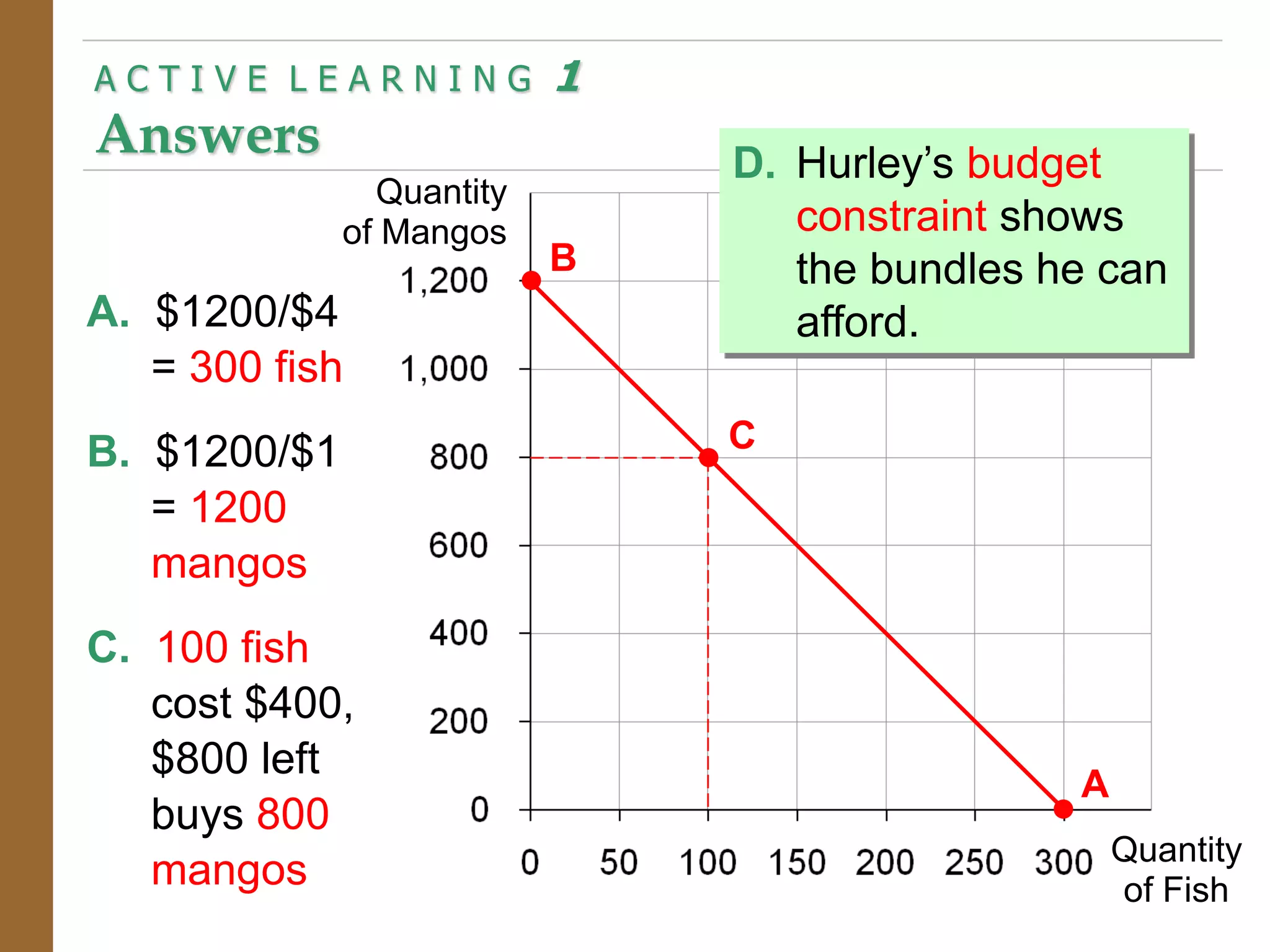
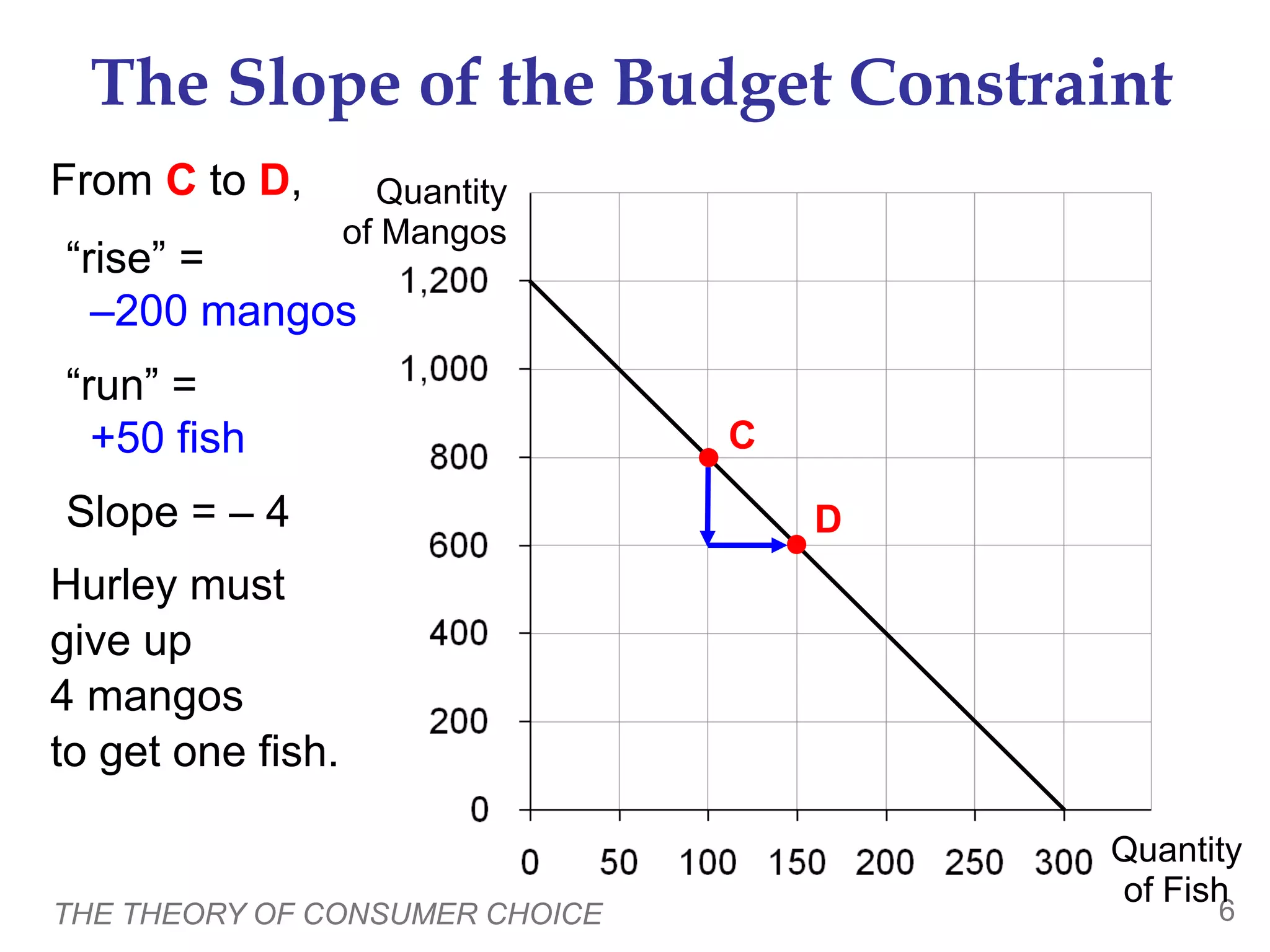
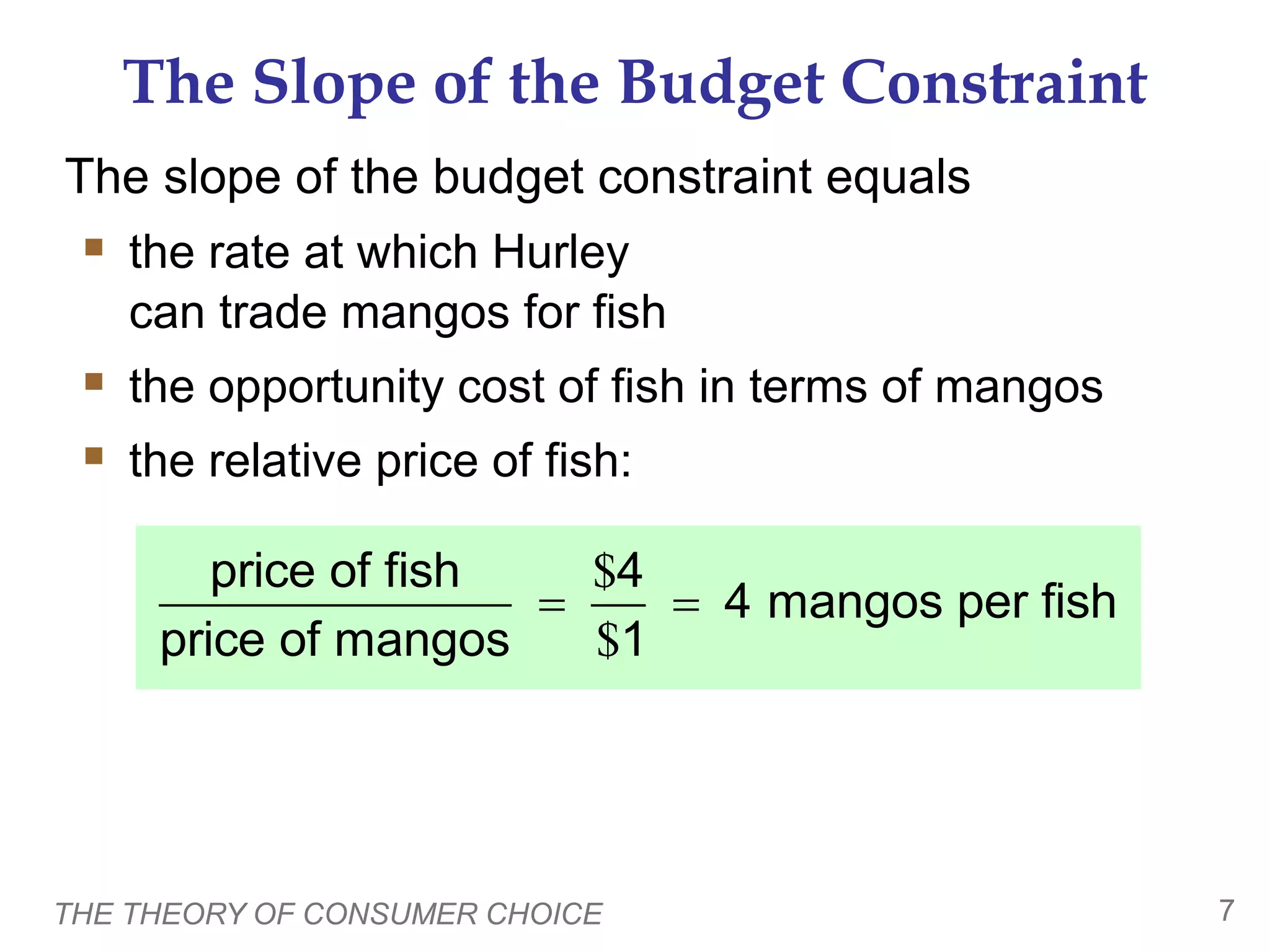
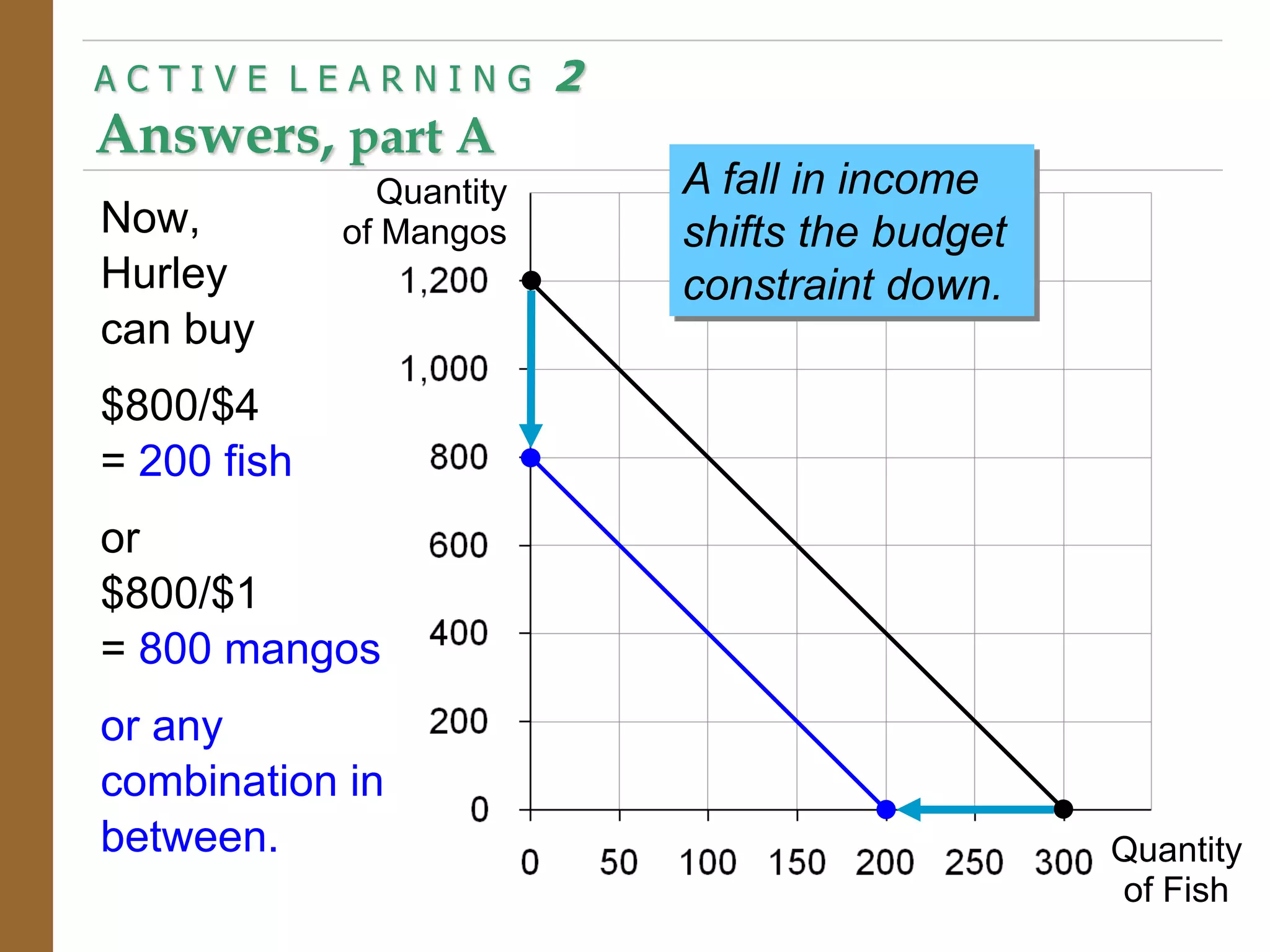
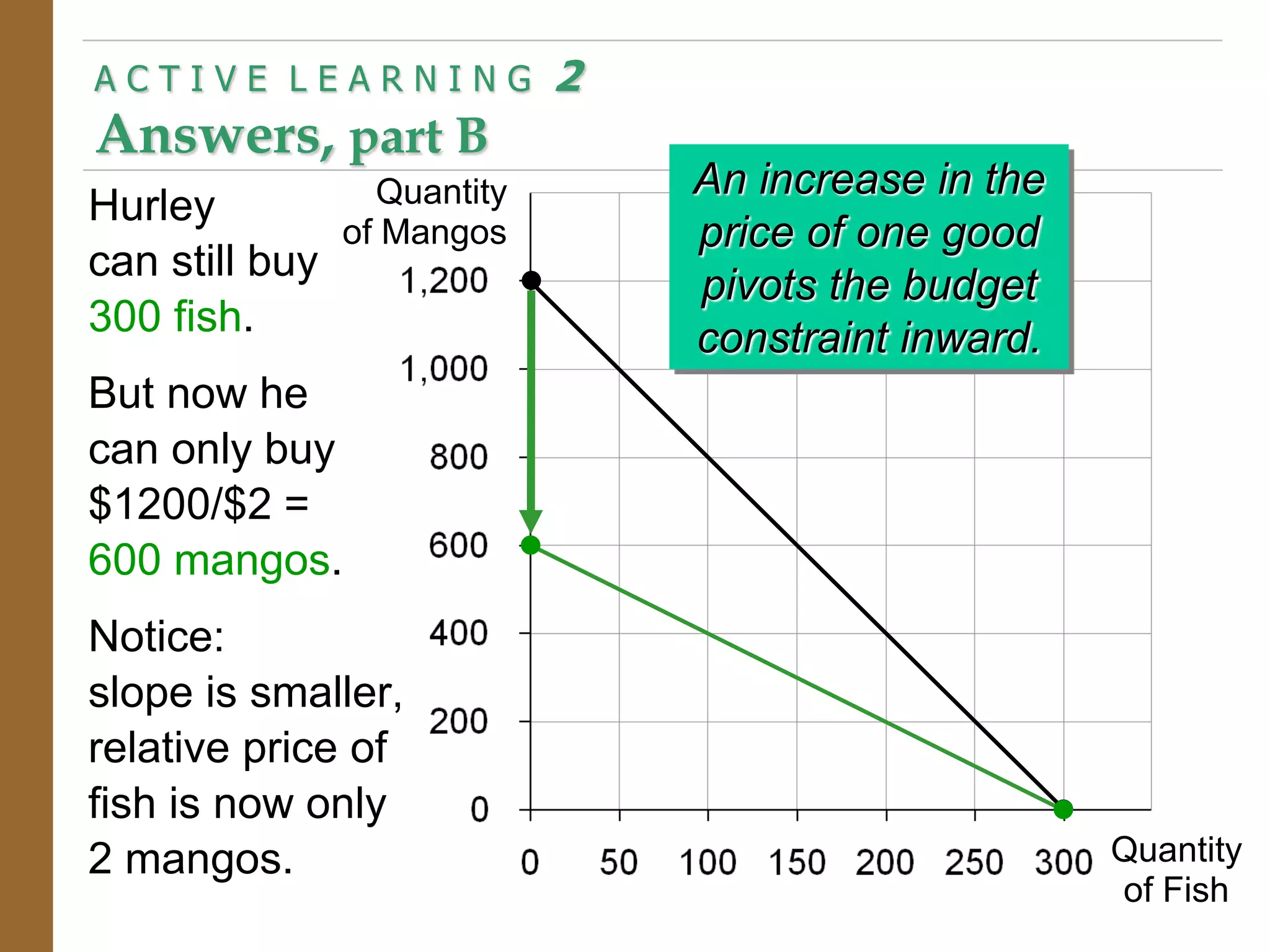
