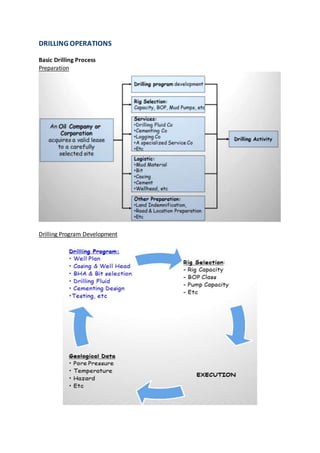
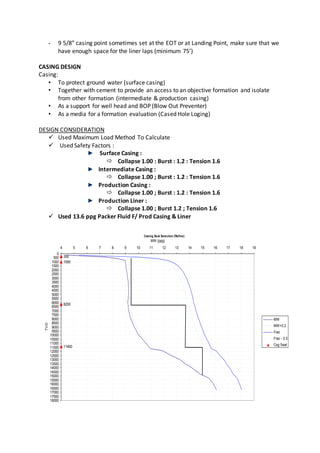
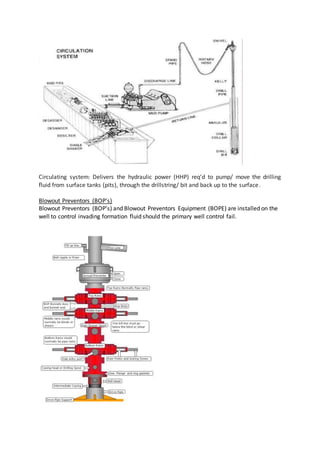
The document discusses drilling operations including directional drilling, casing design, and bottom hole assembly components. Directional drilling involves deviating wellbores from vertical to intersect targets. Key directional drilling types include "J", "S", and slant wells. Casing is designed and set at depths to isolate formations and support wellheads. Bottom hole assemblies use drill pipe, heavy drill pipe, drill collars, and bits to transfer rotation and weight to drill the well.