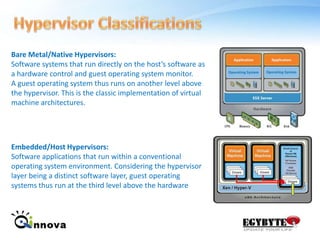
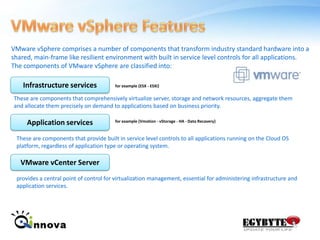
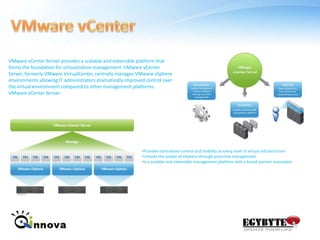
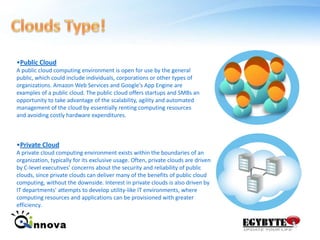
This document provides an overview of virtualization and cloud computing technologies. It defines virtualization as using software to allow multiple operating systems to run on a single hardware host. A hypervisor manages shared access to the physical resources. The document outlines the history of virtualization and describes popular virtualization platforms like Hyper-V, VMware vSphere, and cloud services from Amazon Web Services, Google Apps, and Windows Azure. Benefits of cloud computing include reduced costs, increased storage, flexibility, and mobility. Public, private and hybrid cloud models are discussed along with case studies of major cloud providers.