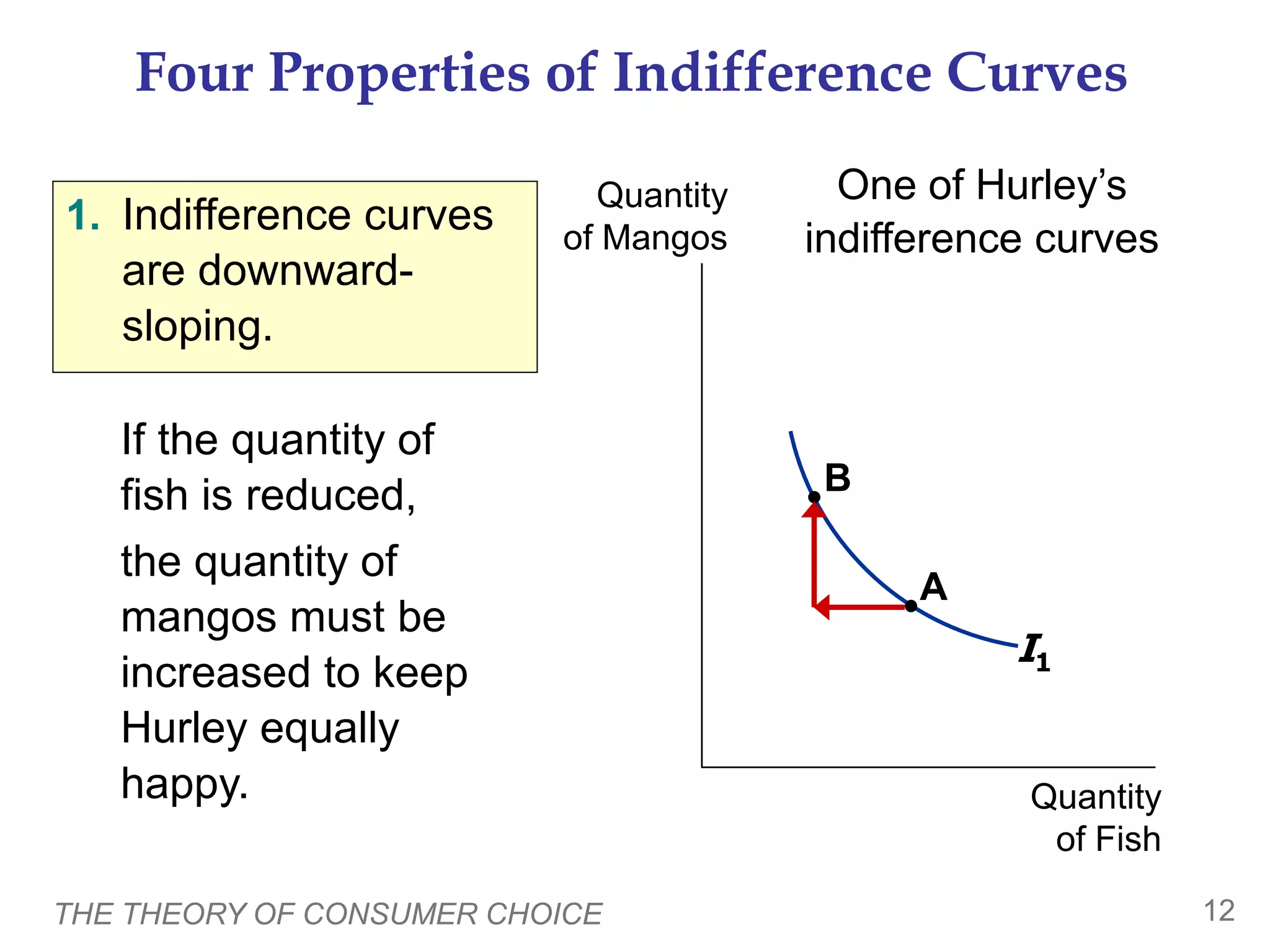
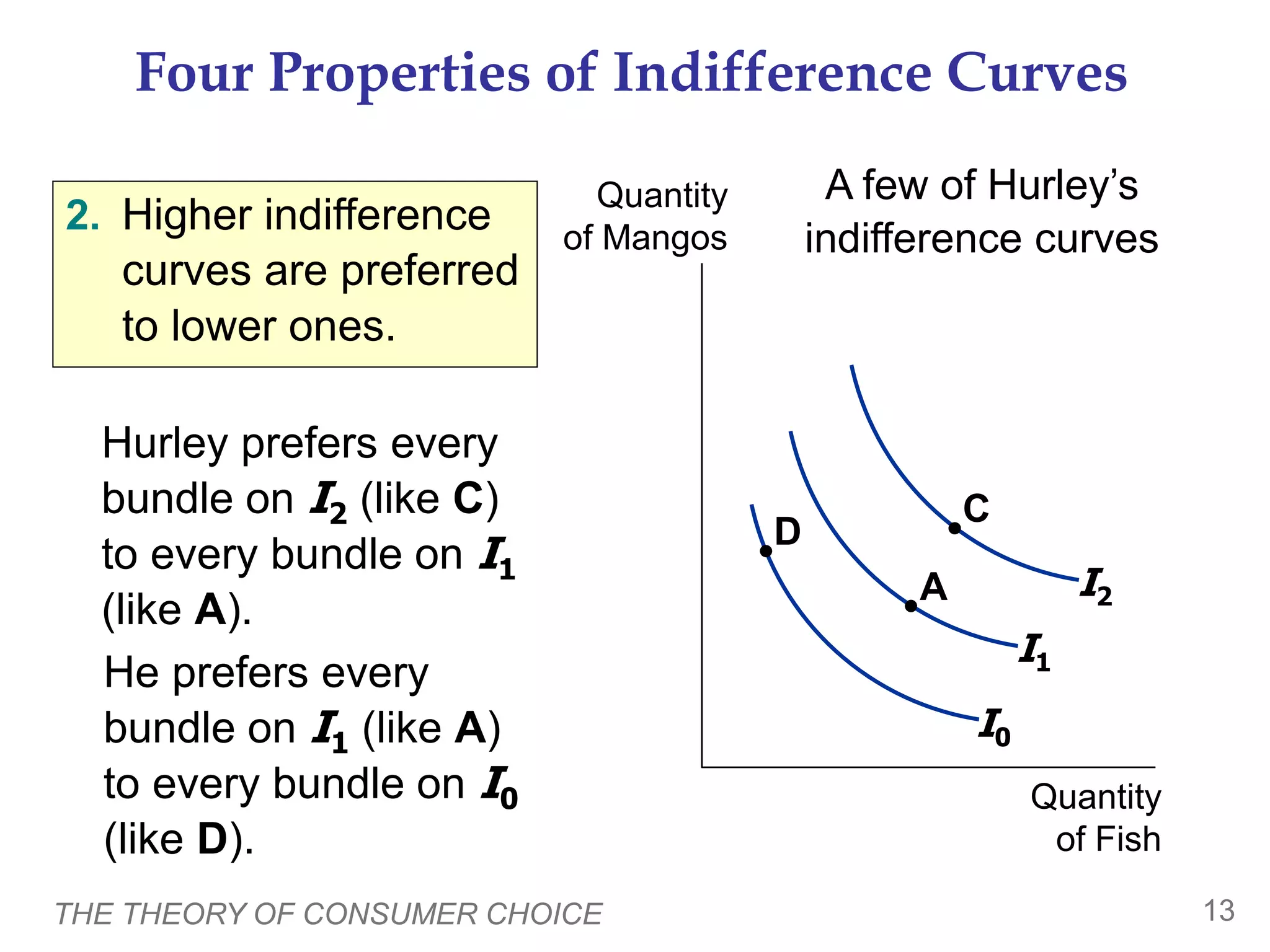
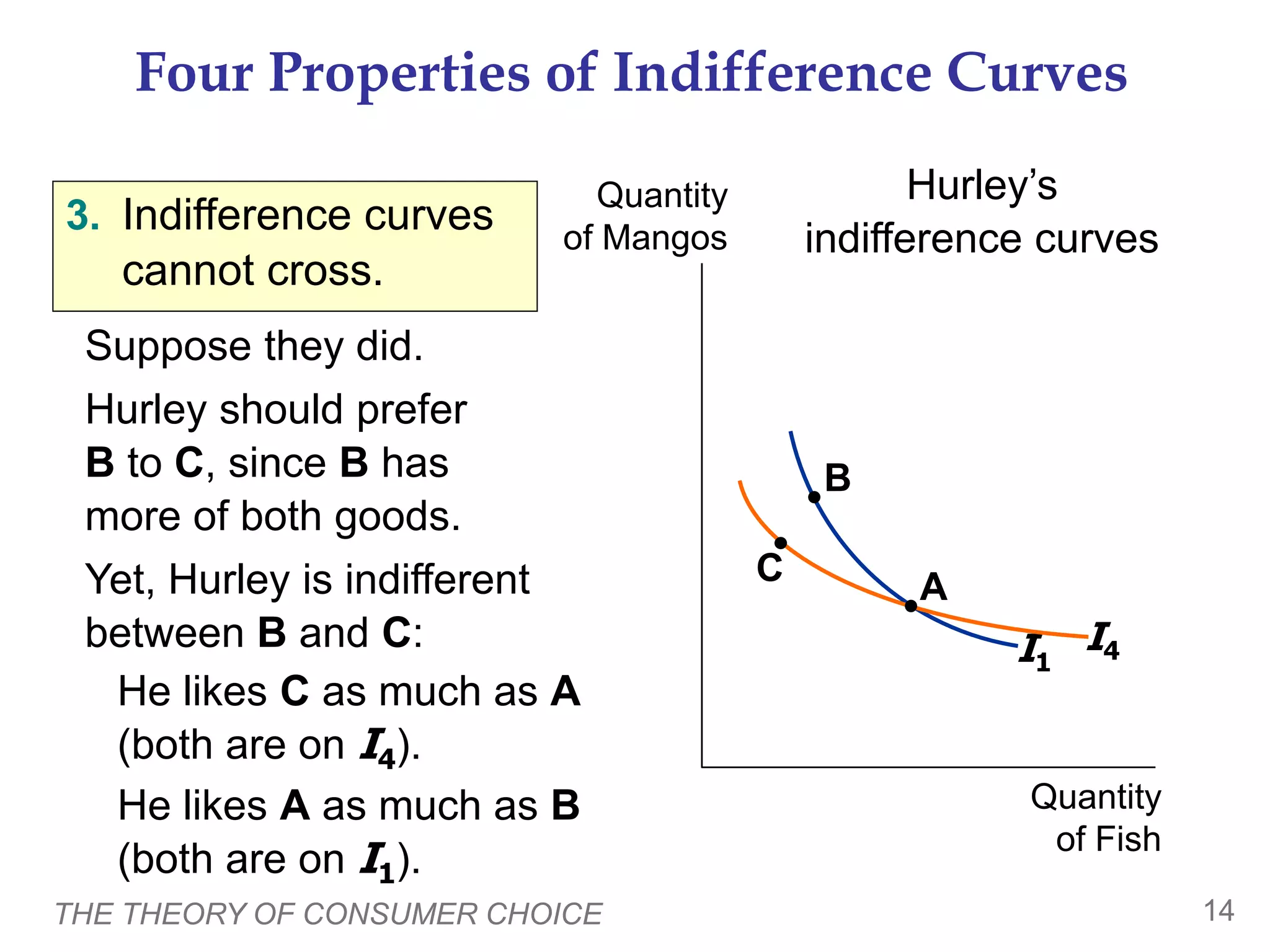
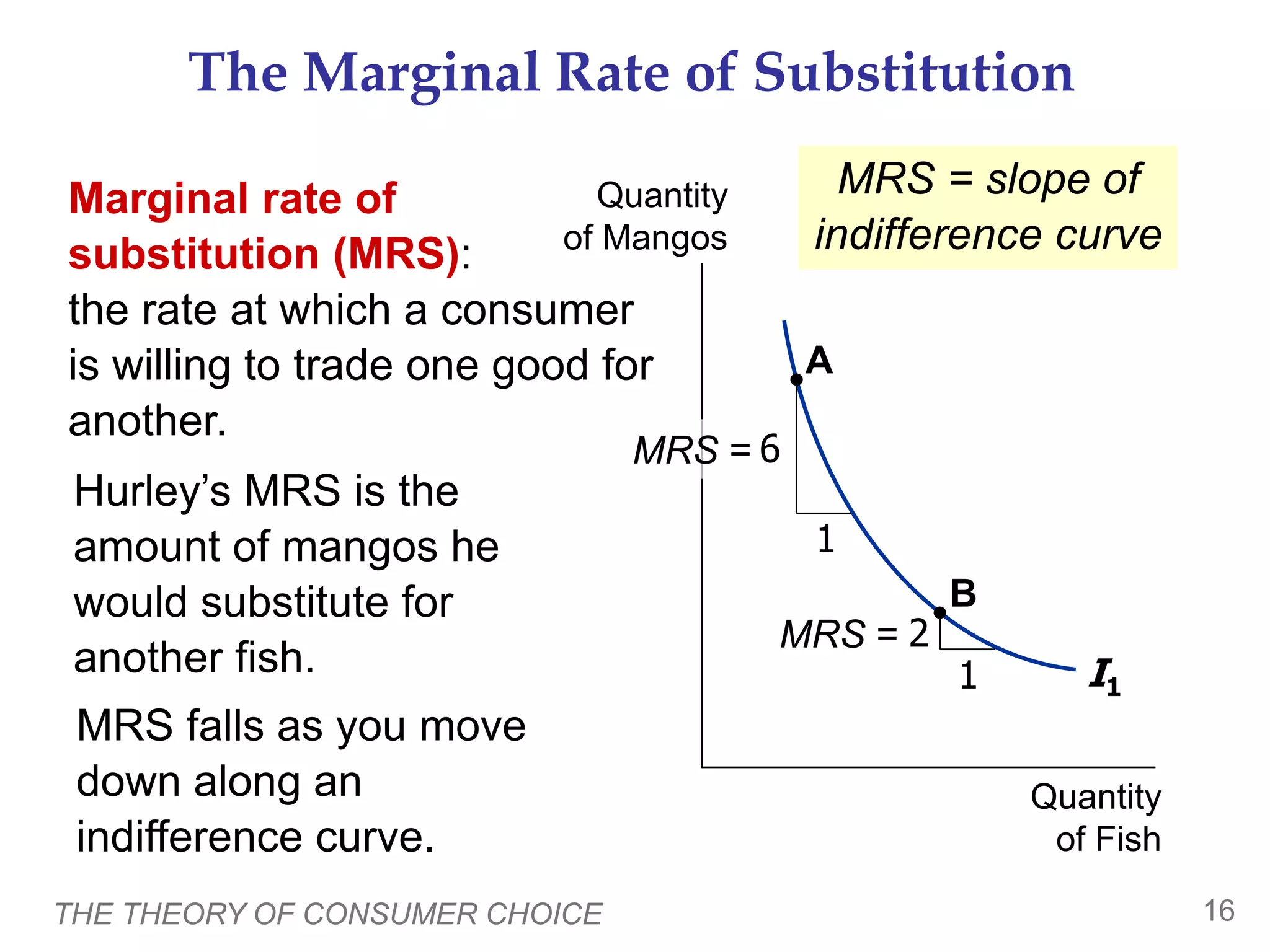
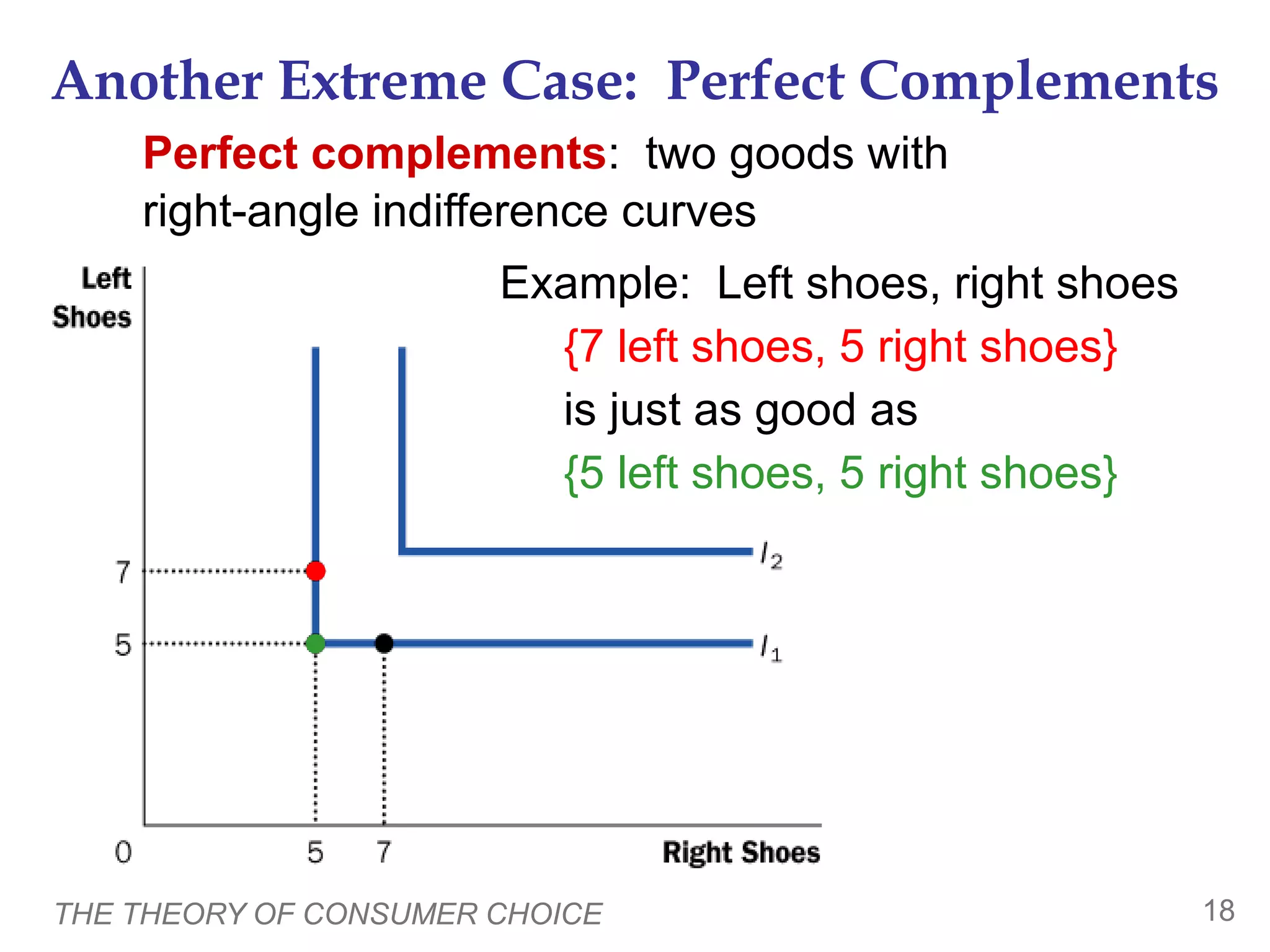
