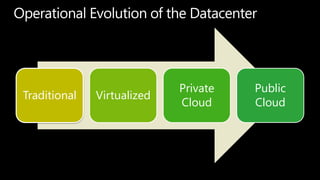
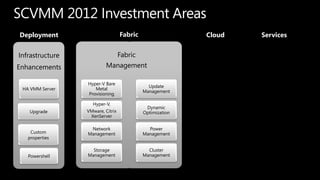
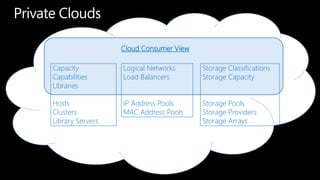
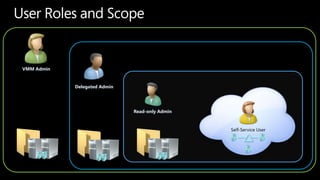
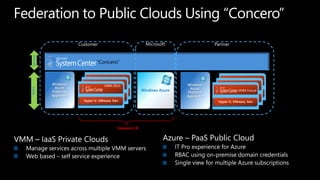
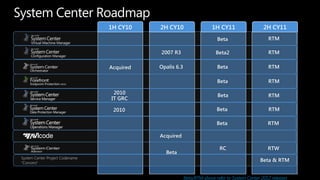
System Center Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) 2012 enables building private clouds and federating them to public clouds. VMM 2012 focuses on fabric management, services, cloud deployment, and fabric management. It allows highly automated management of Hyper-V, storage, networks, and other infrastructure. VMM 2012 also supports building private clouds with capabilities like self-service user roles, quotas, and templates to model multi-tier applications. Additionally, a product called Concero allows extending private clouds built with VMM 2012 into the public Azure cloud for a hybrid approach.