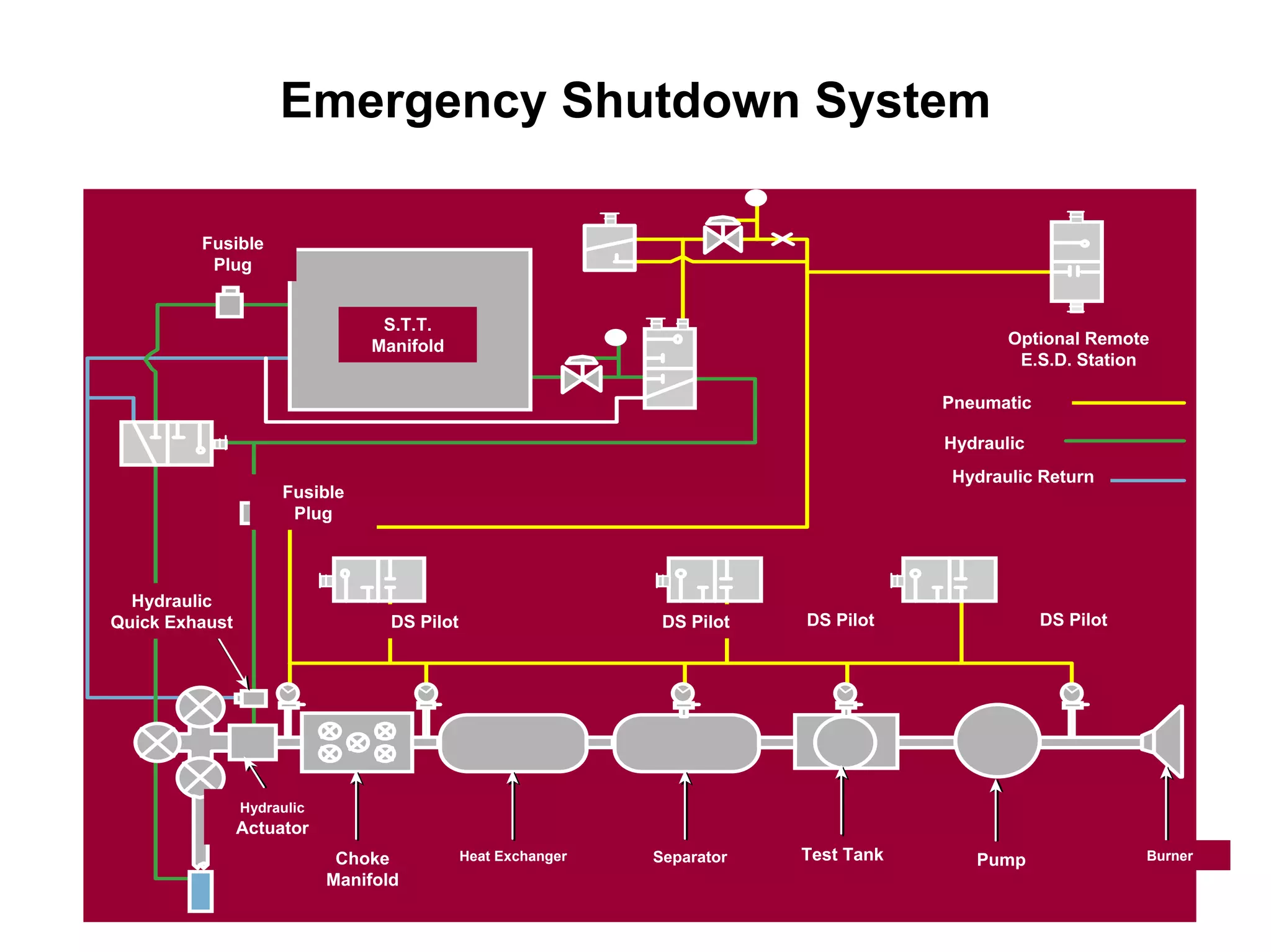
This document provides an overview of well testing equipment and procedures used by Power Well Service Groups and Halliburton to evaluate oil and gas reservoirs. It begins by expressing appreciation for the companies providing well testing presentation materials. It then covers various types of well testing equipment like drill stem testing tools and surface testing packages. The remainder of the document discusses objectives and details of drill stem testing and describes components of typical open hole and cased hole drill stem testing systems. It also covers surface well testing facilities, data acquisition systems, reporting formats, and emergency shutdown systems.