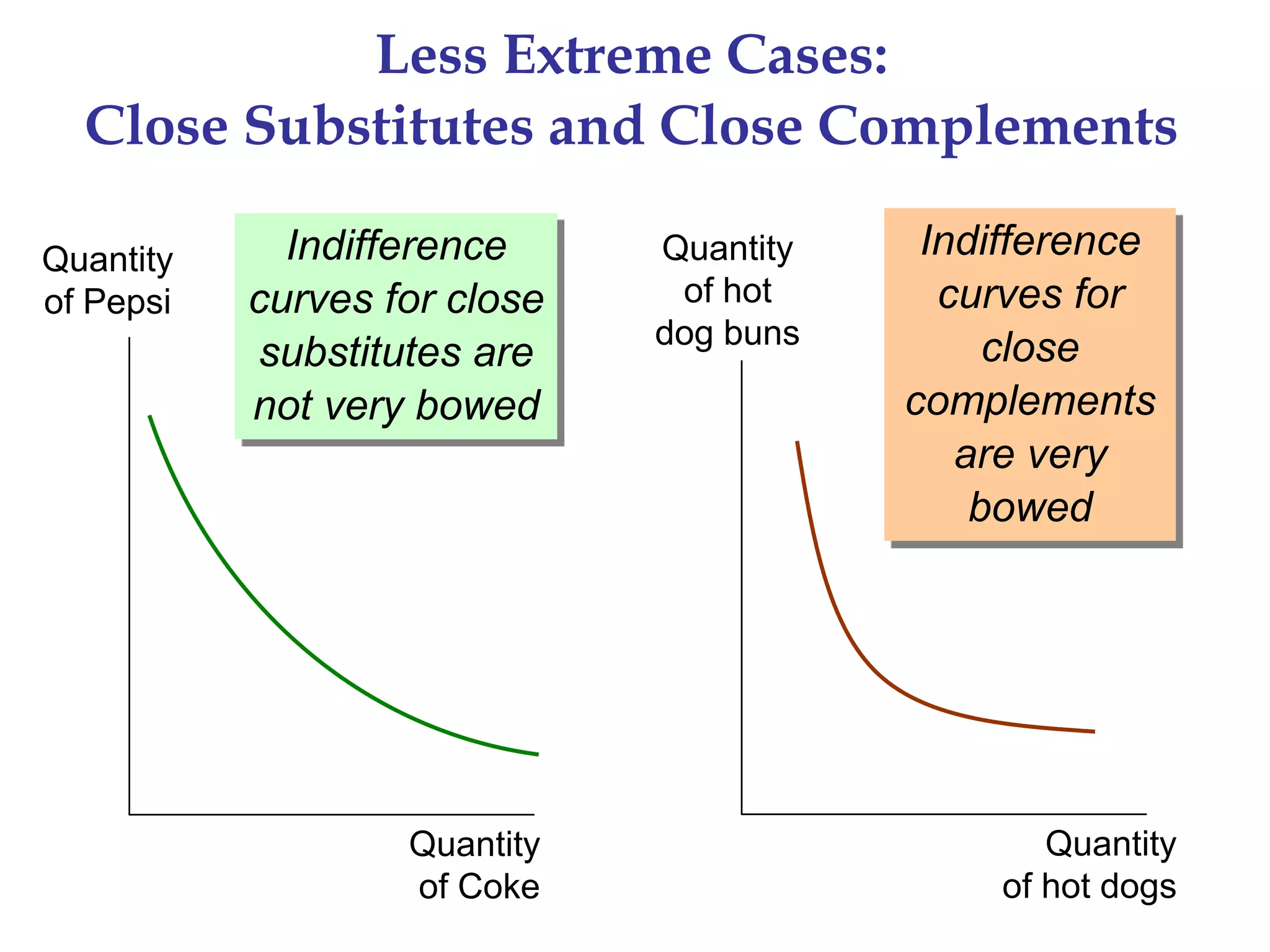
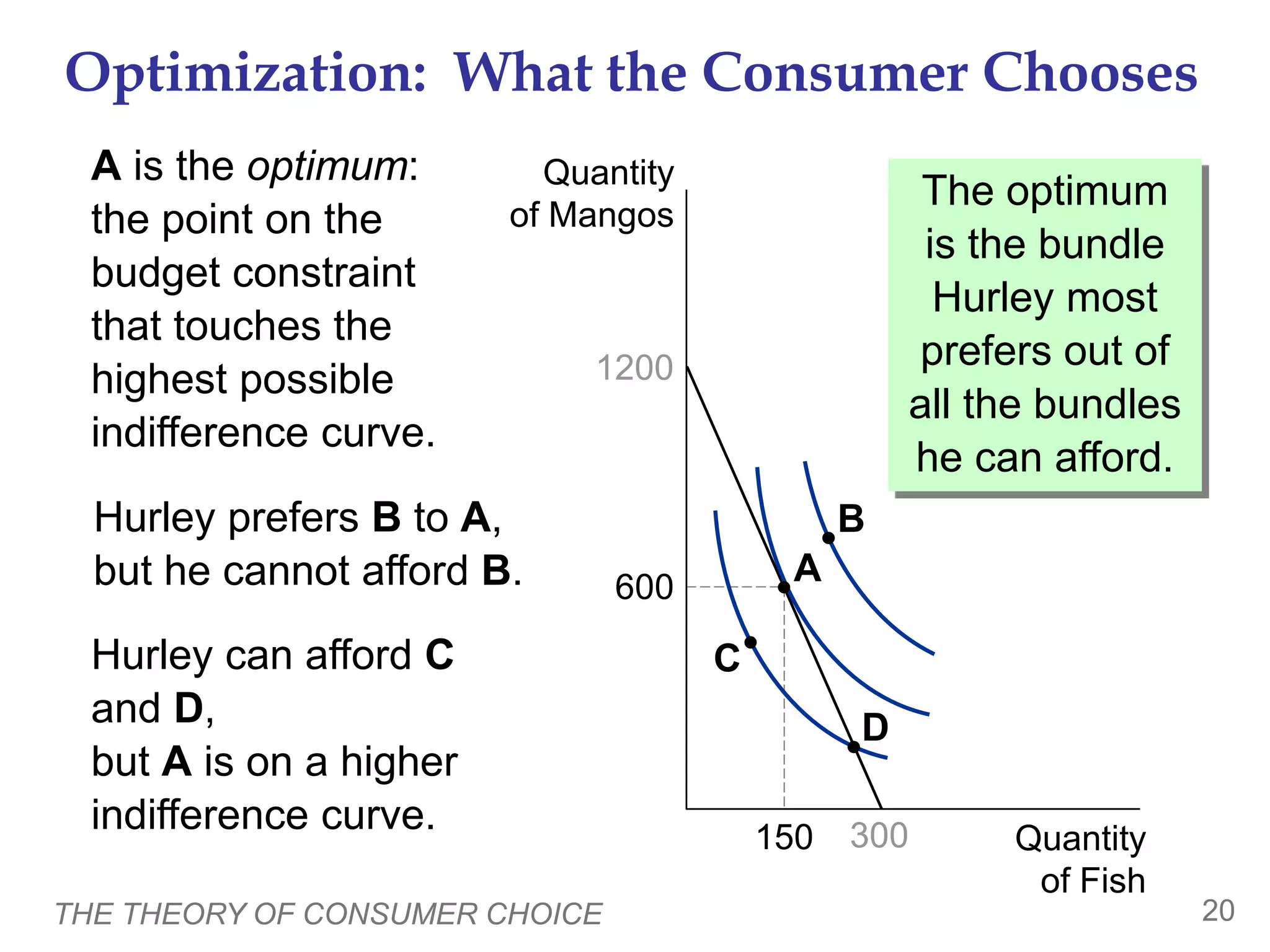
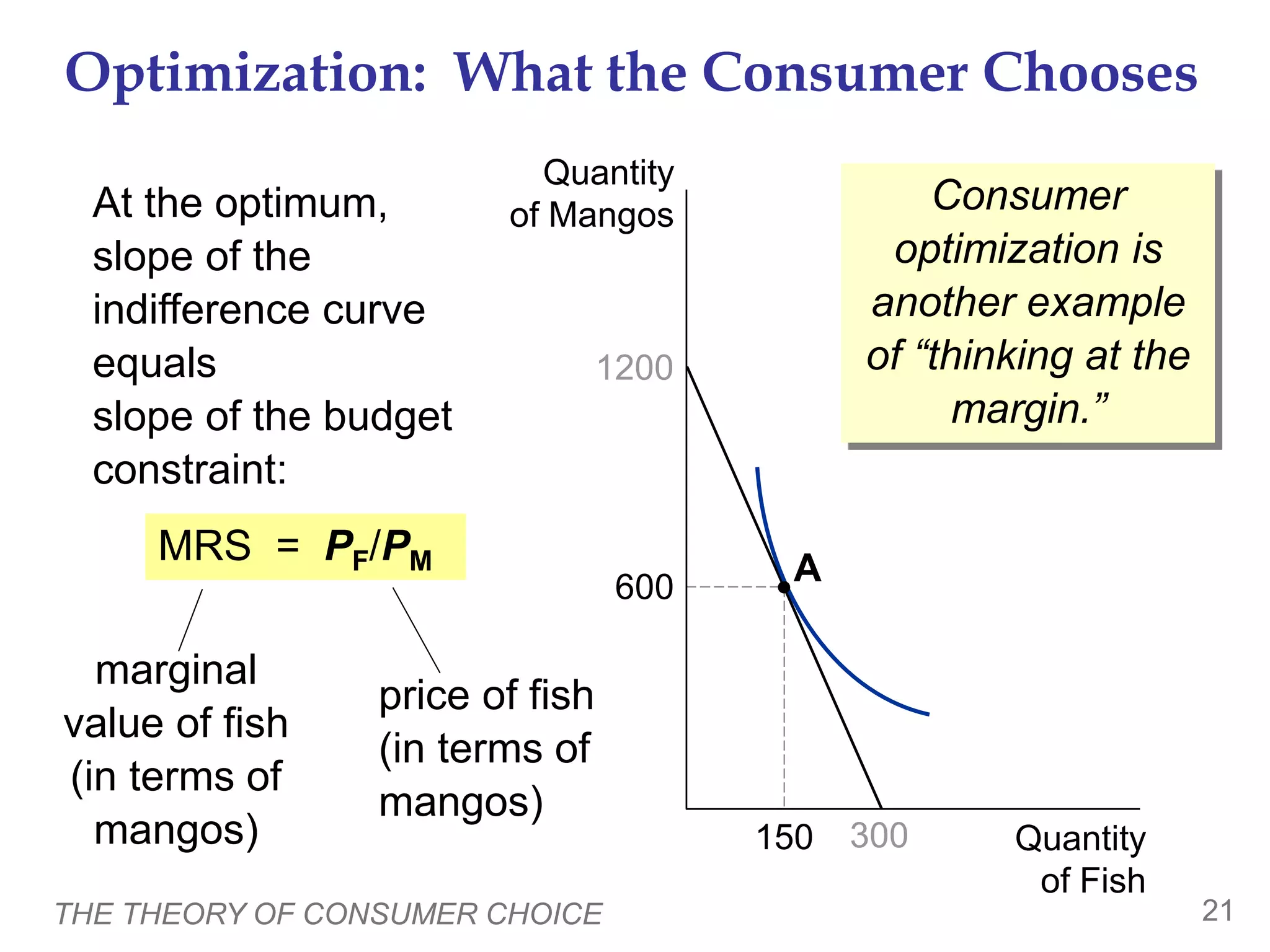
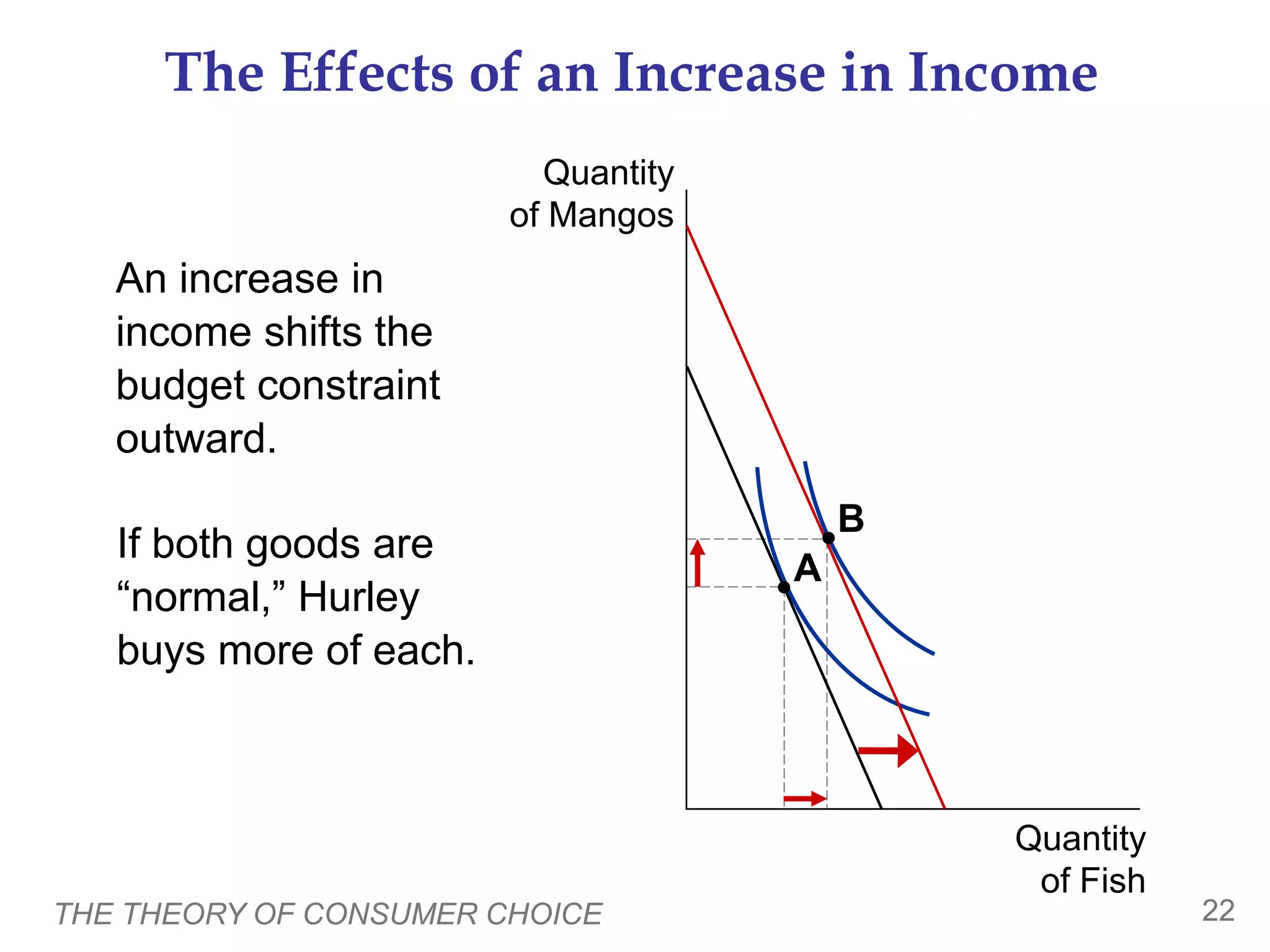
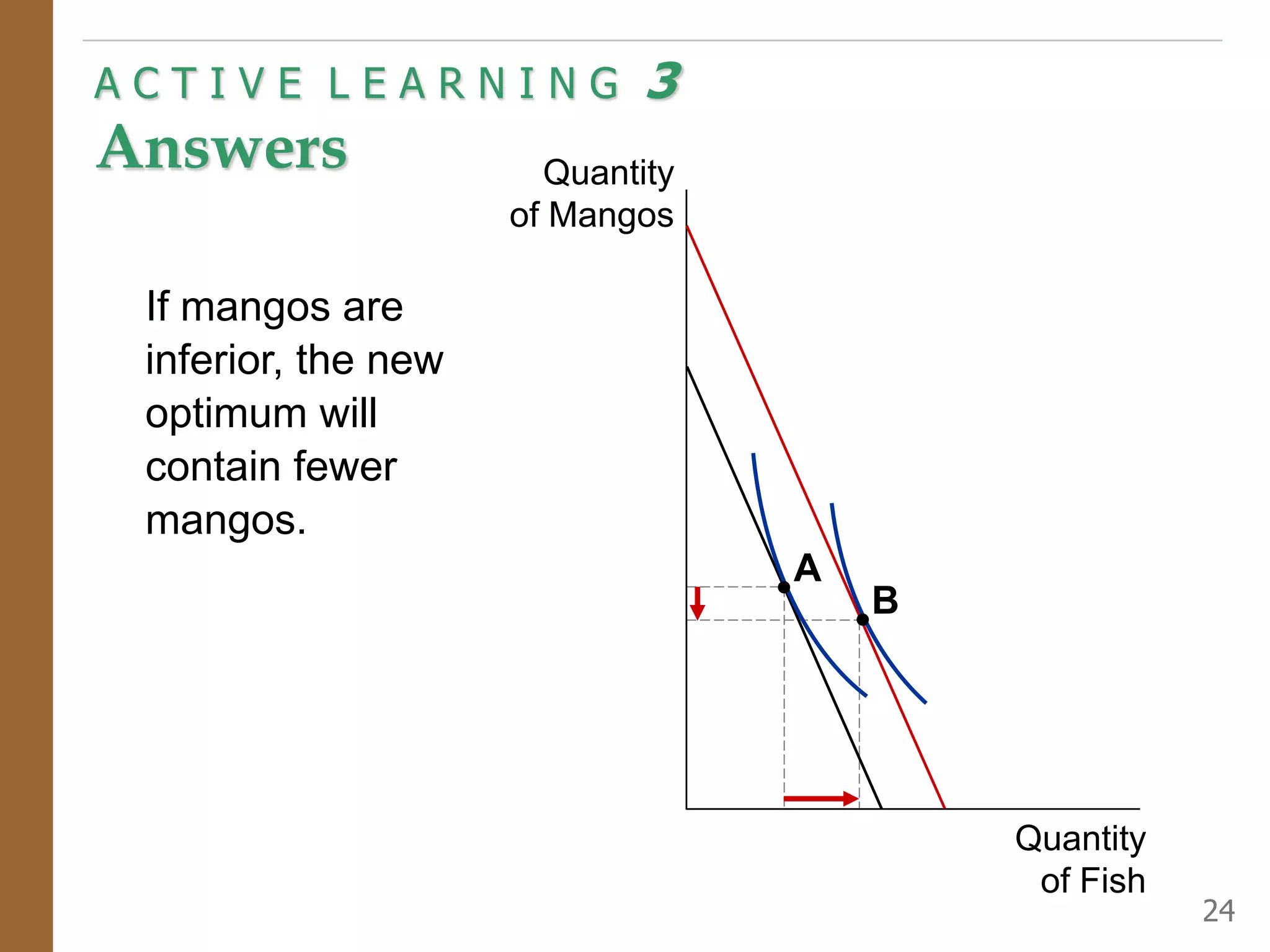
