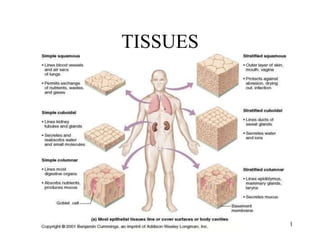
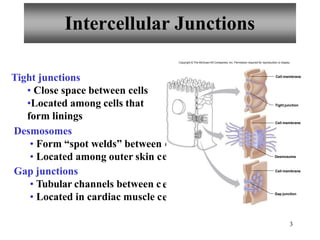
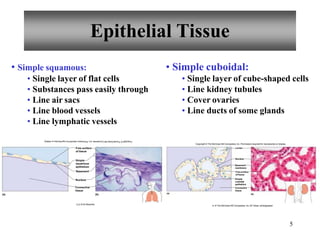
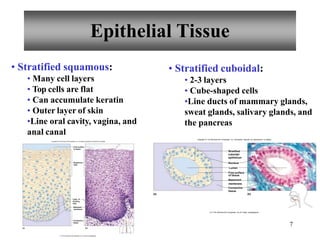
The document summarizes the four primary tissue types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. It provides detailed descriptions of each type including their functions, major cells, and classifications. For epithelial tissue, it describes the different shapes of epithelial cells and how they are classified. It also discusses glandular epithelial tissue and the two main types of glands.