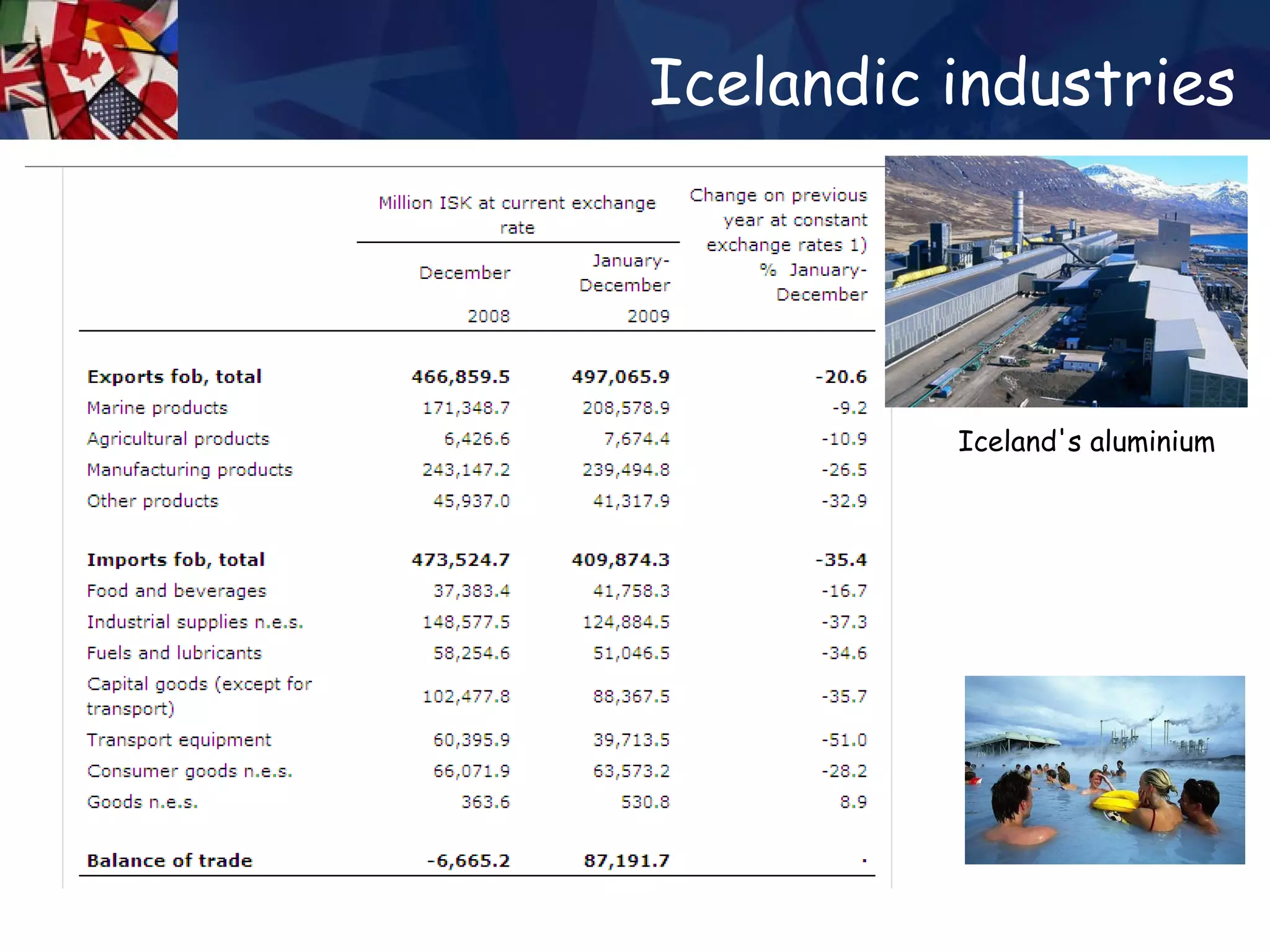
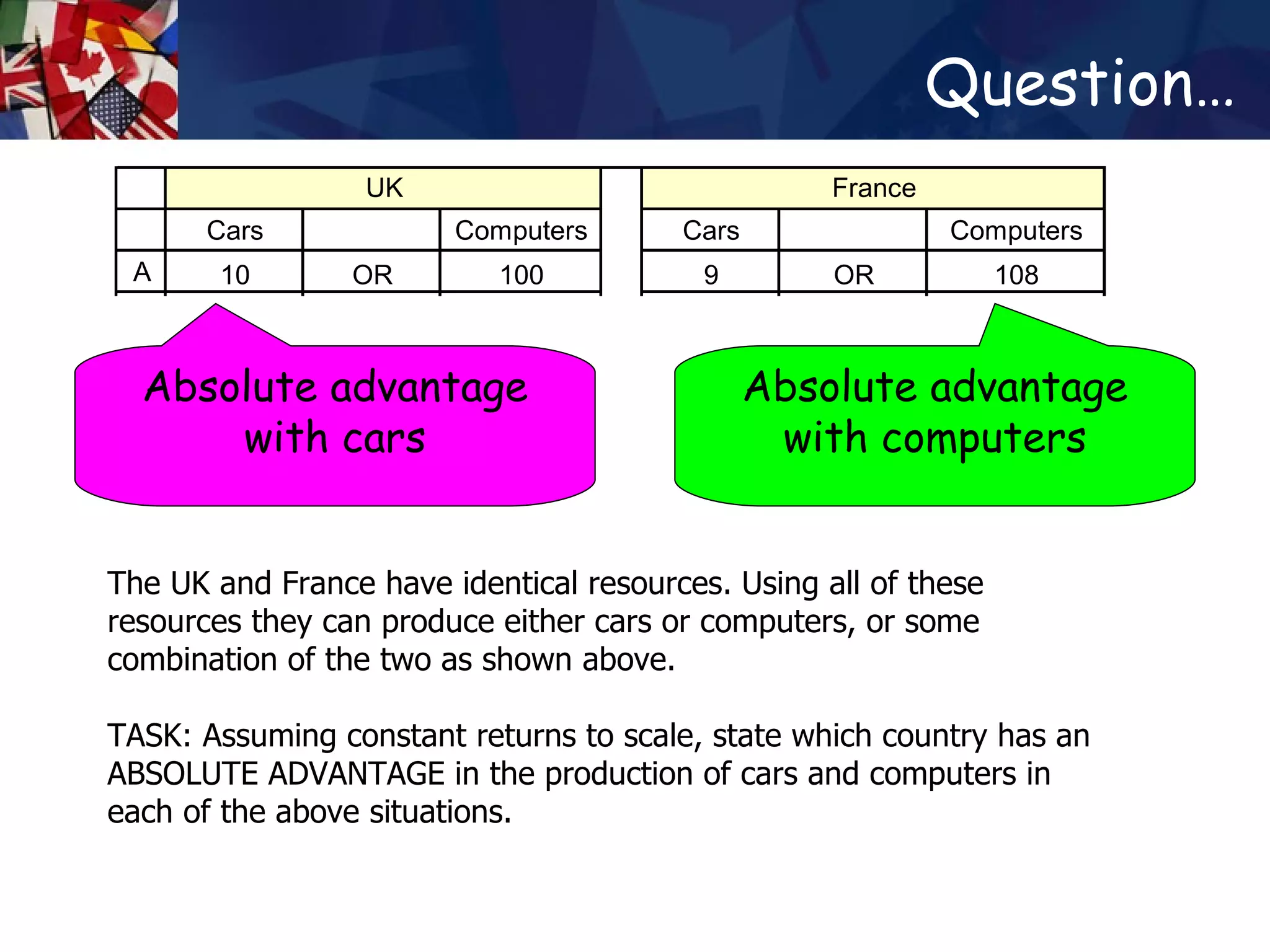
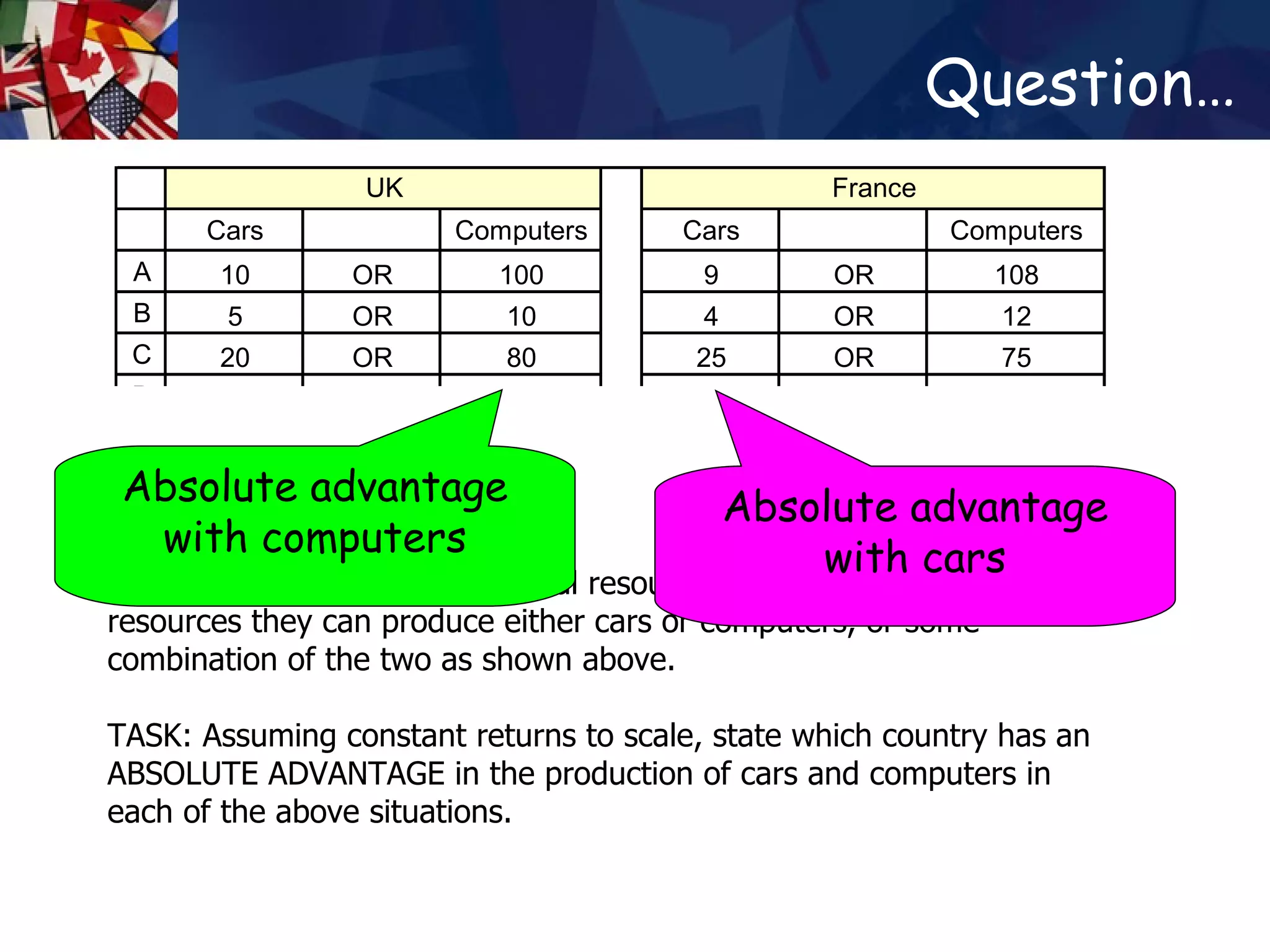
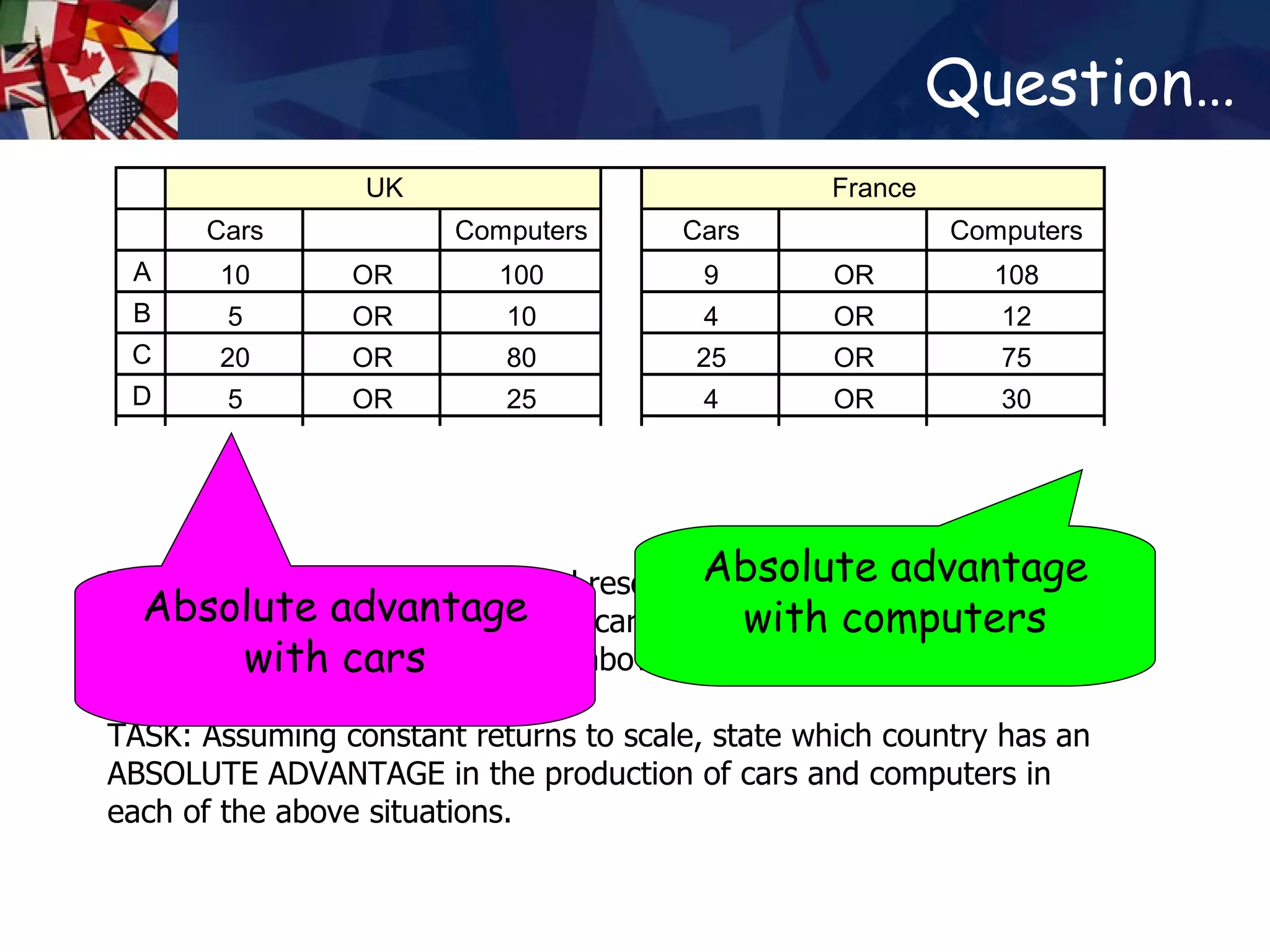