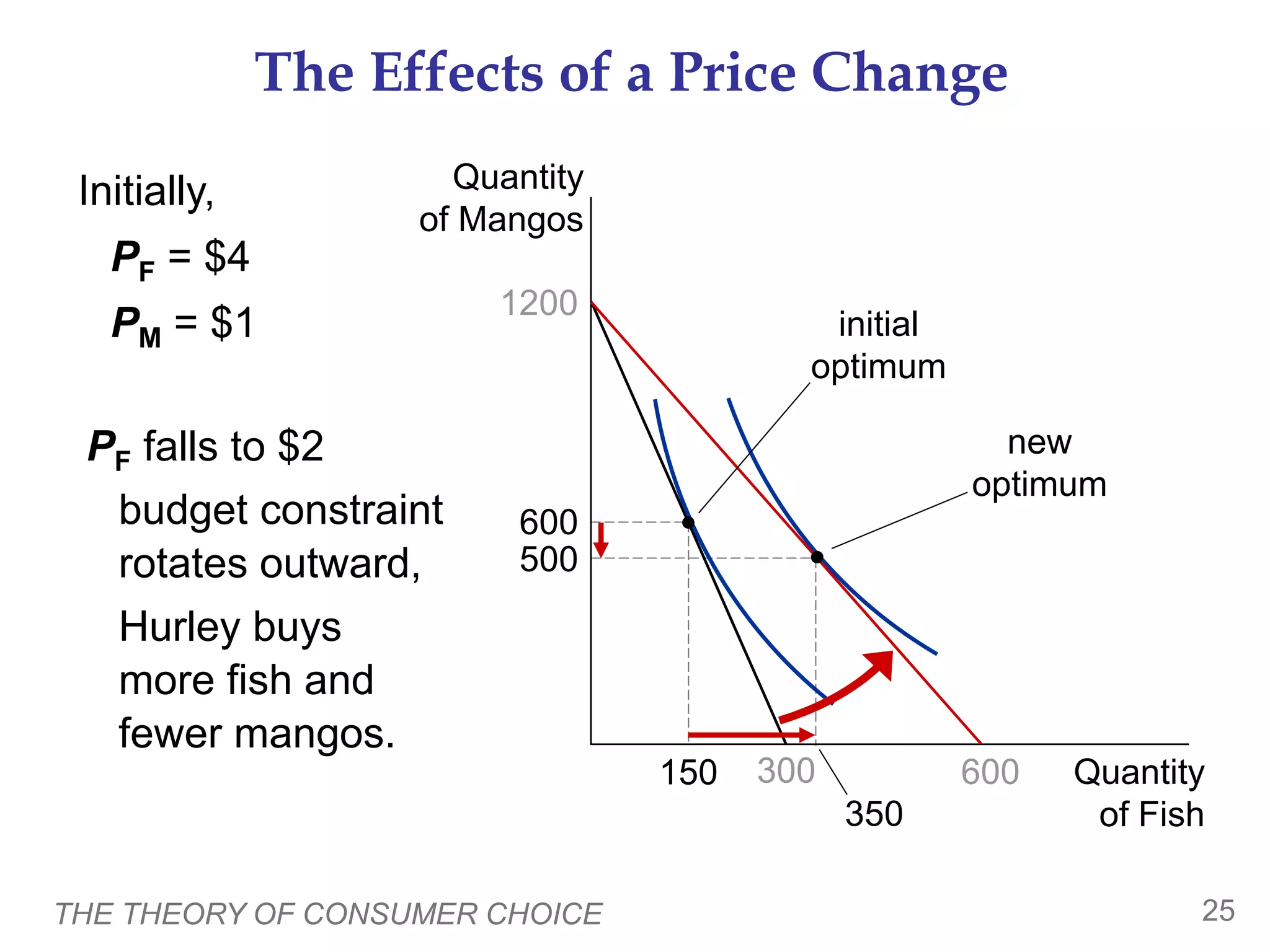
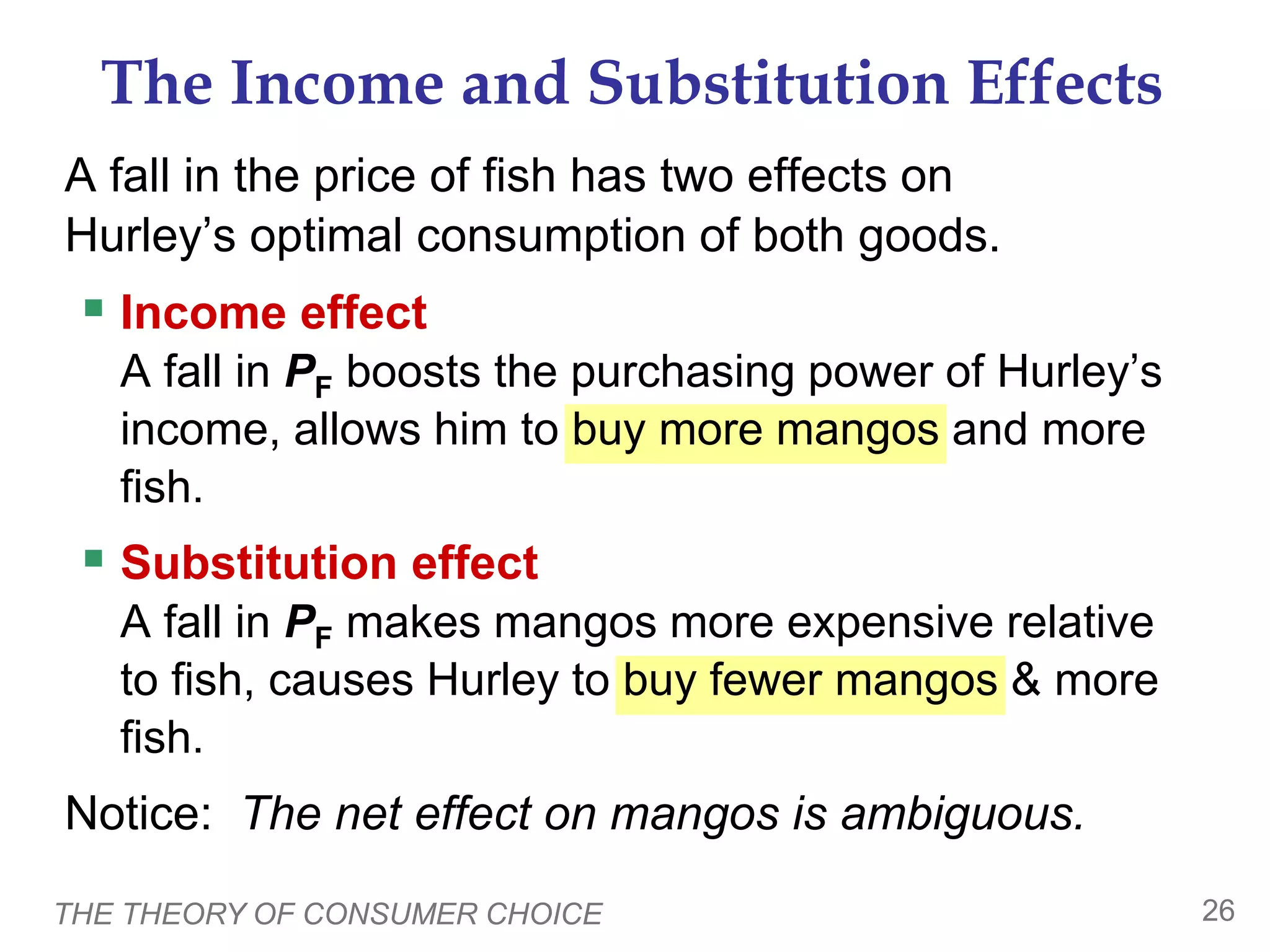
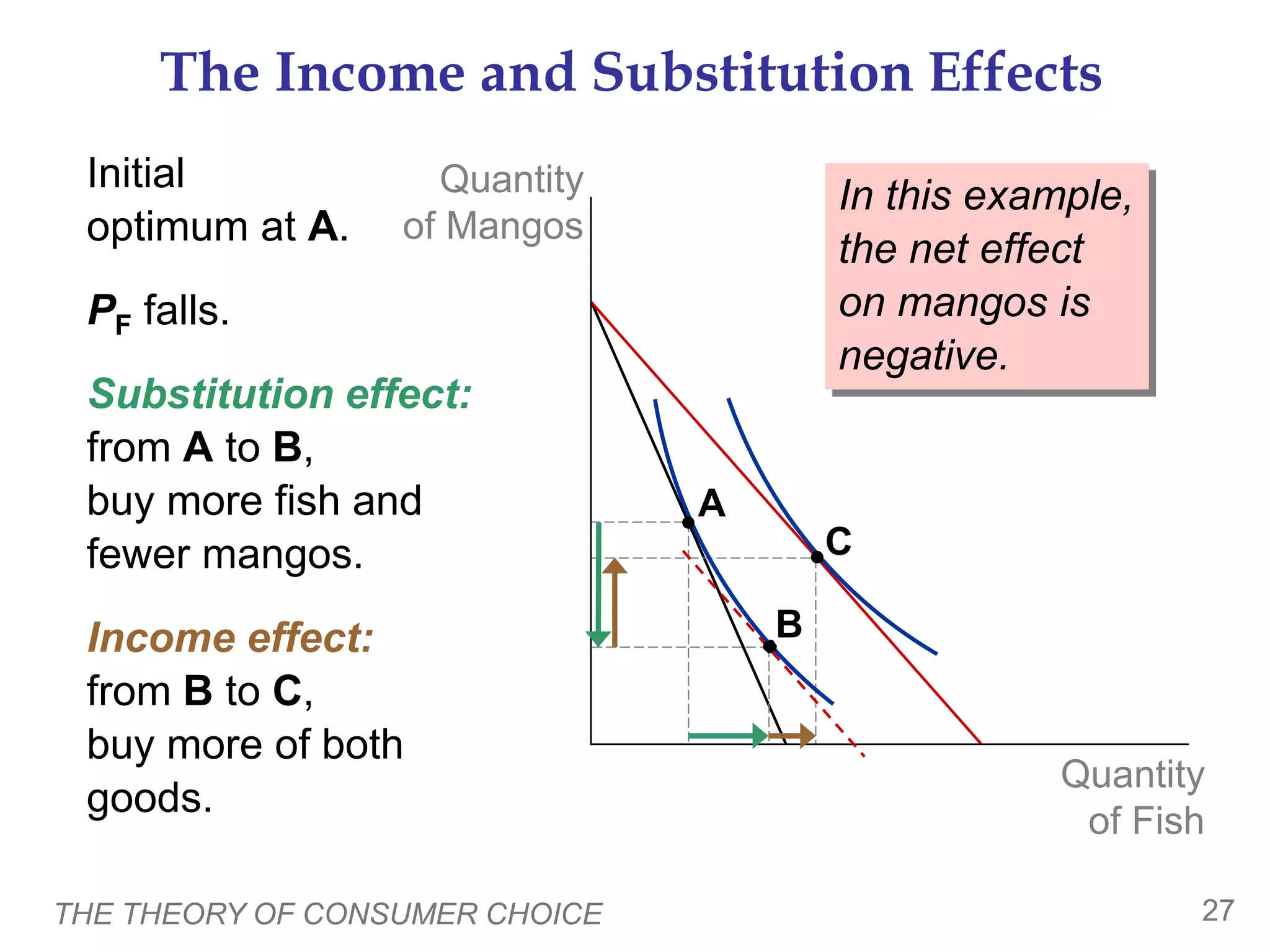
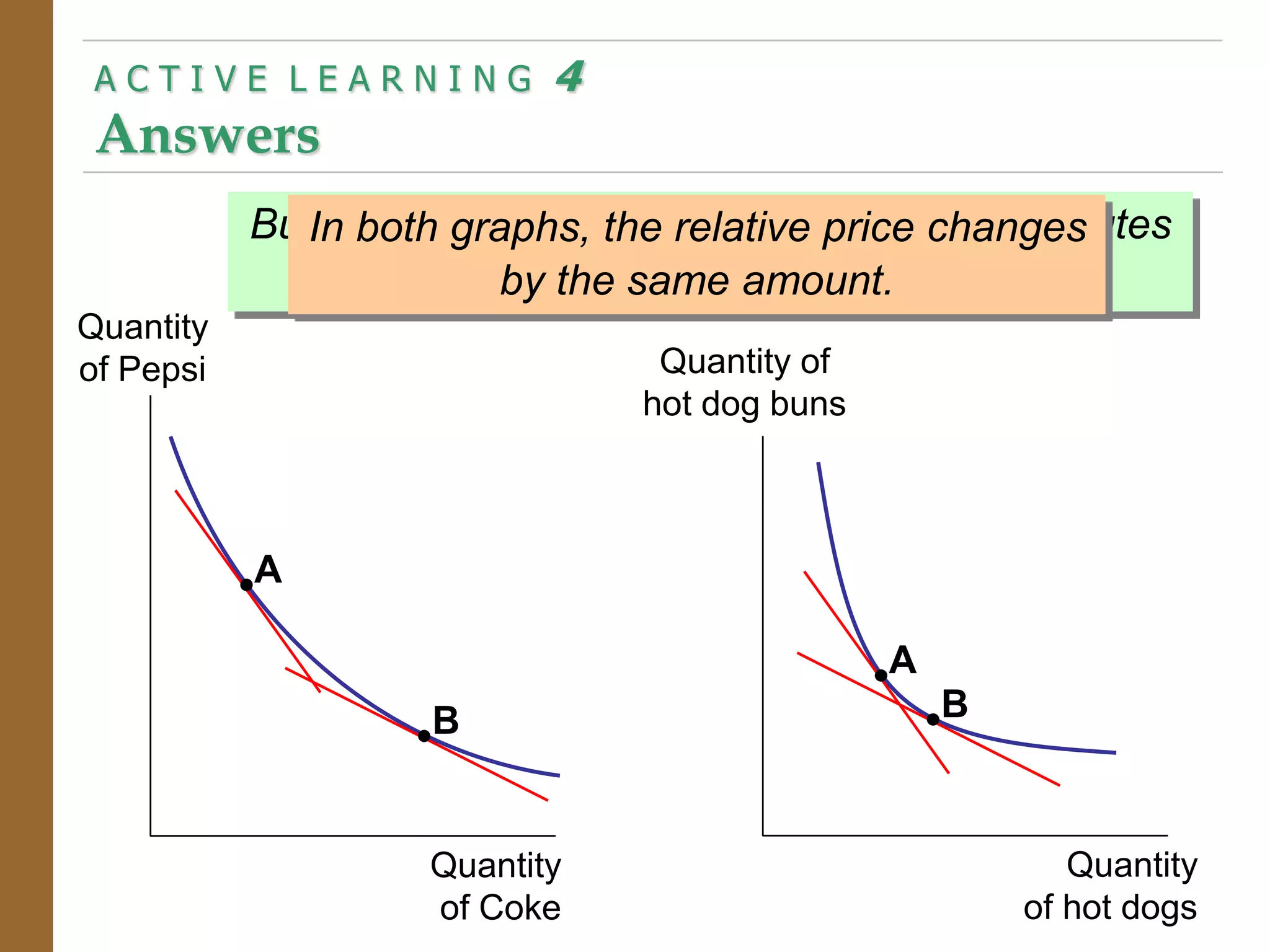
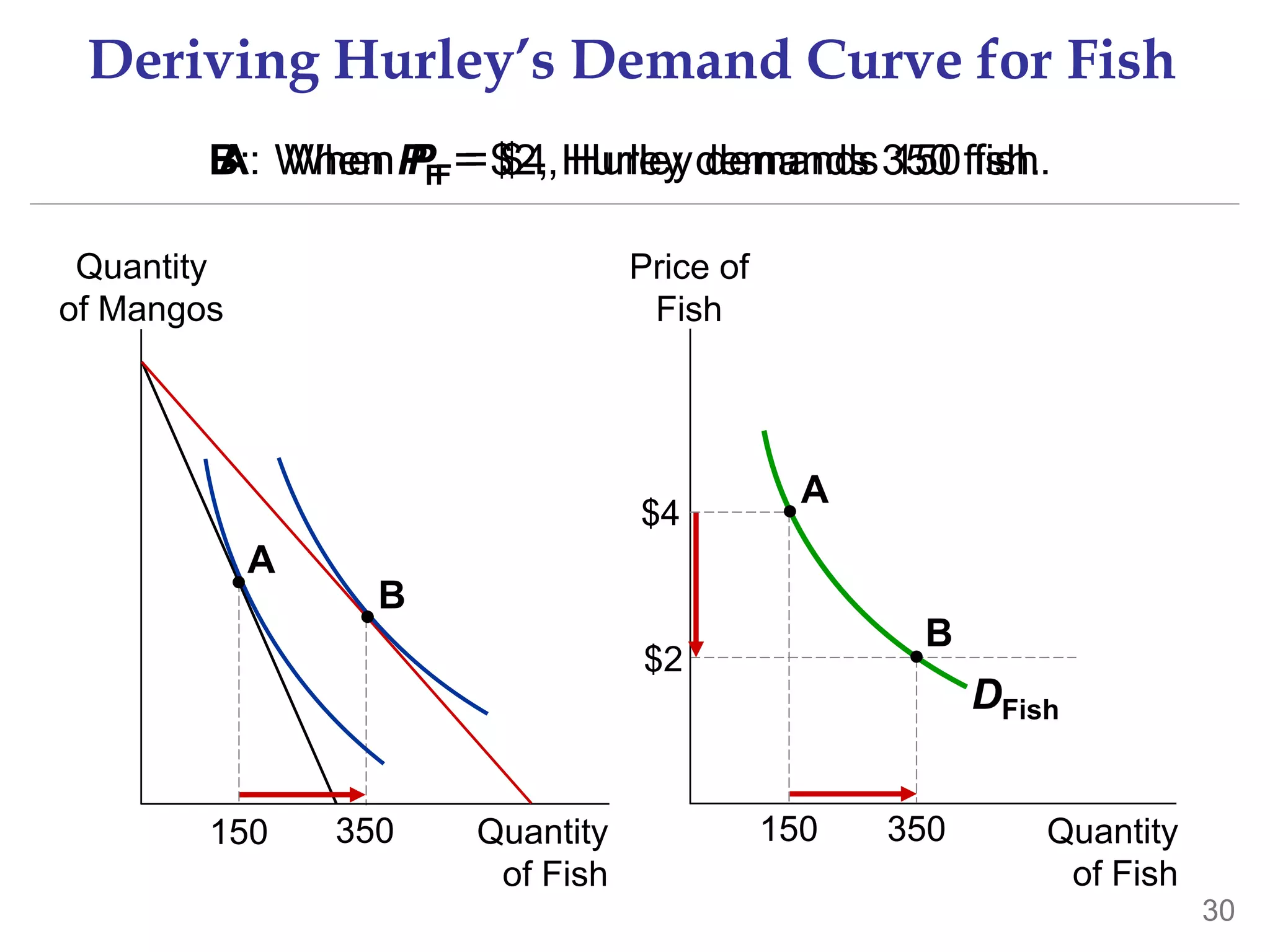
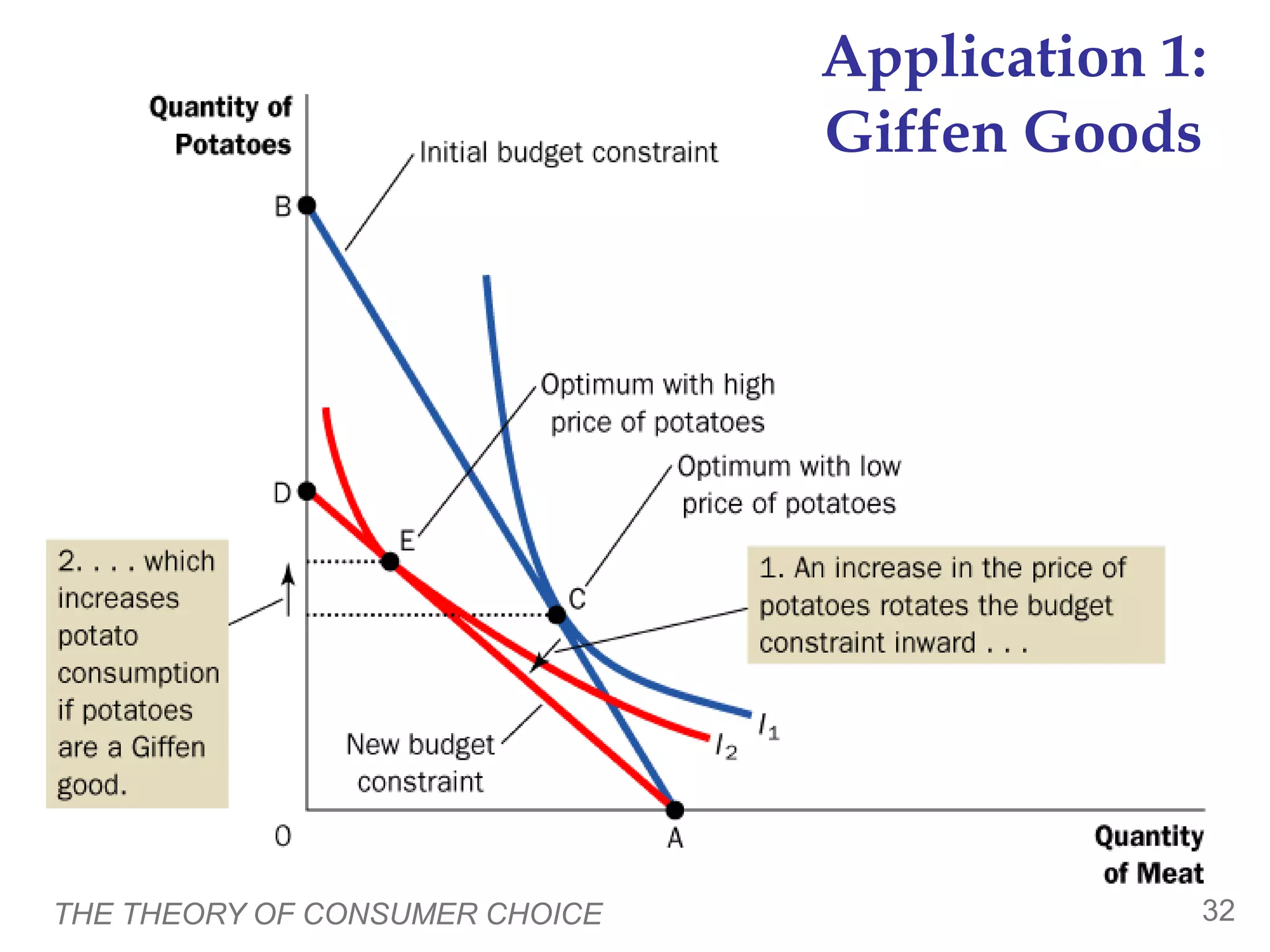
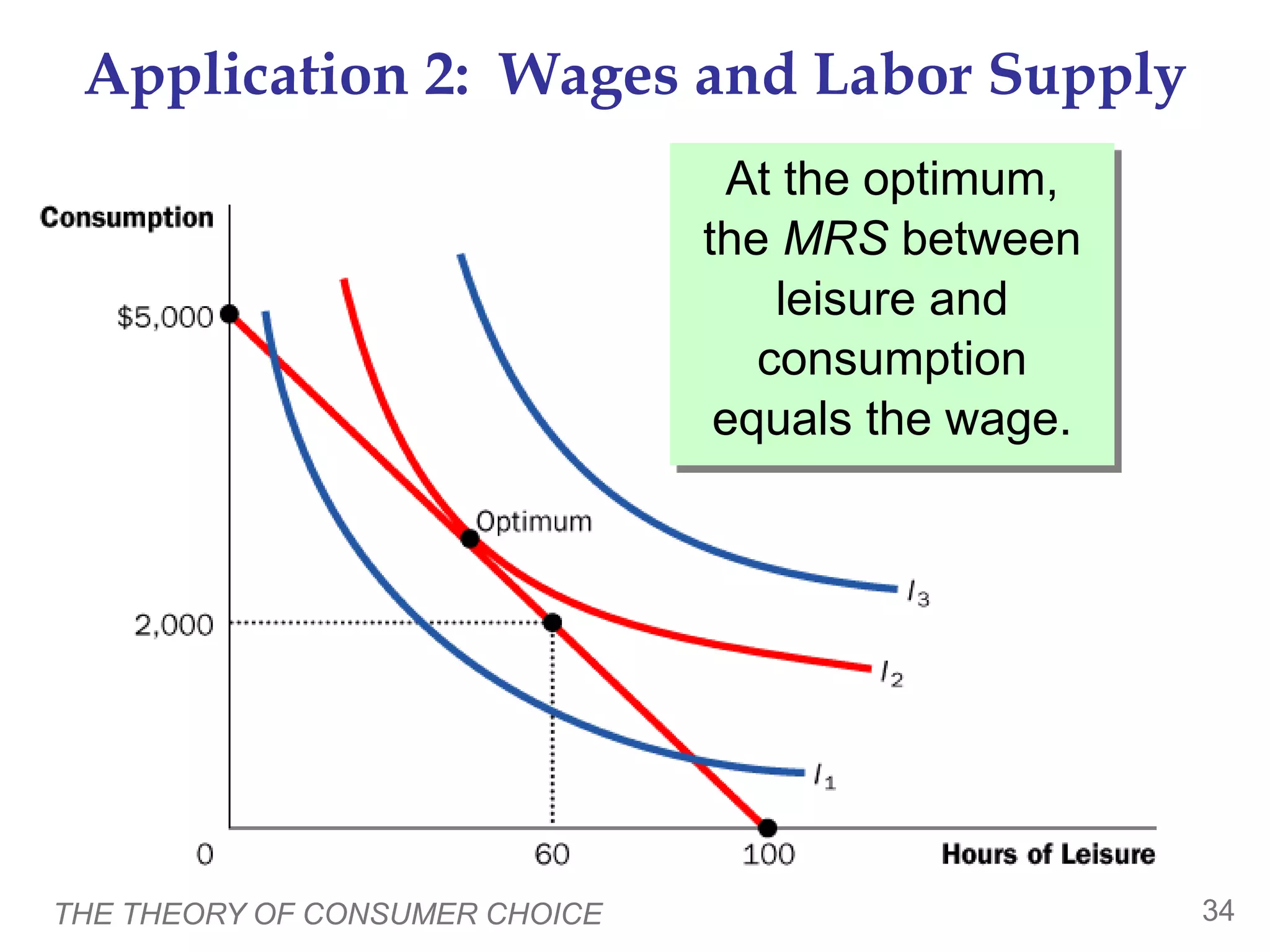
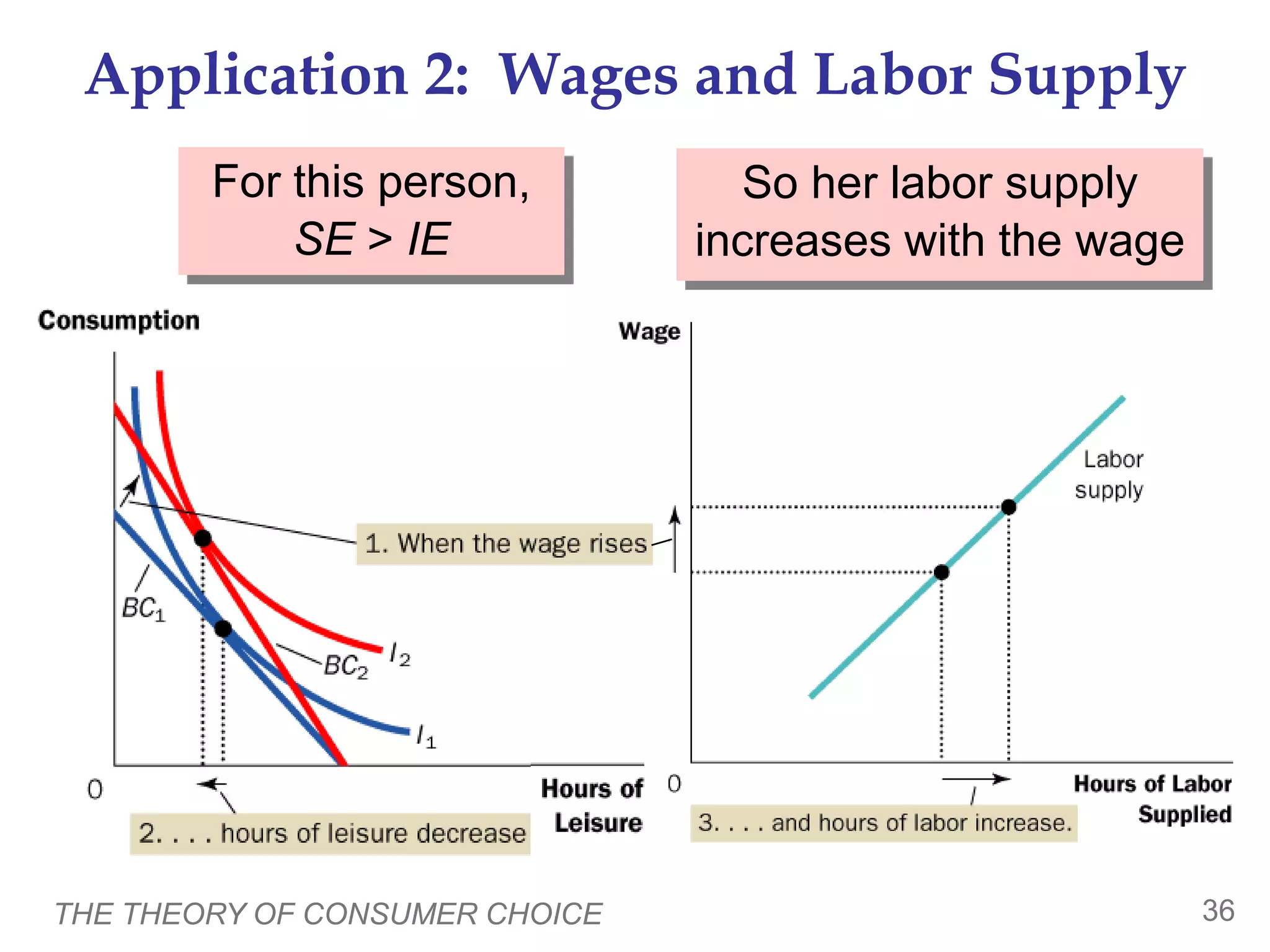
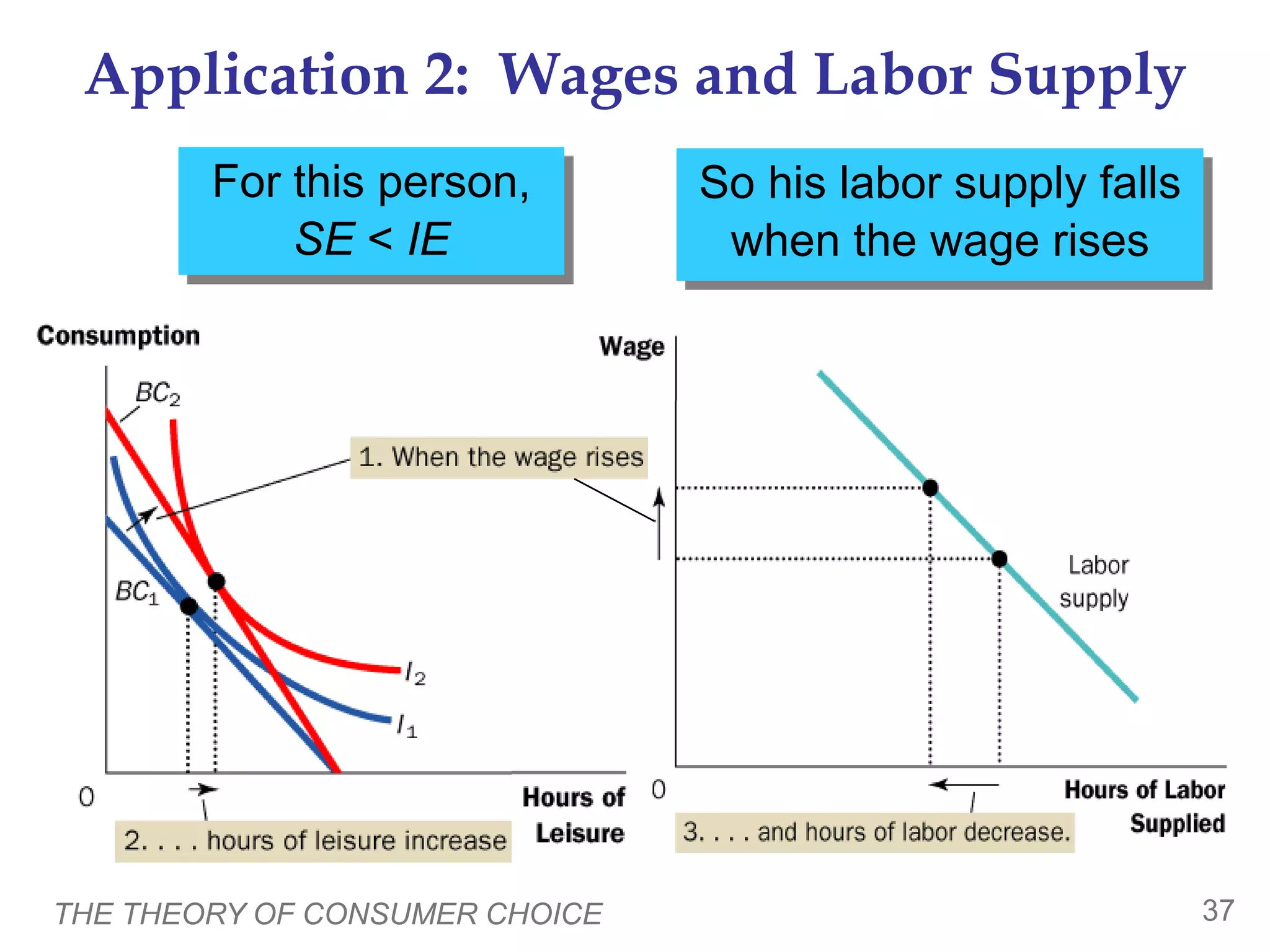
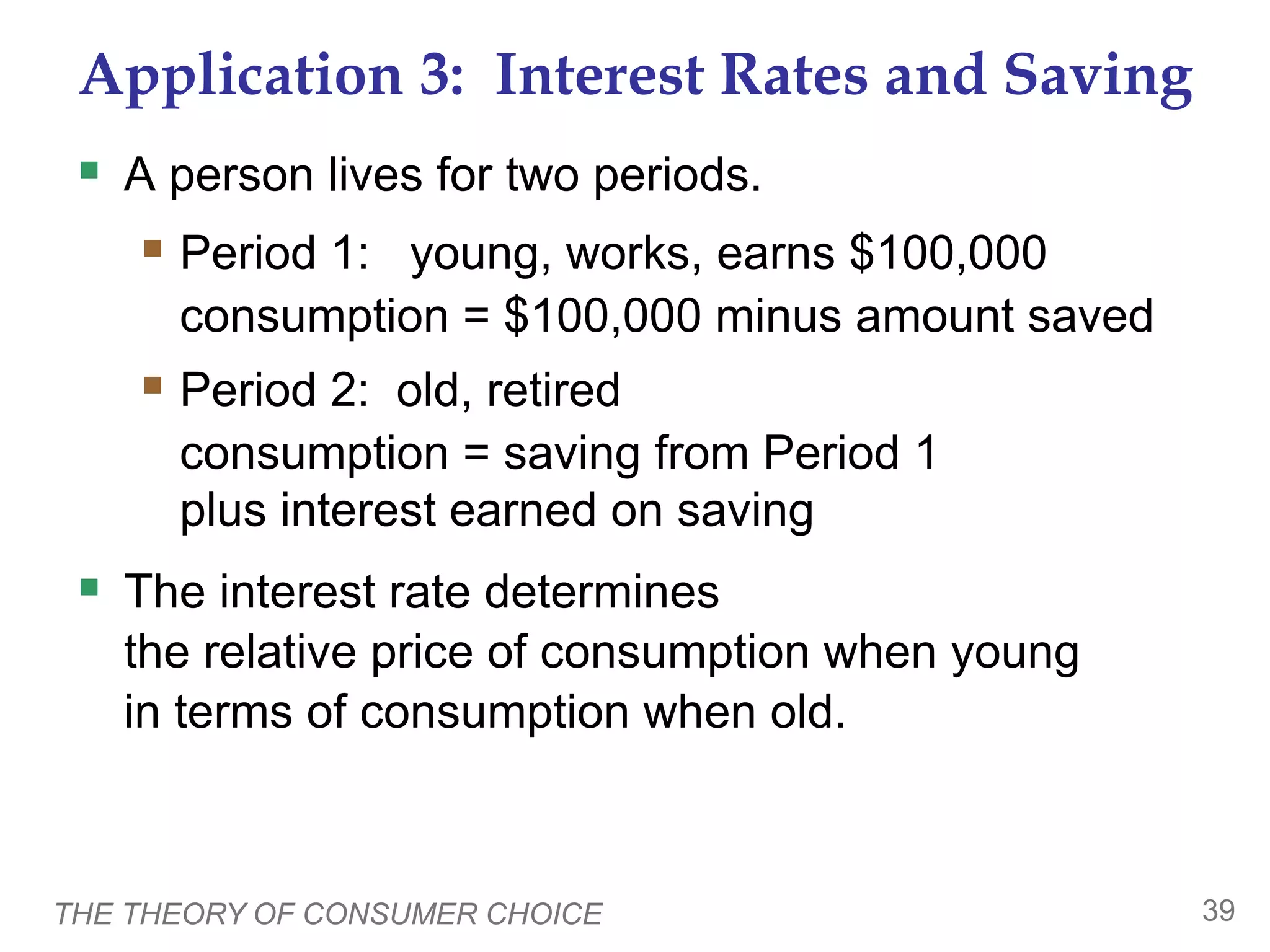
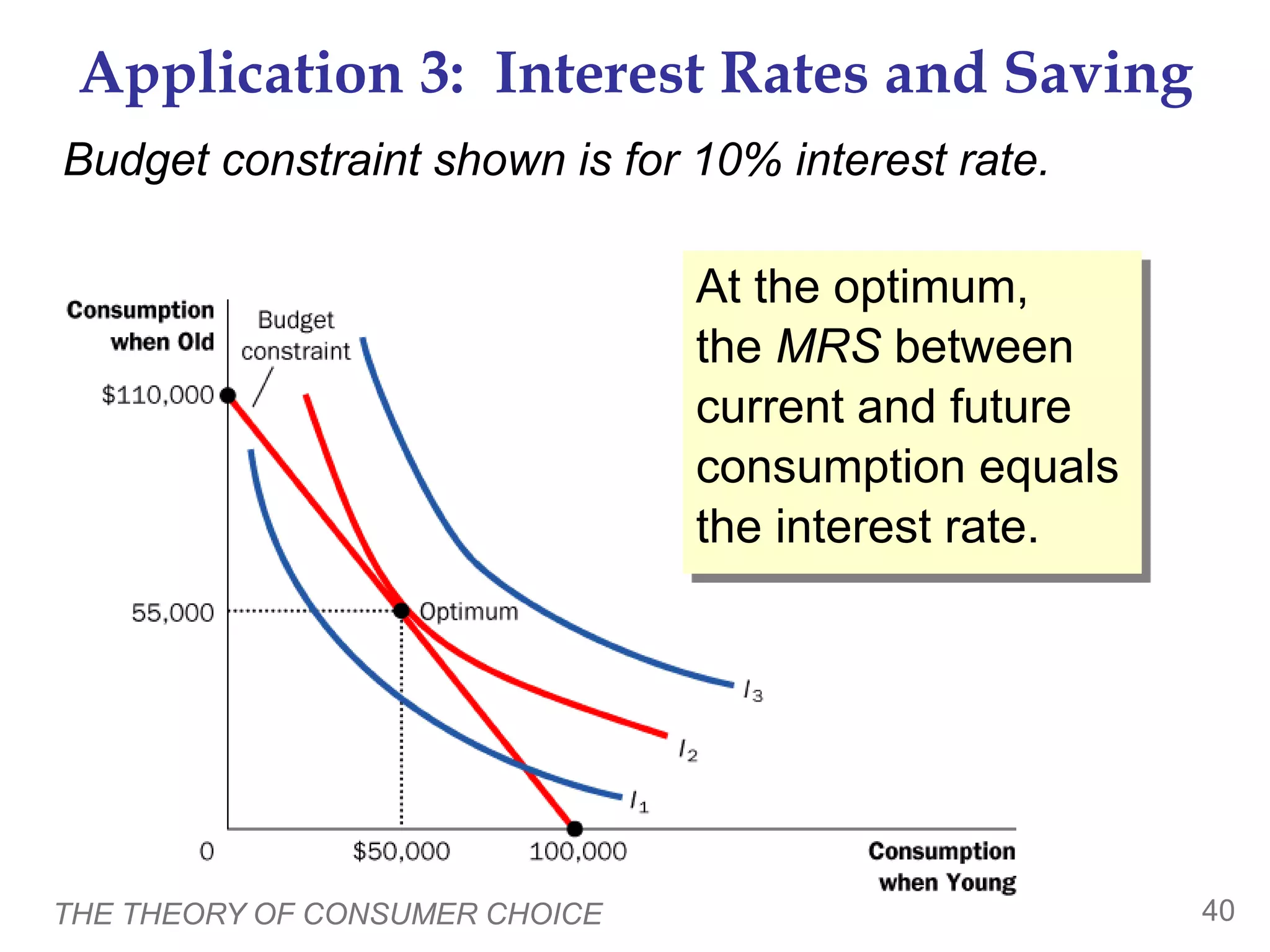