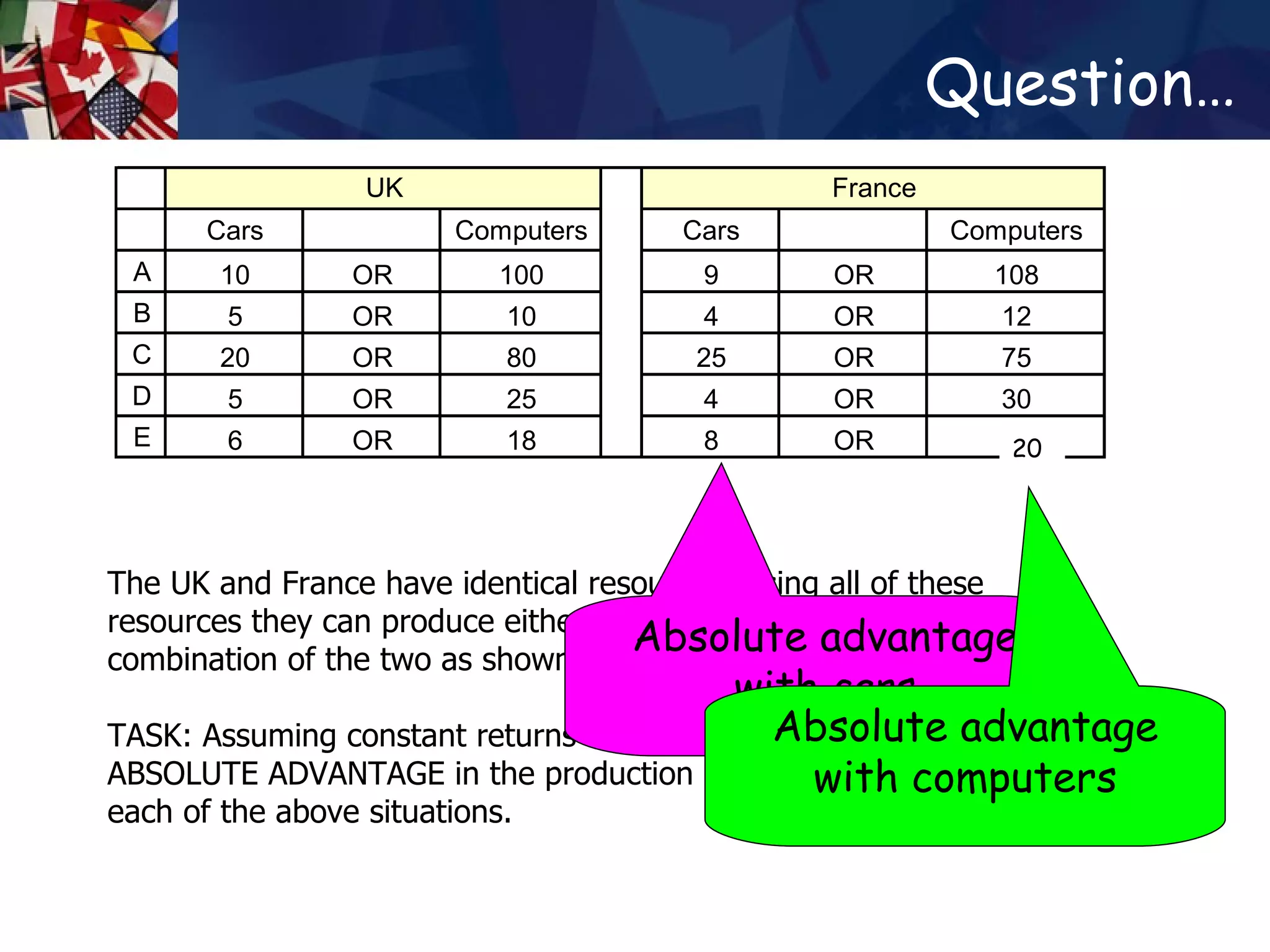
The document discusses concepts related to international trade including specialization, absolute advantage, and comparative advantage. It provides examples to illustrate key theories such as how specialization allows countries to increase total output through division of labor. Absolute advantage refers to a country being able to produce more of a good using the same resources. Comparative advantage depends on opportunity costs and is measured based on what a country must give up to produce more of a good. Trade can benefit countries even if one has an absolute advantage in all goods by allowing specialization based on comparative advantage.