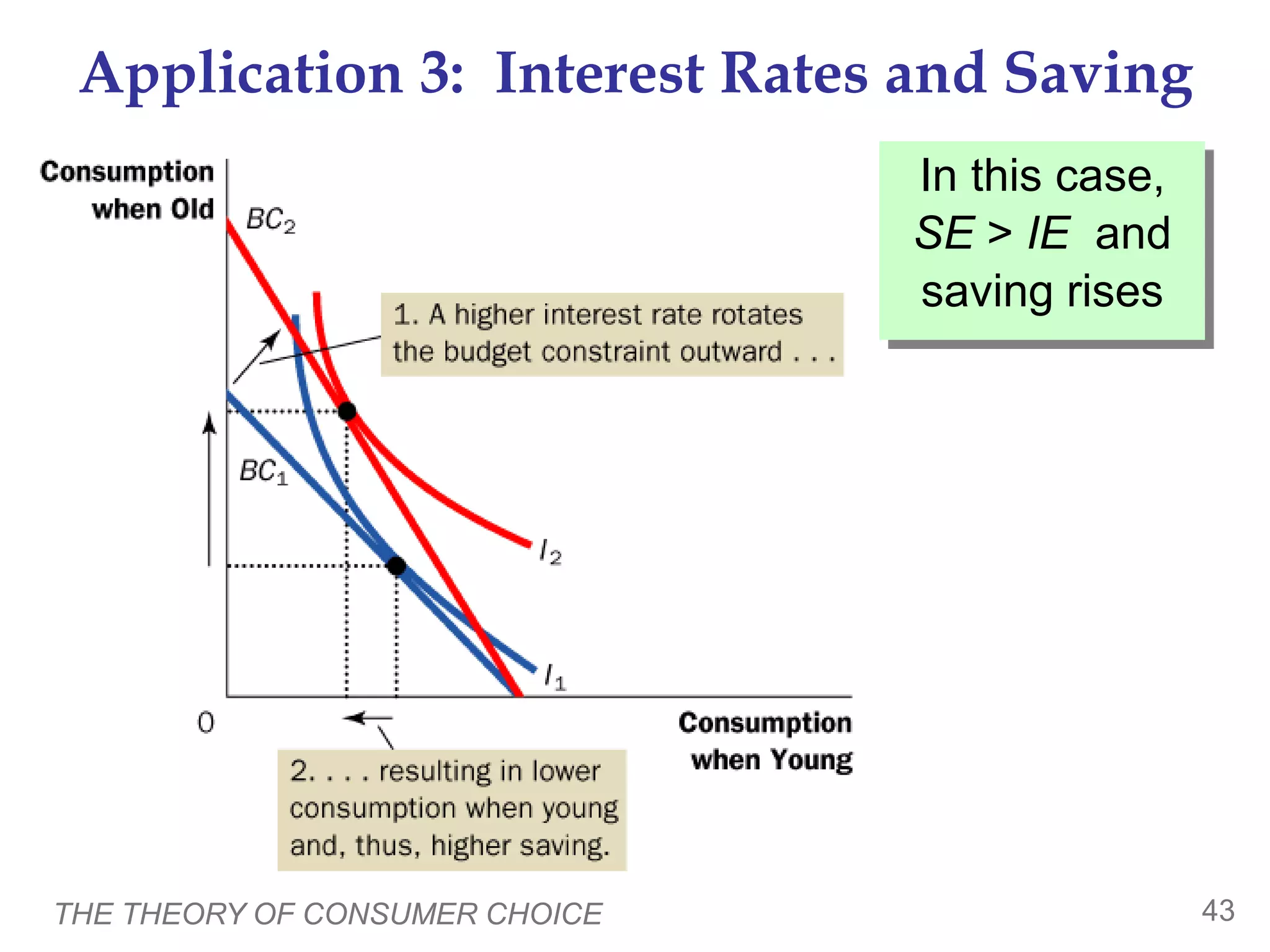
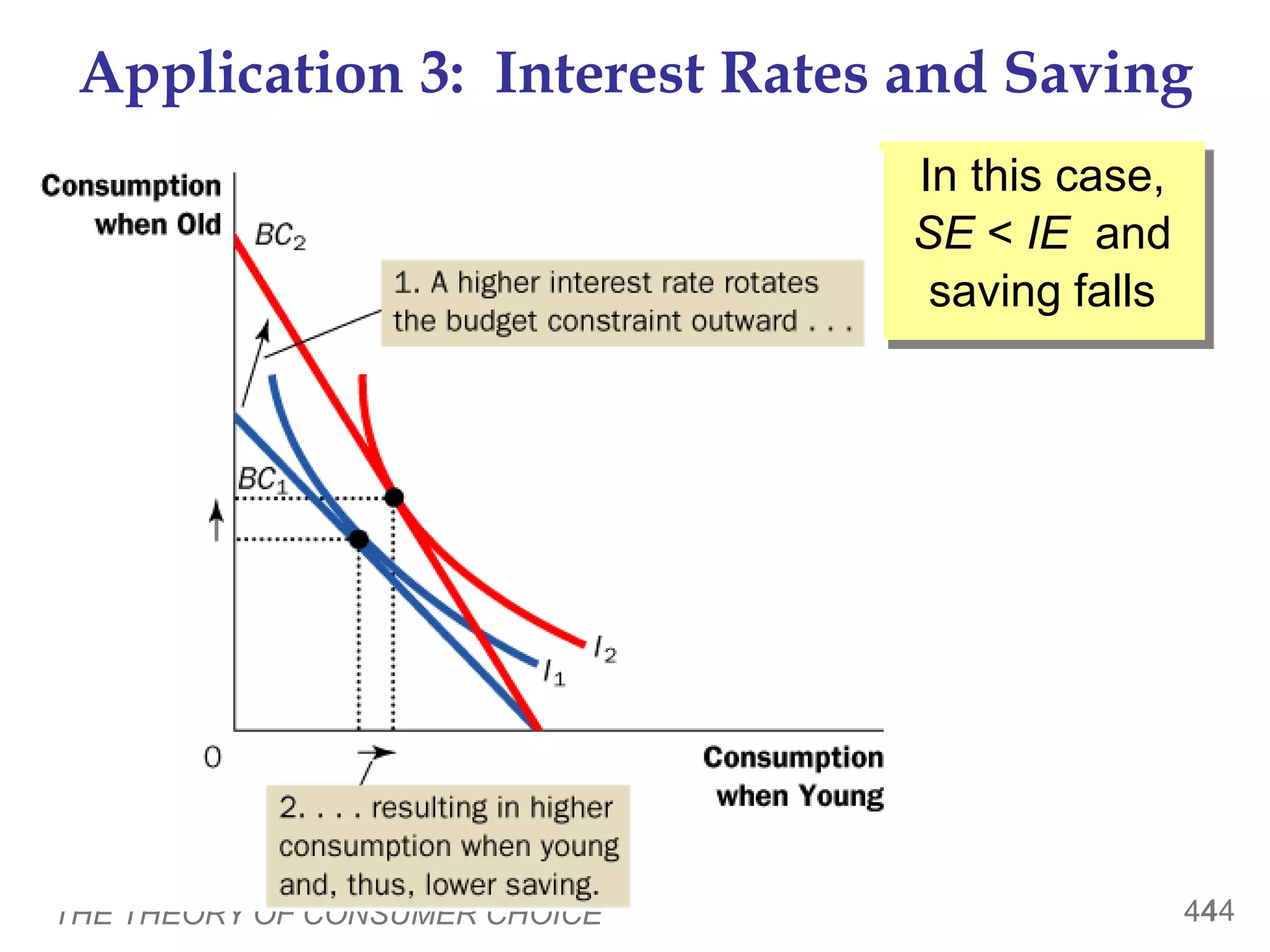
The document discusses the theory of consumer choice. It explains that consumers face budget constraints based on their income and prices, and have preferences represented by indifference curves. Consumers will optimize their choice of goods by selecting the bundle on their budget constraint that is tangent to the highest indifference curve, where the marginal rate of substitution equals the relative price ratio. Changes in income or prices can shift the budget constraint or change relative prices, impacting the optimal bundle.